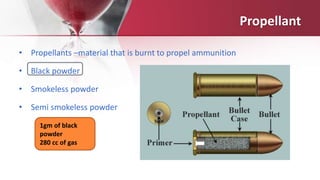
Gunpowder, also known as black powder, is an explosive mixture of sulfur, charcoal and potassium nitrate that was invented in China in the 9th century and later spread worldwide. It functions as a propellant by producing hot gases when ignited, and was widely used in firearms until being replaced by smokeless powder in the late 19th century. Traces of gunpowder residues can be detected on the hands and clothing of someone who fires a gun through various chemical tests and analytical techniques like atomic absorption spectroscopy. Finding these residues is an indicator that the person discharged a firearm. Unburnt gunpowder residues can also penetrate the skin and cause tattooing injuries.