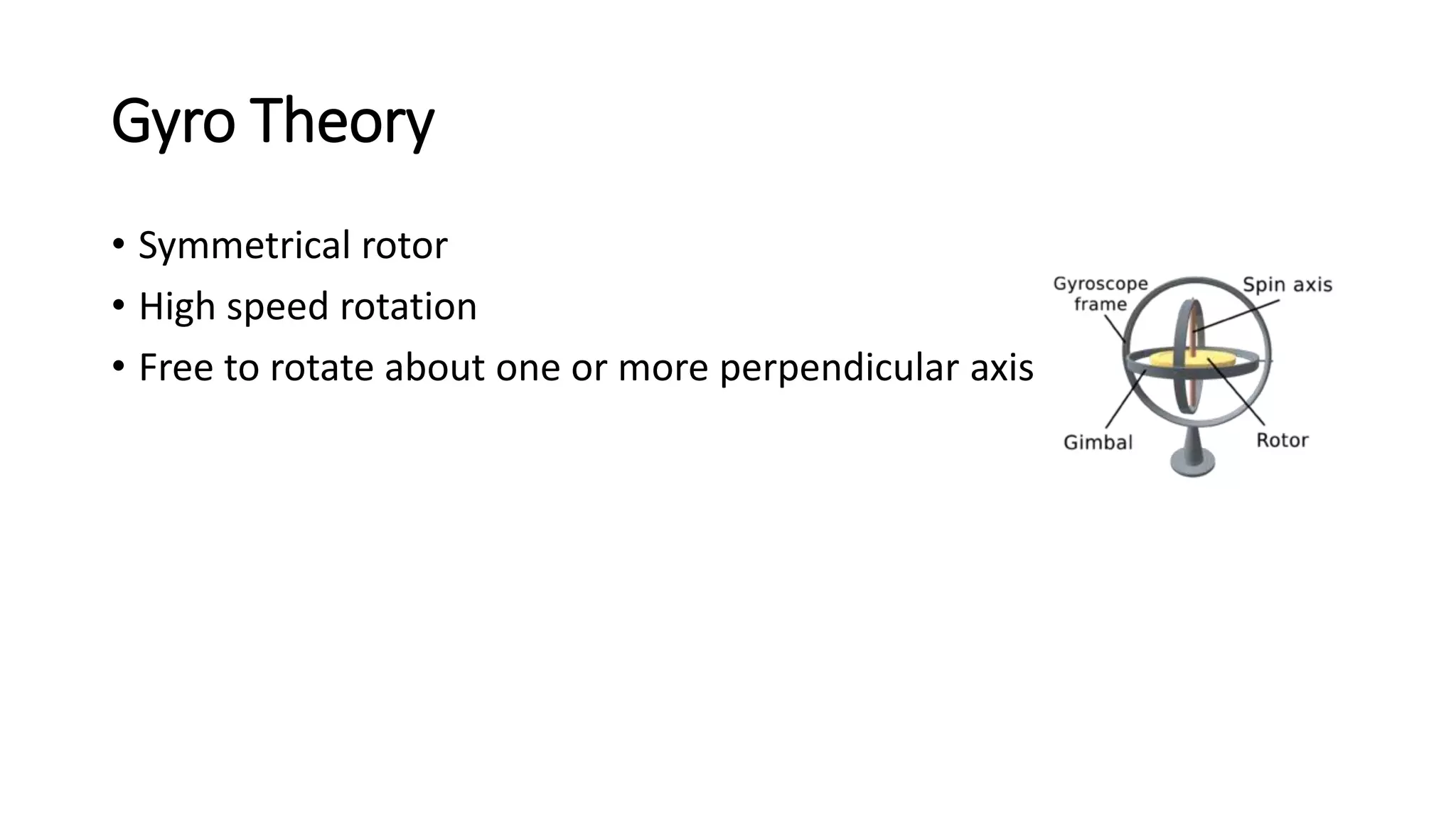
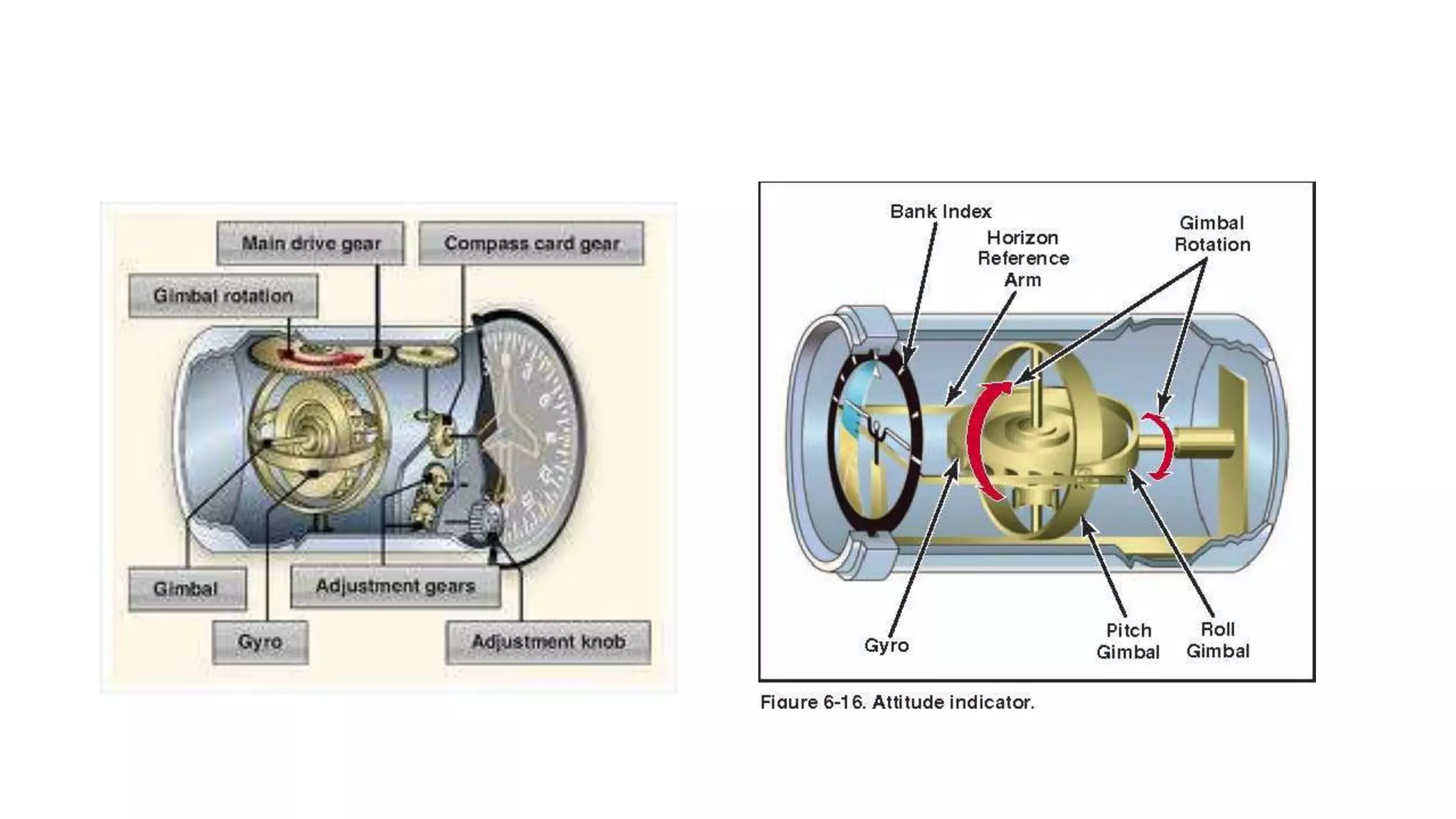
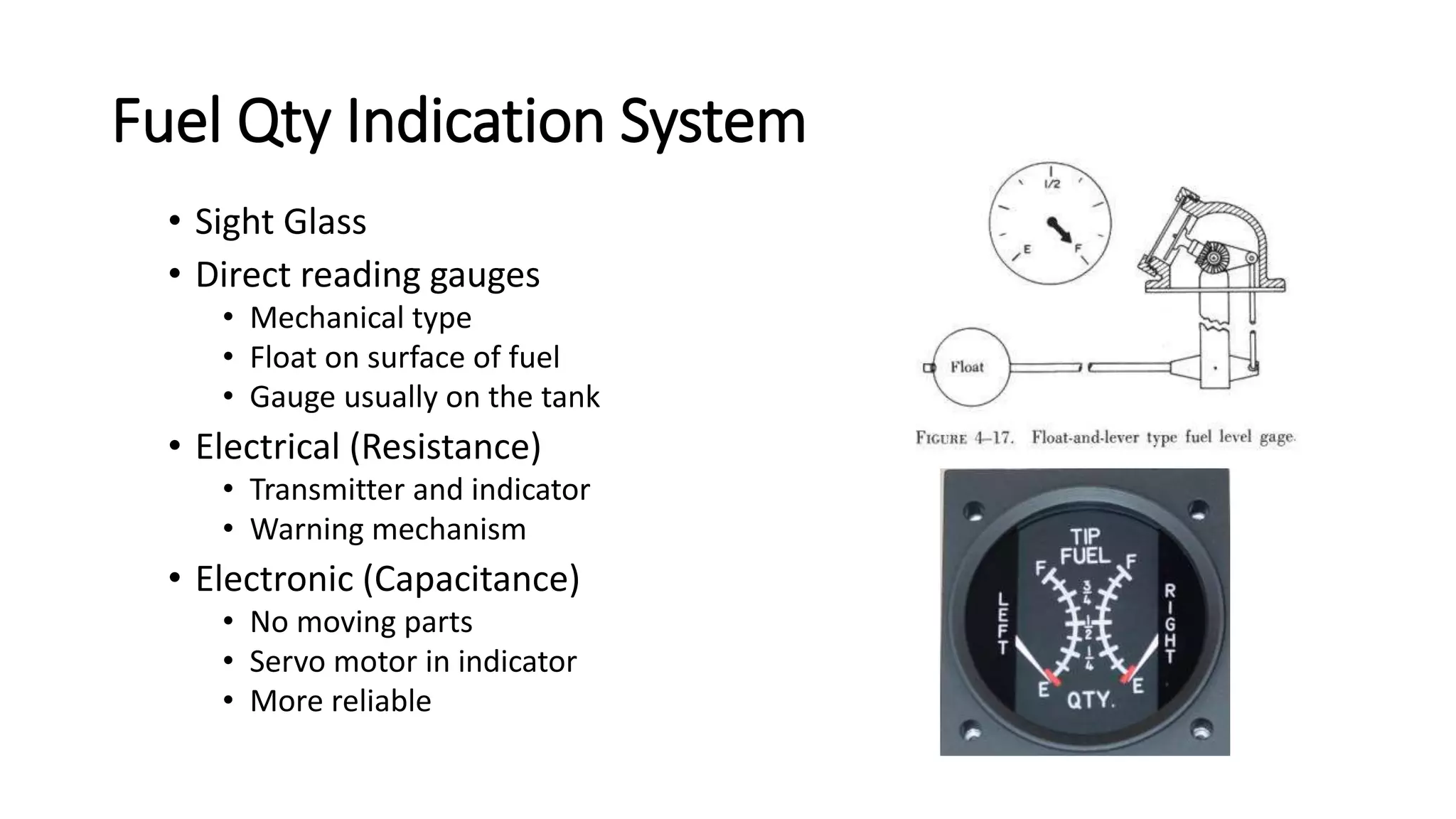
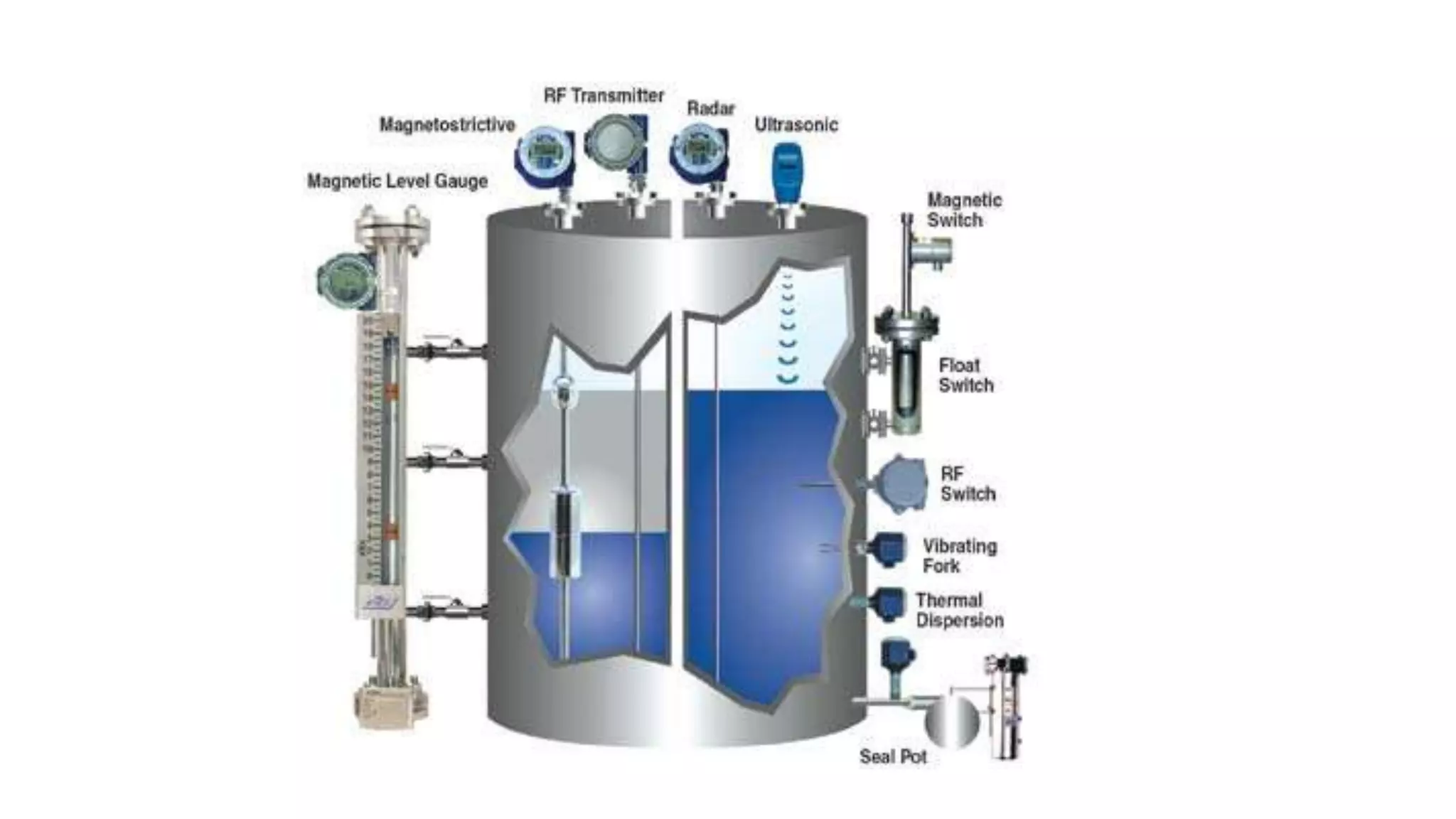
This document discusses gyroscopic instruments and their principles of operation. It explains that a gyroscope will maintain its orientation in space due to its high-speed rotation and angular momentum. It can rotate about perpendicular axes, with any change in its axis of rotation called precession. It describes different types of gyroscopes like attitude gyros and rate gyros, and errors they may experience like drift, wander, gimbal lock, and gimbal error. It also briefly discusses directional gyros, gyro horizons, and fuel quantity indication systems using sight glasses, mechanical floats, electrical resistance transmitters, and electronic capacitance sensors.