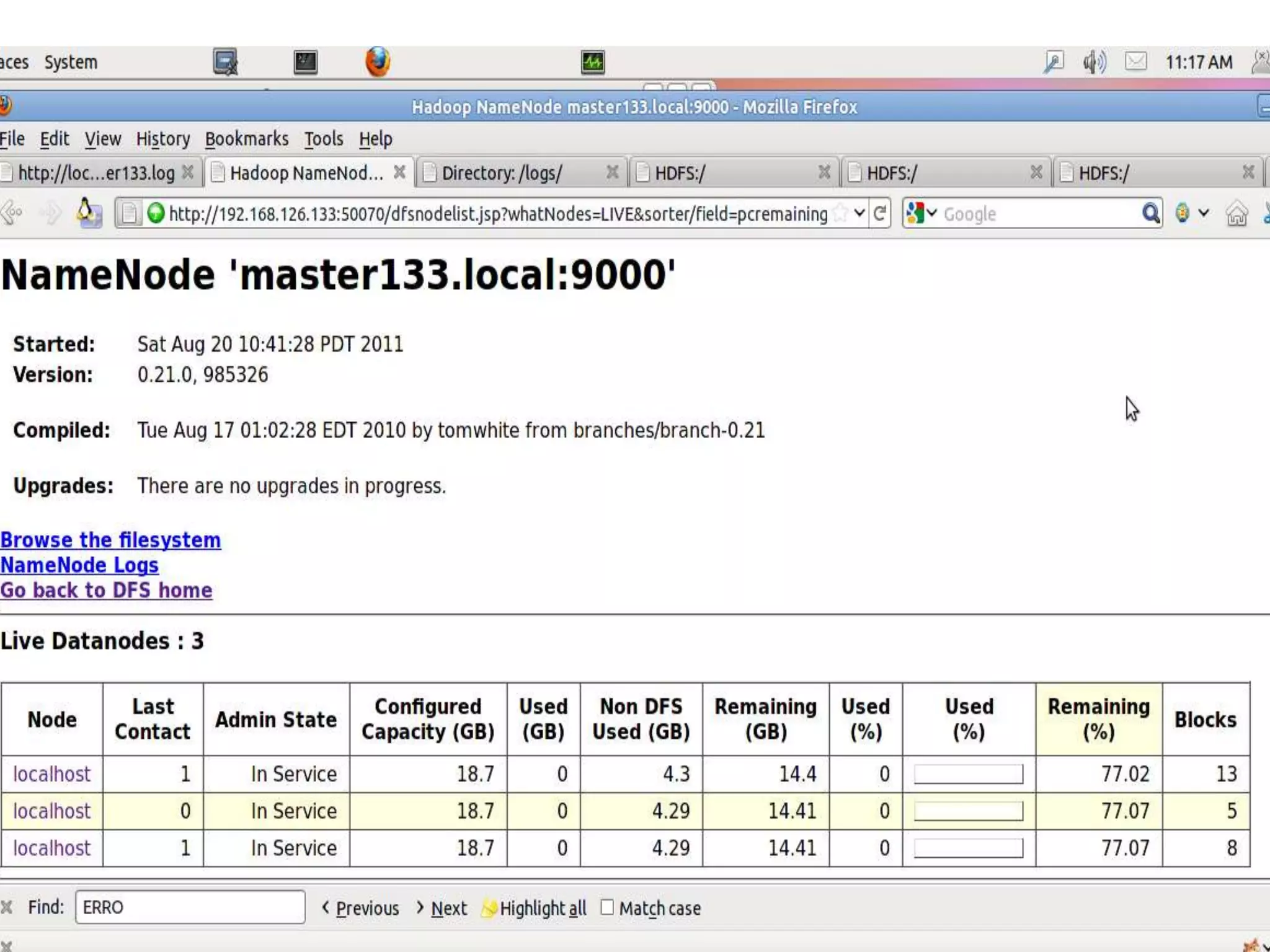
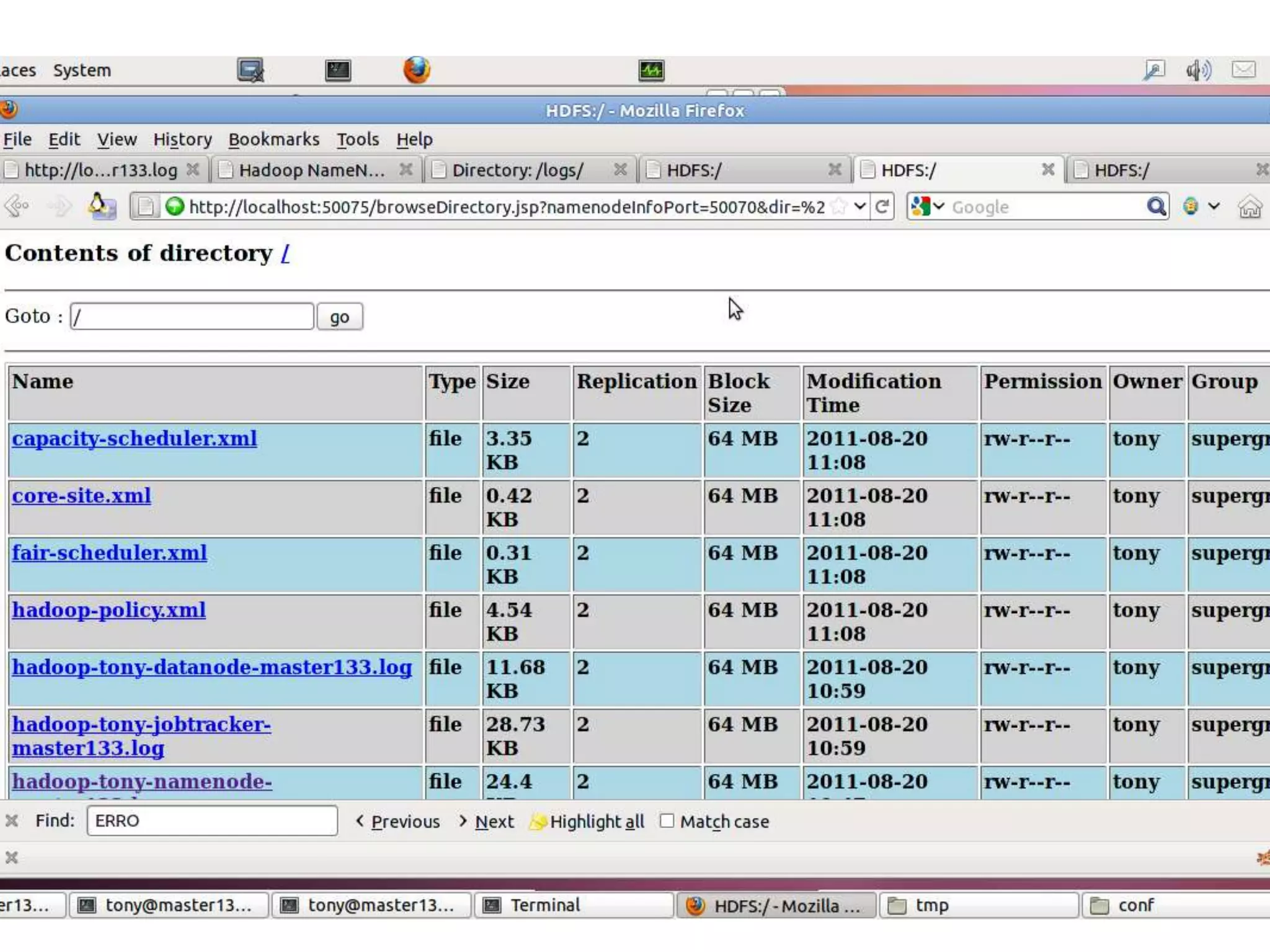
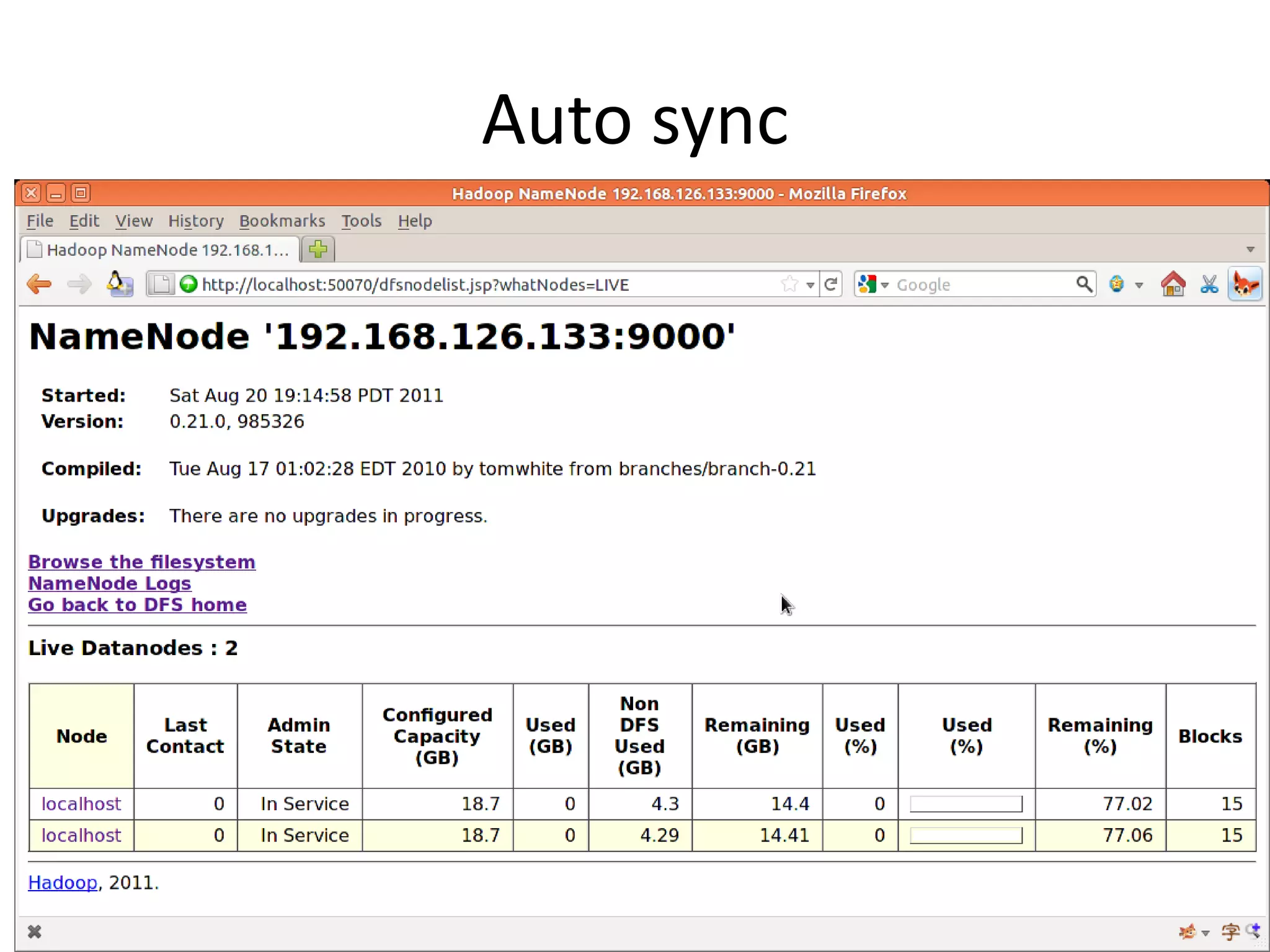
Hadoop is an open-source software framework for distributed storage and processing of large datasets across clusters of computers. The core of Hadoop includes HDFS for distributed storage, and MapReduce for distributed processing. Other Hadoop projects include Pig for data flows, ZooKeeper for coordination, and YARN for job scheduling. Key Hadoop daemons include the NameNode, Secondary NameNode, DataNodes, JobTracker and TaskTrackers.






