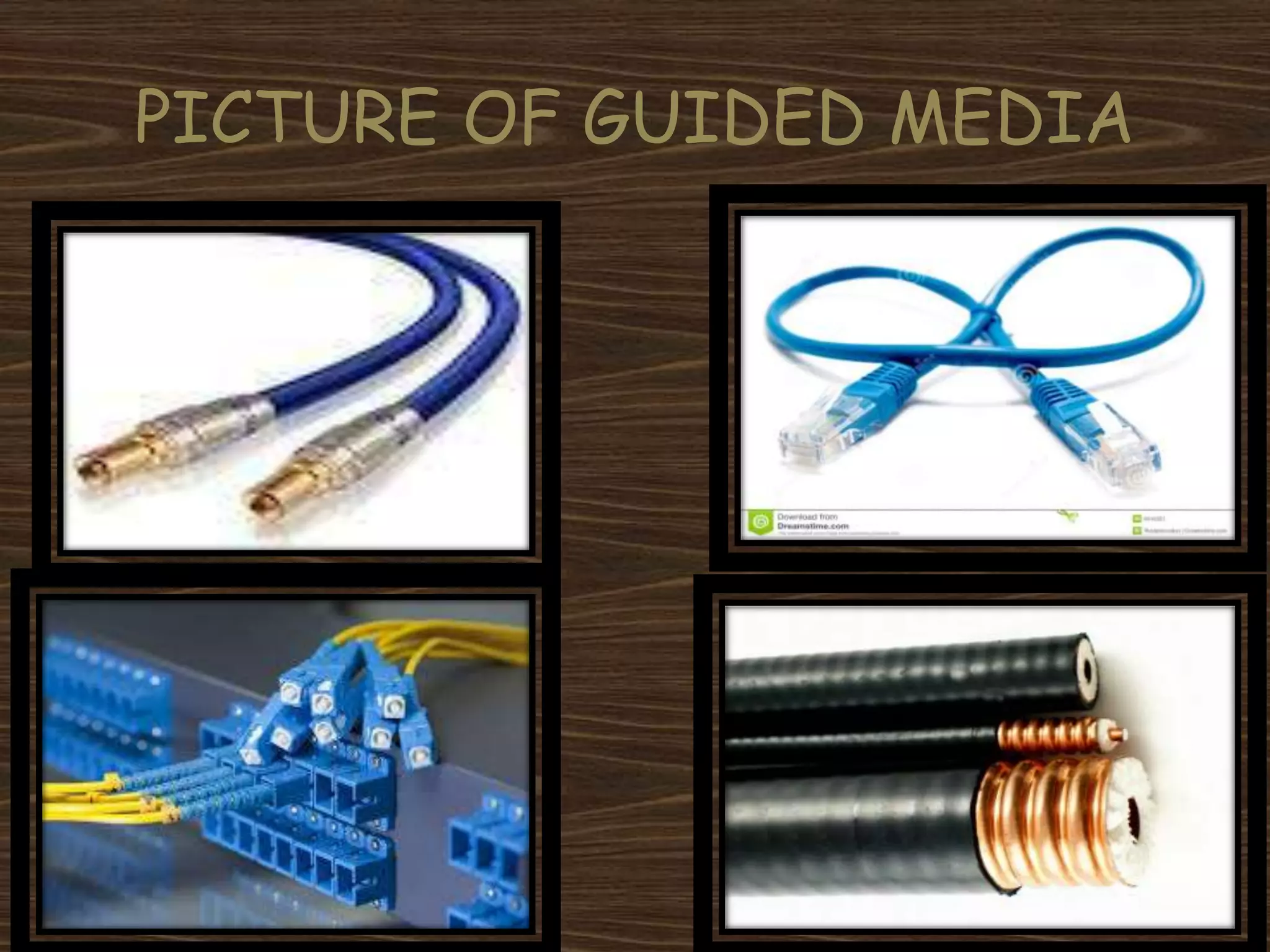
The document discusses guided and unguided media in networking, detailing the types and characteristics of each, such as twisted pair cables, fiber-optic cables, and coaxial cables for guided media, and explaining unguided media as transmission without physical pathways. It also covers various network topologies like star, ring, bus, and mesh, outlining their configurations and advantages. The conclusion reflects the author's appreciation for the learning experience provided by the project.