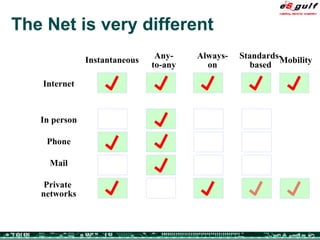
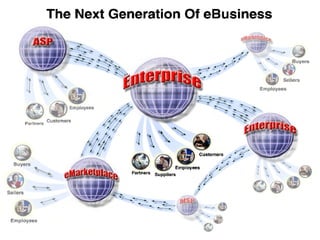
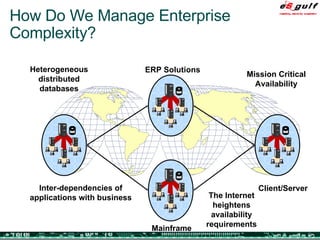
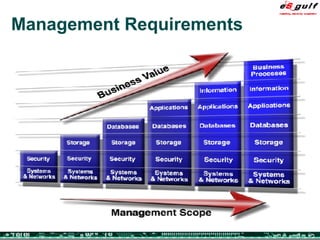
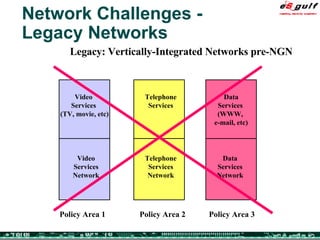
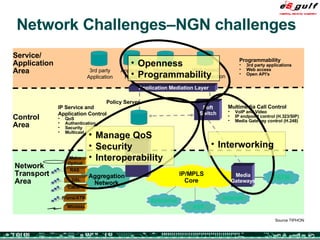
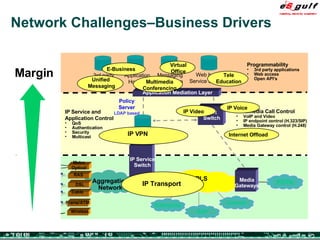
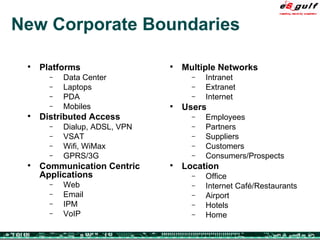
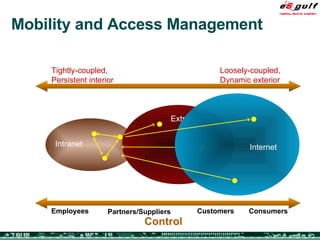
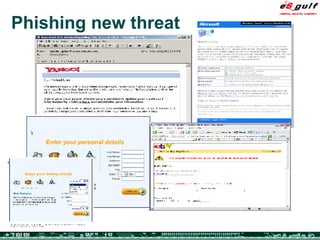
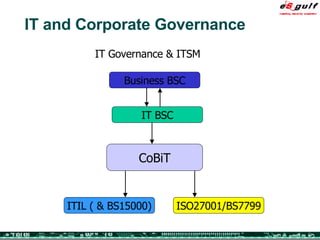
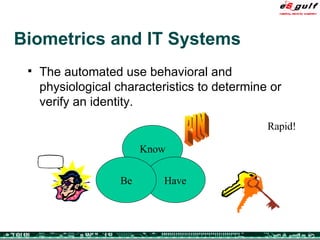
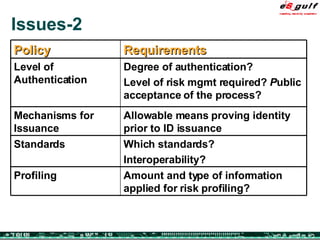
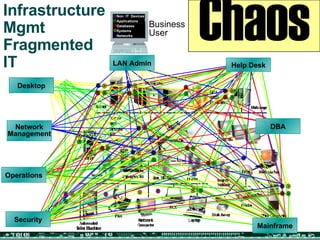
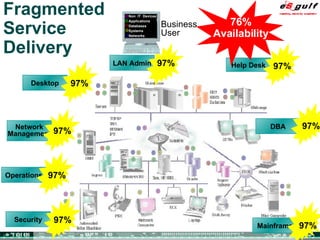
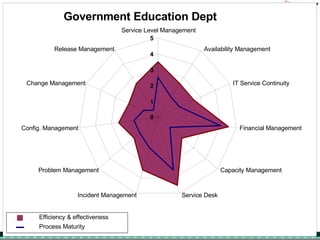
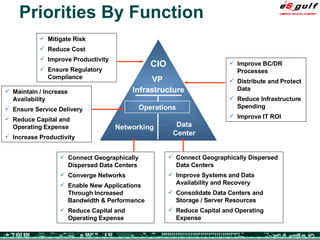
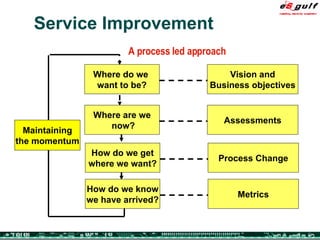
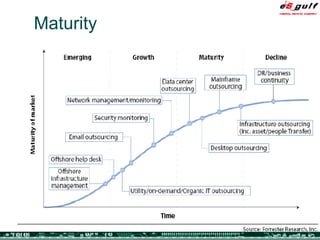
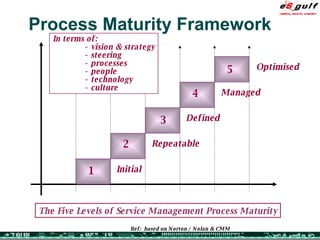
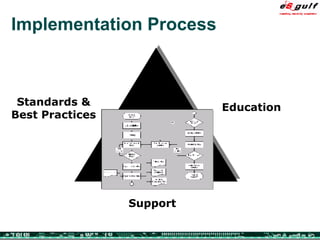
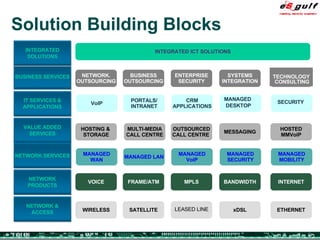
The document discusses the evolving complexities of IT management, highlighting strategic challenges such as user education, technology adoption, and compliance risks. It emphasizes the necessity for effective infrastructure management and the integration of new technologies, while also addressing privacy concerns and the need for systematized governance. The text advocates for a balanced approach to professional development and emphasizes the importance of metrics in assessing service management processes.
![Insight into today's IT Strategic Challenges Jorge Sebastião Founder and CEO [email_address] www.esgulf.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/esguf-profile-short-v-34-1200591700270026-2/85/Insight-into-IT-Strategic-Challenges-1-320.jpg)