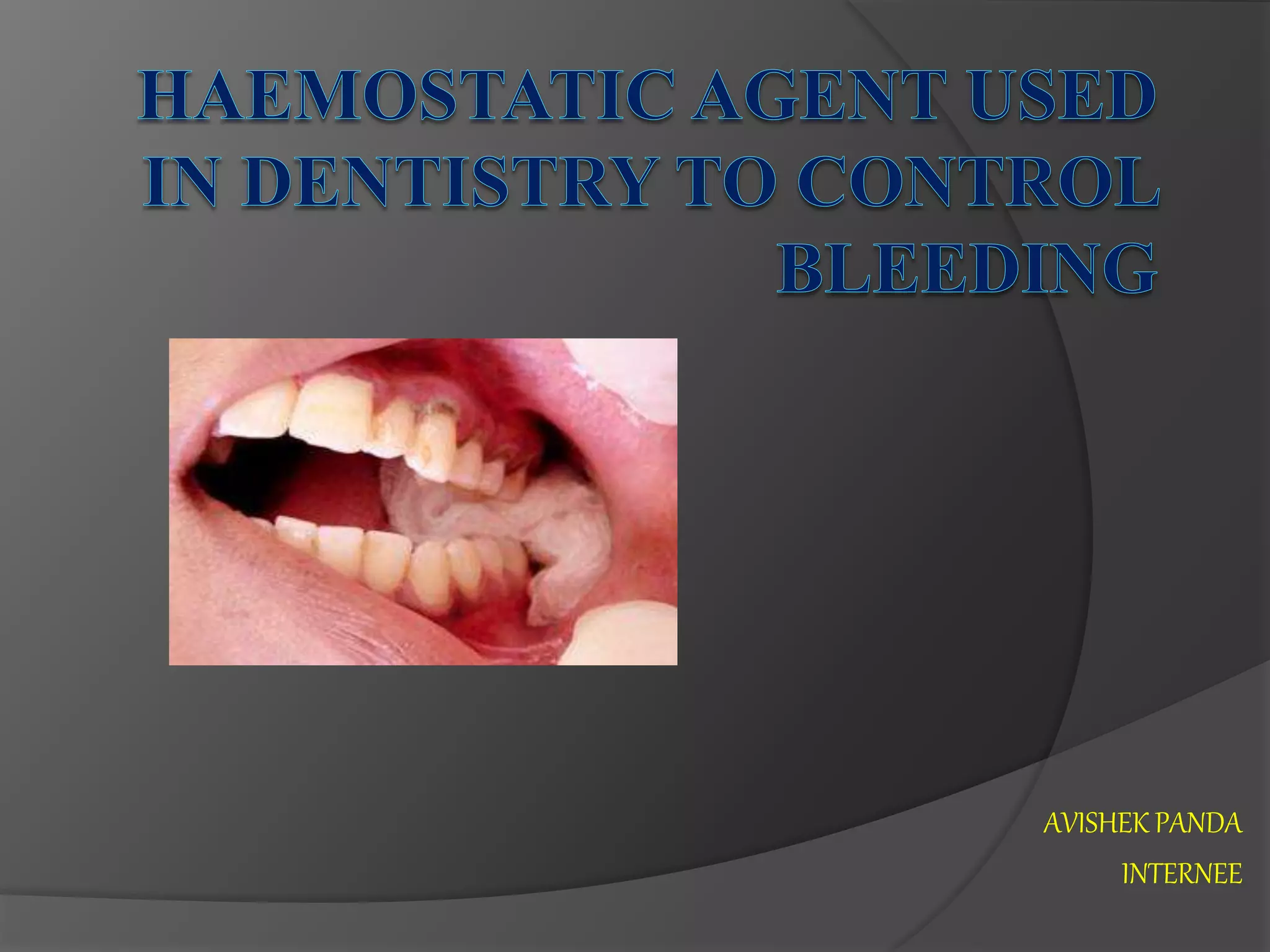
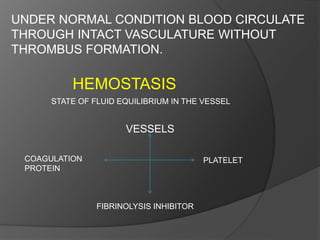
Hemostasis is the process of stopping bleeding. The key phases are primary hemostasis involving platelet plug formation and secondary hemostasis involving the coagulation cascade and fibrin clot formation. Several factors can influence surgical bleeding relating to the procedure, patient, and anatomical site. A variety of hemostatic agents exist to help control bleeding, including mechanical methods, energy-based methods, pharmacological agents, topical agents that are passive or active, and sealants. The ideal hemostatic agent stops bleeding quickly, is easy to use, durable, and safe.