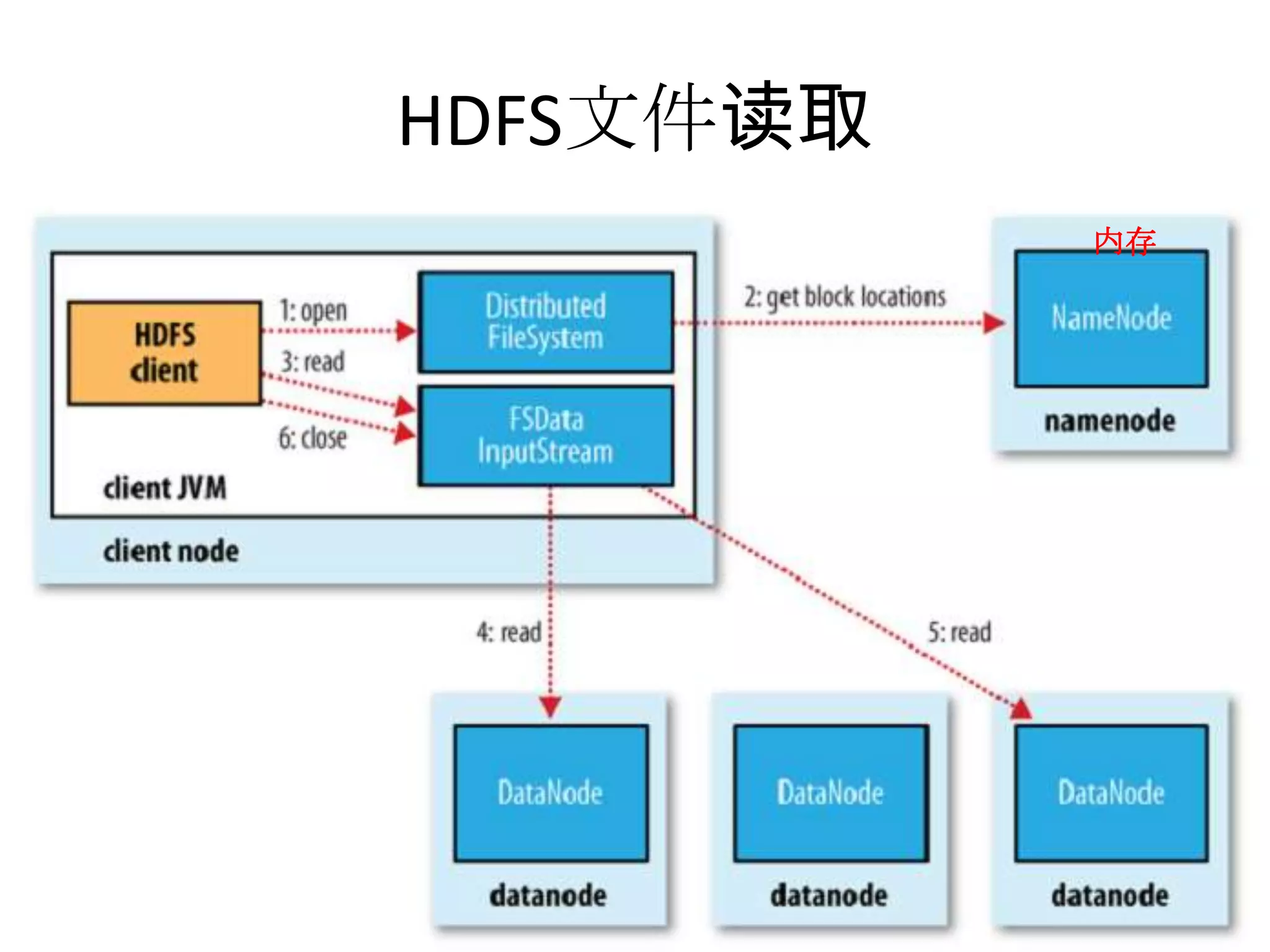
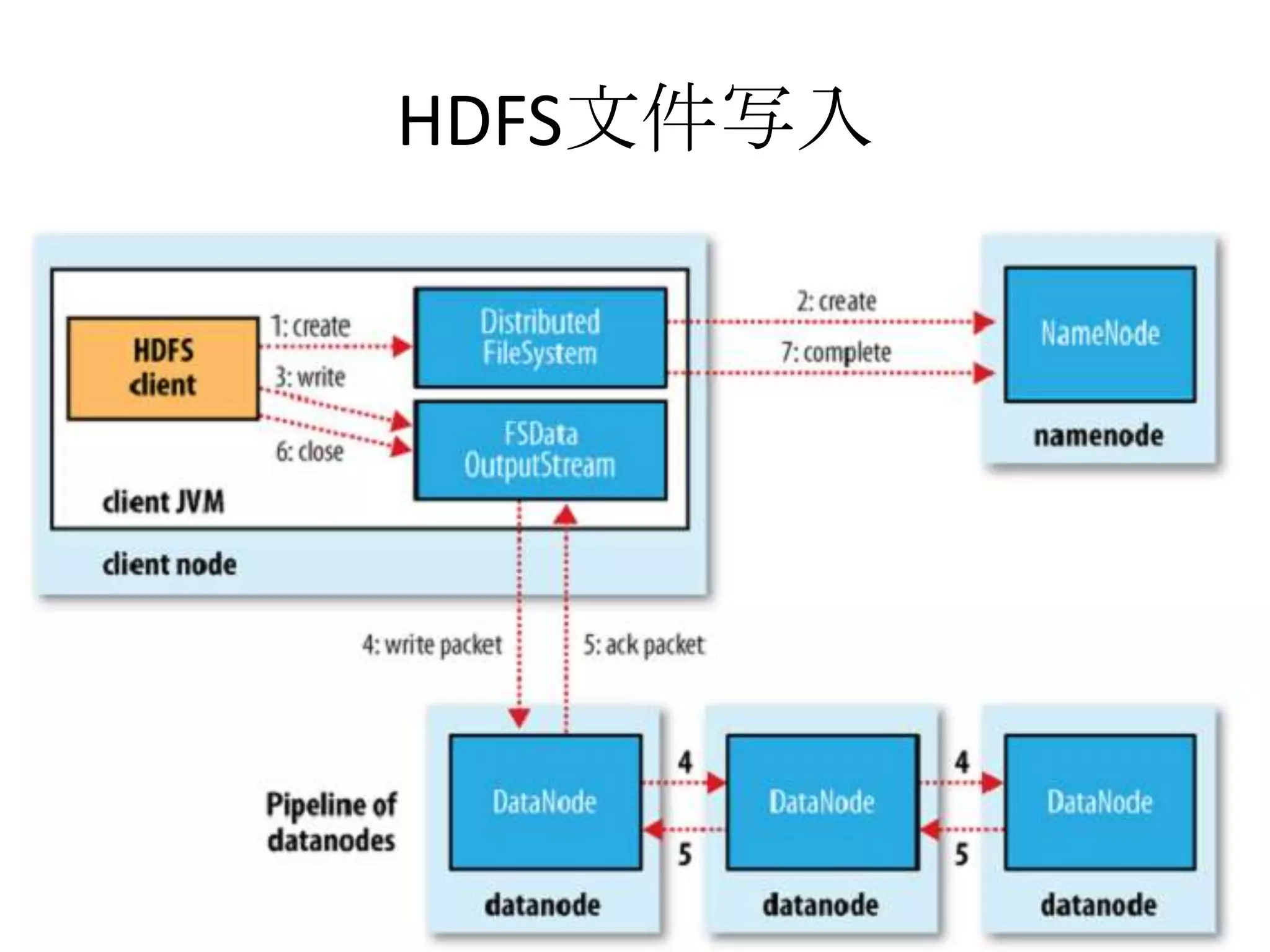
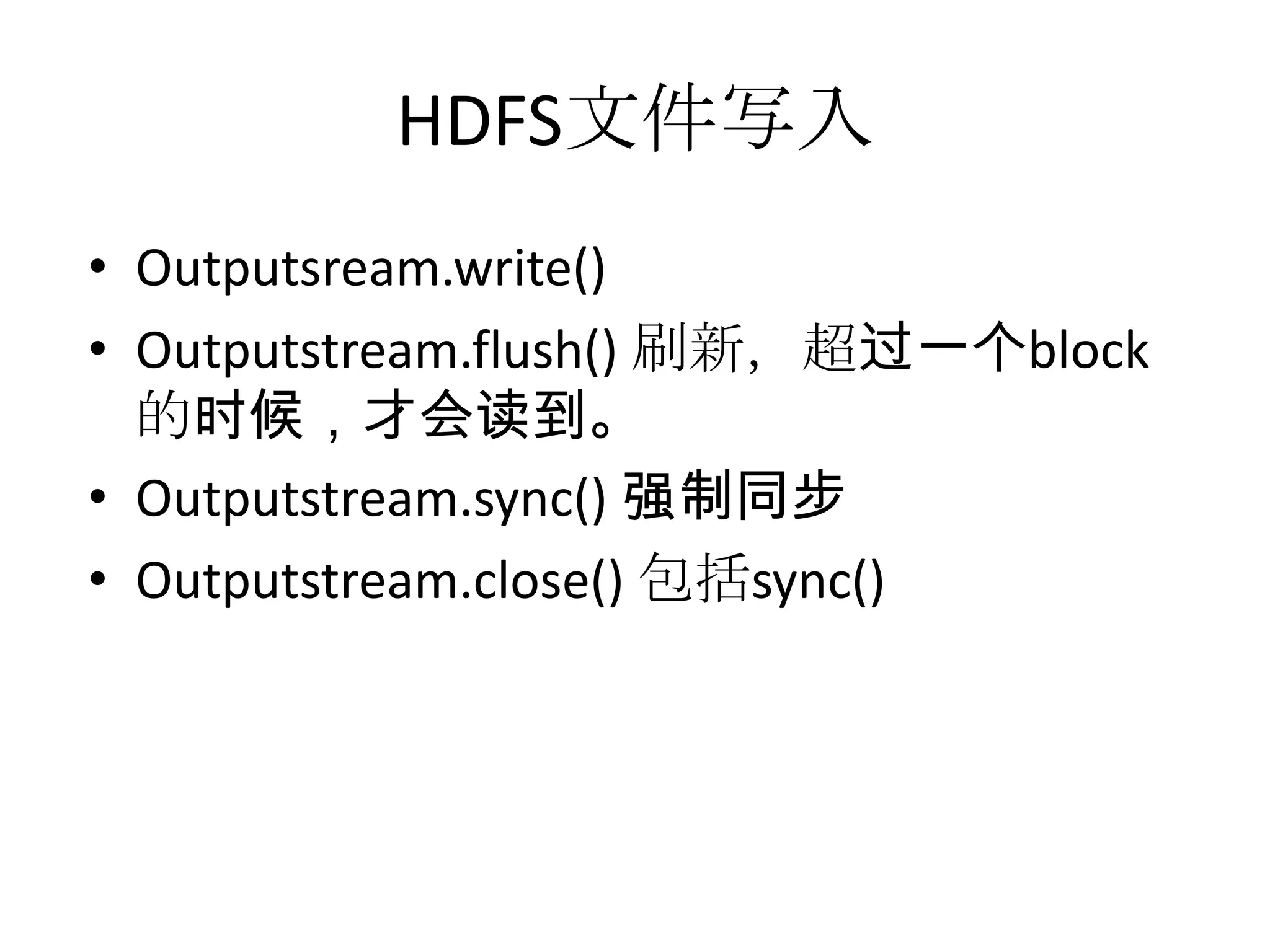


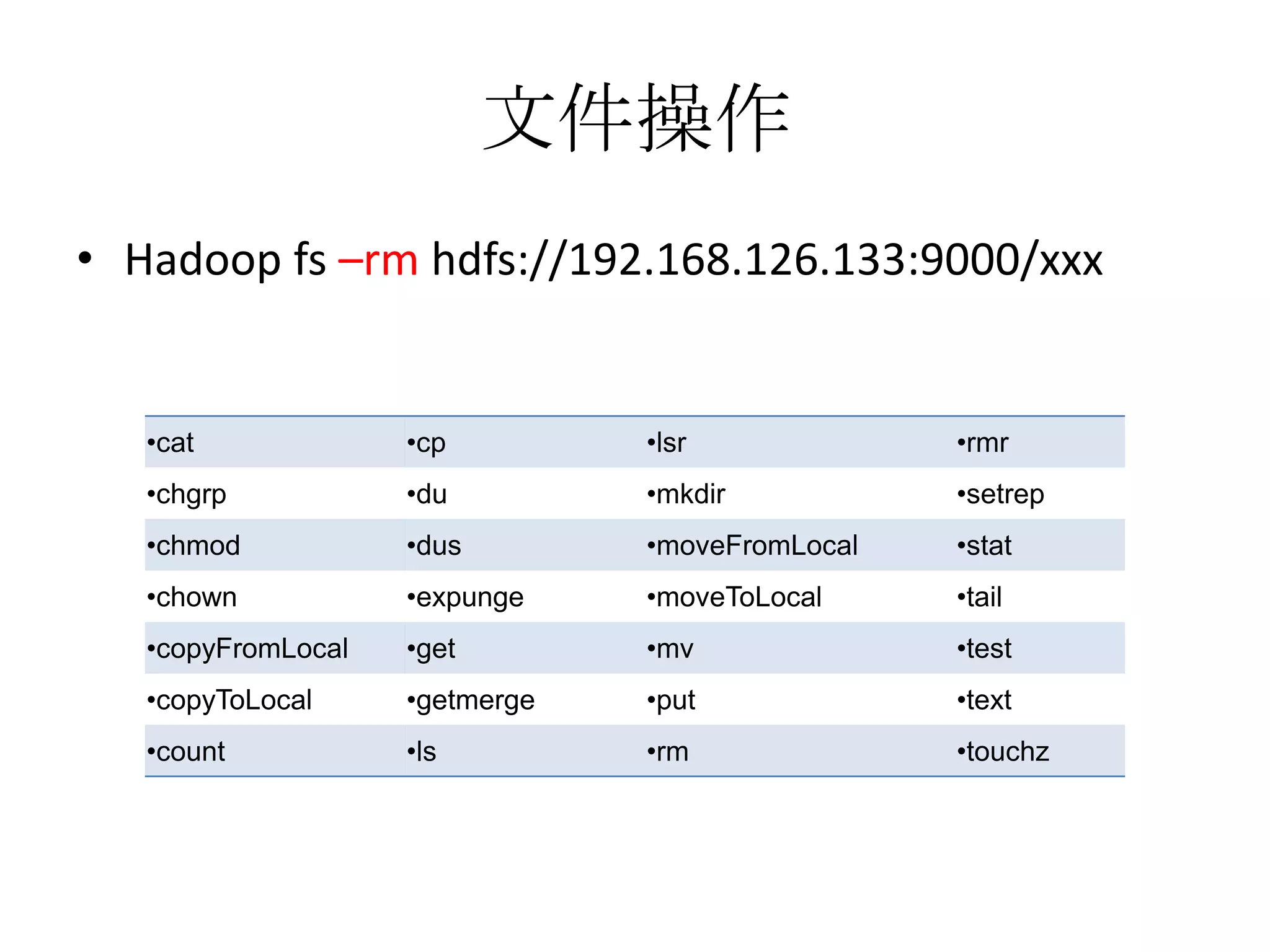












![Read From Hadoop URL
• //execute: hadoop ReadFromHDFS
• public class ReadFromHDFS {
• static {
• URL.setURLStreamHandlerFactory(new FsUrlStreamHandlerFactory());
• }
• public static void main(String[] args){
• try {
• URL uri = new URL("hdfs://192.168.126.133:9000/t1/a1.txt");
• IOUtils.copyBytes(uri.openStream(), System.out, 4096, false);
