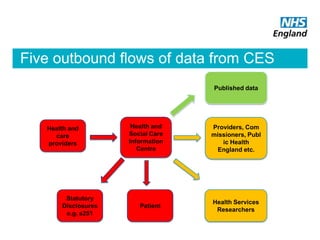
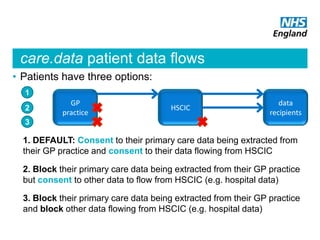
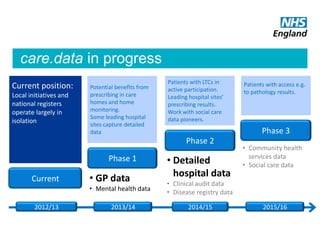
The document summarizes the care.data program in the NHS which aims to improve patient care through better use of data. It will provide comprehensive and timely healthcare data to patients, professionals, providers and researchers. The program will extract primary care data from GP practices with patient consent to join it with other hospital data. It is being rolled out in phases and aims to eventually include social care and community health data. Strict information governance standards are in place to protect patient privacy and data security. The goal is to help identify variations or gaps in care quality, monitor outcomes over time, and support health services research.