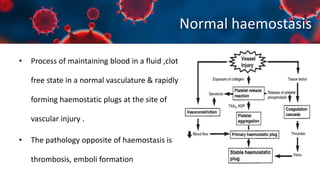
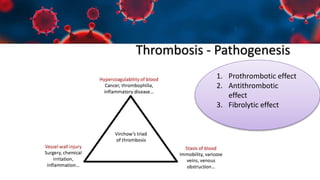
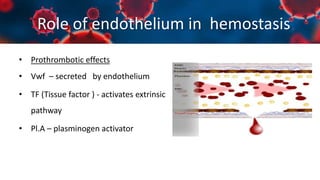
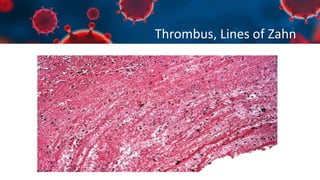
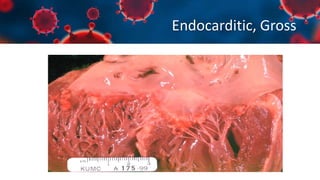
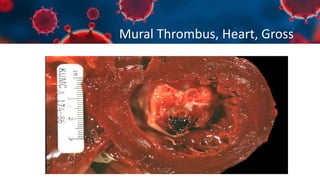
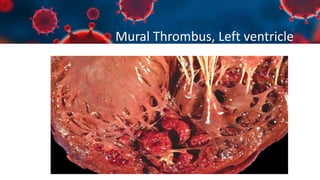
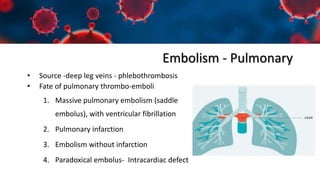
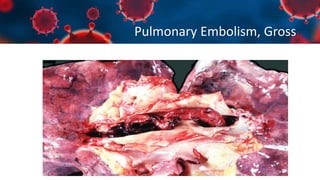
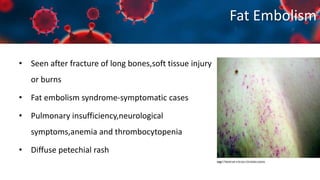
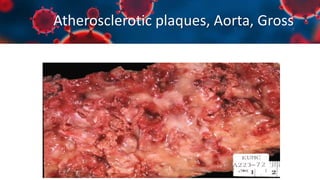
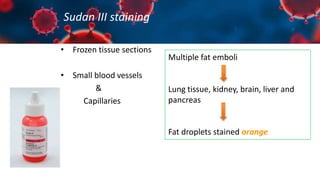
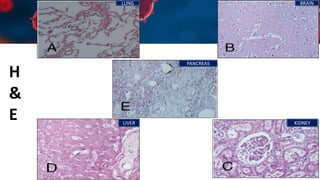
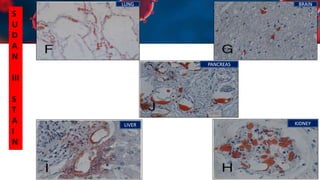
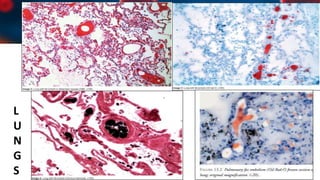
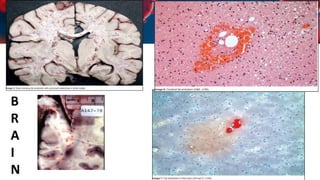
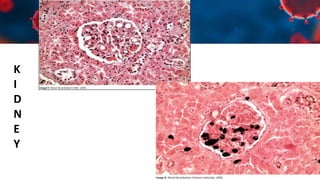
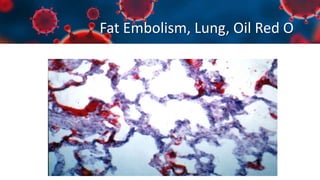
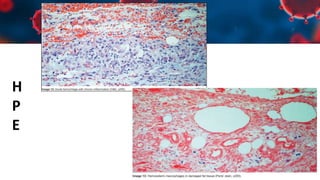
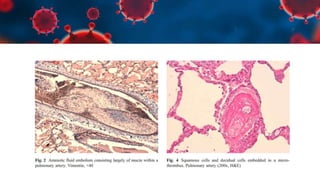
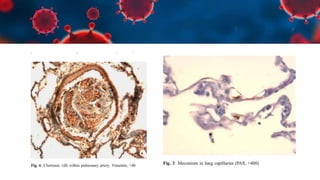
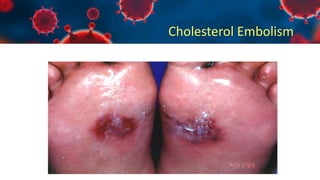
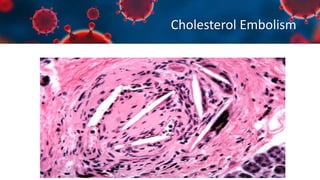
This document discusses various types of thromboembolism including definitions, pathogenesis, and histopathology findings. It covers topics such as normal hemostasis, thrombosis (arterial and venous), embolism (types like thromboembolism, fat, amniotic fluid), and complications. Specific conditions discussed include pulmonary embolism, myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, and fat, amniotic fluid, and cholesterol embolism. Gross and microscopic pathology photos are also presented.