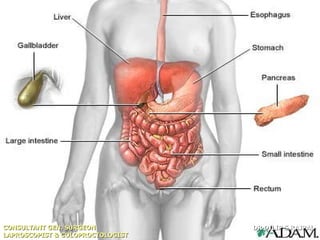
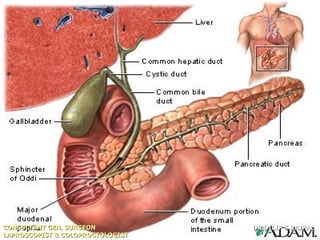
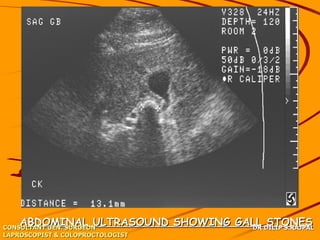
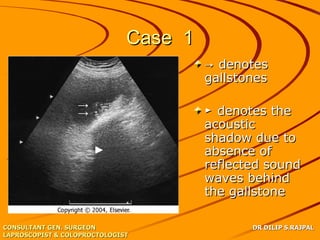
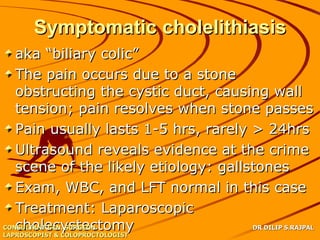
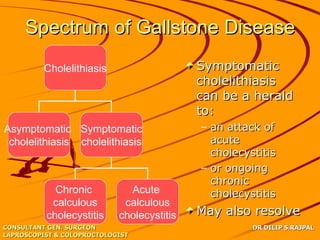
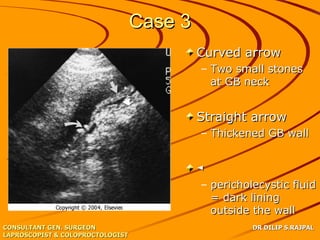
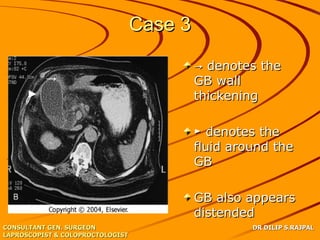
Based on the limited information provided, this case is most consistent with acute cholangitis. The classic triad of right upper quadrant pain, jaundice, and fever is seen in about 70% of cases of acute cholangitis. Further workup would be needed to identify the underlying cause, such as gallstones in the common bile duct or a stricture. Treatment would involve antibiotics and consideration of ERCP for drainage or stenting.