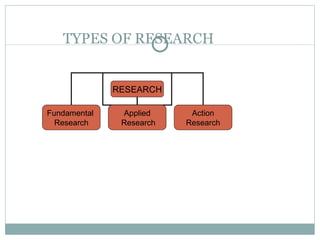
The document discusses action research and its application in education. It defines action research as research conducted by teachers and administrators to improve decision making and practice. It notes action research focuses on addressing real problems in local contexts rather than developing universal theories. The document then outlines the key steps of action research, including identifying an issue, analyzing causes, developing hypotheses for action, designing a study, and evaluating results. As an example, it proposes an action research study to address students not completing math homework. The study would check homework, punish defaulters, and evaluate if this improves homework completion rates.