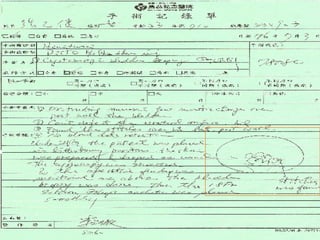
1. A 31-year-old pregnant woman experienced acute fetal distress during labor and underwent an emergency cesarean section, delivering a healthy baby girl.
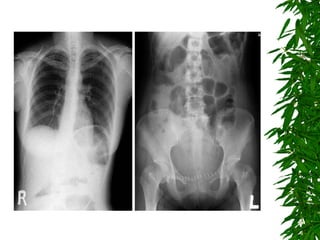
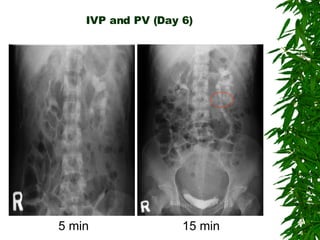
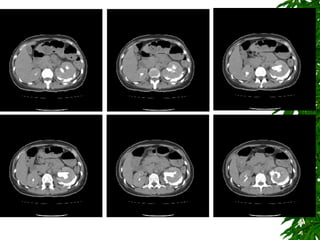
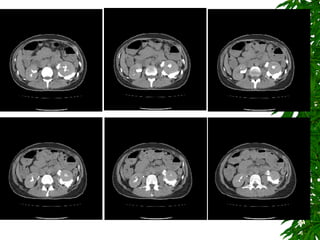
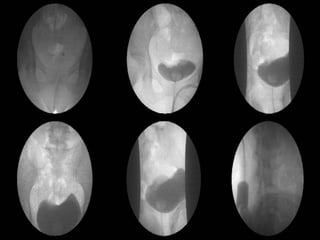
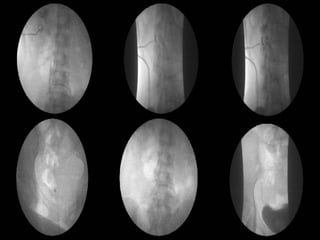
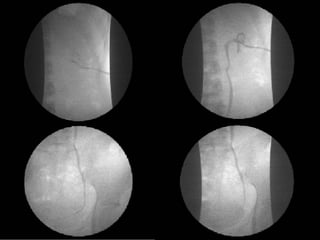
2. Postpartum, the woman developed hematuria and left flank pain. Imaging revealed a tear in her left renal pelvis causing hydronephrosis.
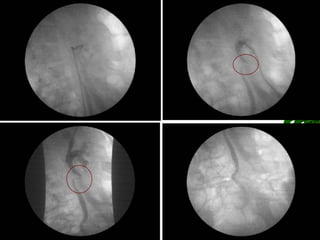
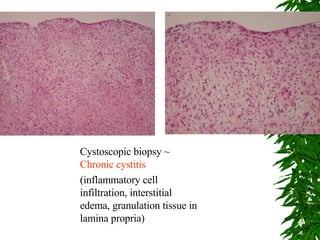
3. She underwent left percutaneous nephrostomy and cystoscopy, which identified a bladder injury possibly related to stitches from the cesarean section. The injuries were successfully treated without need for nephrectomy.