• }catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
• e.printStackTrace();
• } catch (IOException e) {
• e.printStackTrace();
• }
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadoop20111117-111116102349-phpapp02/75/Hadoop-20111117-35-2048.jpg)
![Read By FileSystem API
• //execute : hadoop ReadByFileSystemAPI
• public class ReadByFileSystemAPI {
• public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
• String uri = ("hdfs://192.168.126.133:9000/t1/a2.txt");;
• Configuration conf = new Configuration();
• FileSystem fs = FileSystem.get(URI.create(uri), conf);
• FSDataInputStream in = null;
• try {
• in = fs.open(new Path(uri));
• IOUtils.copyBytes(in, System.out, 4096, false);
• } finally {
• IOUtils.closeStream(in);
• }
• }
• }](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadoop20111117-111116102349-phpapp02/75/Hadoop-20111117-36-2048.jpg)
![FileSystemAPI
• Path path = new Path(URI.create("hdfs://192.168.126.133:9000/t1/tt/"));
• if(fs.exists(path)){
• fs.delete(path,true);
• System.out.println("deleted-----------");
• }else{
• fs.mkdirs(path);
• System.out.println("creted=====");
• }
• /**
• * List files
• */
• FileStatus[] fileStatuses = fs.listStatus(new Path(URI.create("hdfs://192.168.126.133:9000/")));
• for(FileStatus fileStatus : fileStatuses){
• System.out.println("" + fileStatus.getPath().toUri().toString() + " dir:" + fileStatus.isDirectory());
• }
• PathFilter pathFilter = new PathFilter(){
• @Override
• public boolean accept(Path path) {
• return true;
• }
• };](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/hadoop20111117-111116102349-phpapp02/75/Hadoop-20111117-37-2048.jpg)