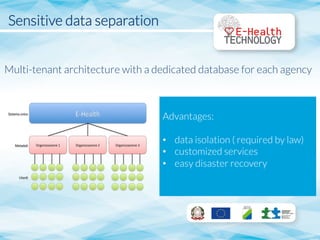
The document outlines guidelines for technological development in e-health applications, emphasizing the need for improved data management and security. It discusses the role of the University of L'Aquila in researching cloud computing solutions, user authentication, user authorization, and data encryption. Additionally, it highlights the necessity of a multi-tenant architecture for data isolation and assures legal compliance in handling sensitive information.