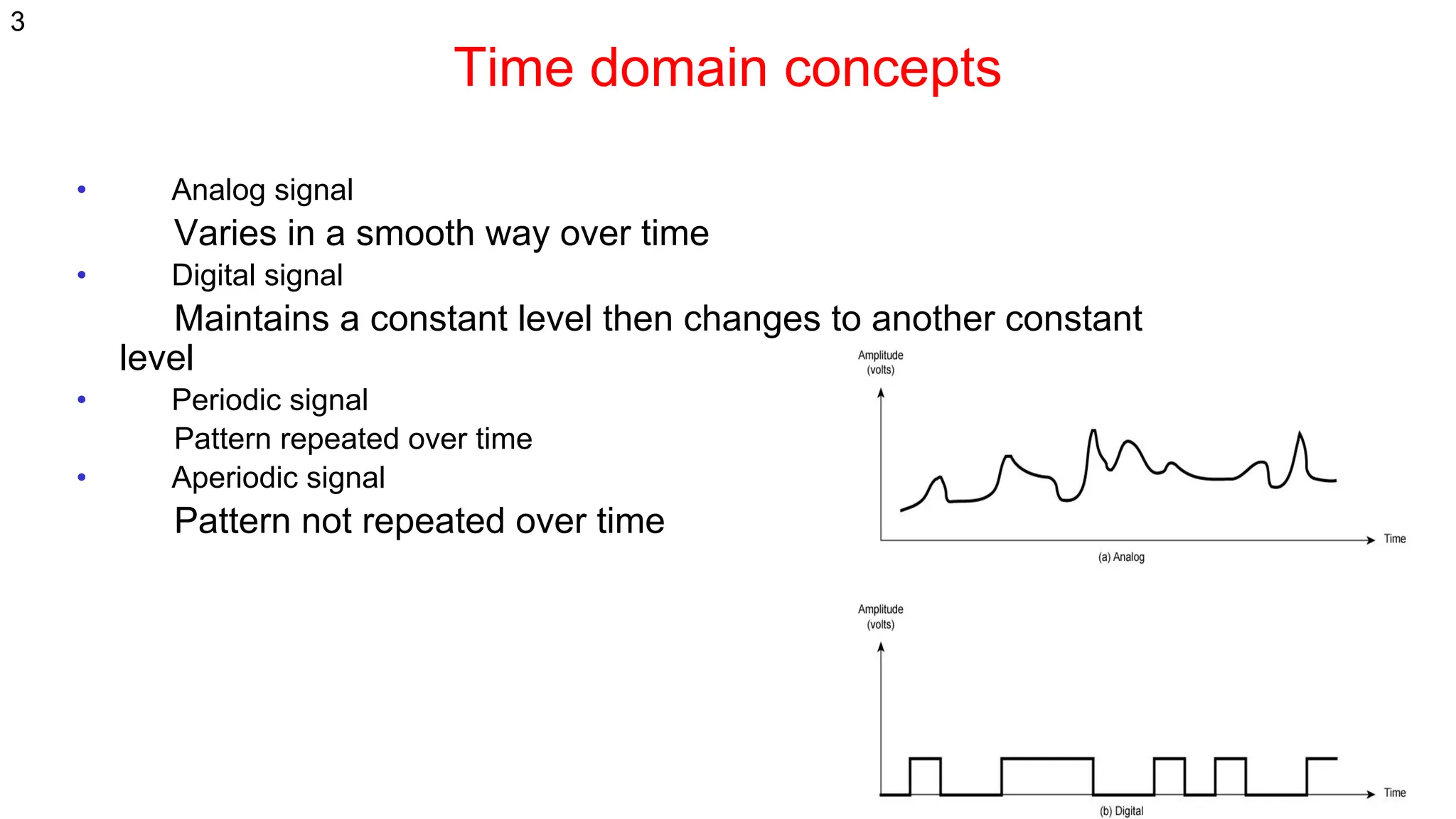
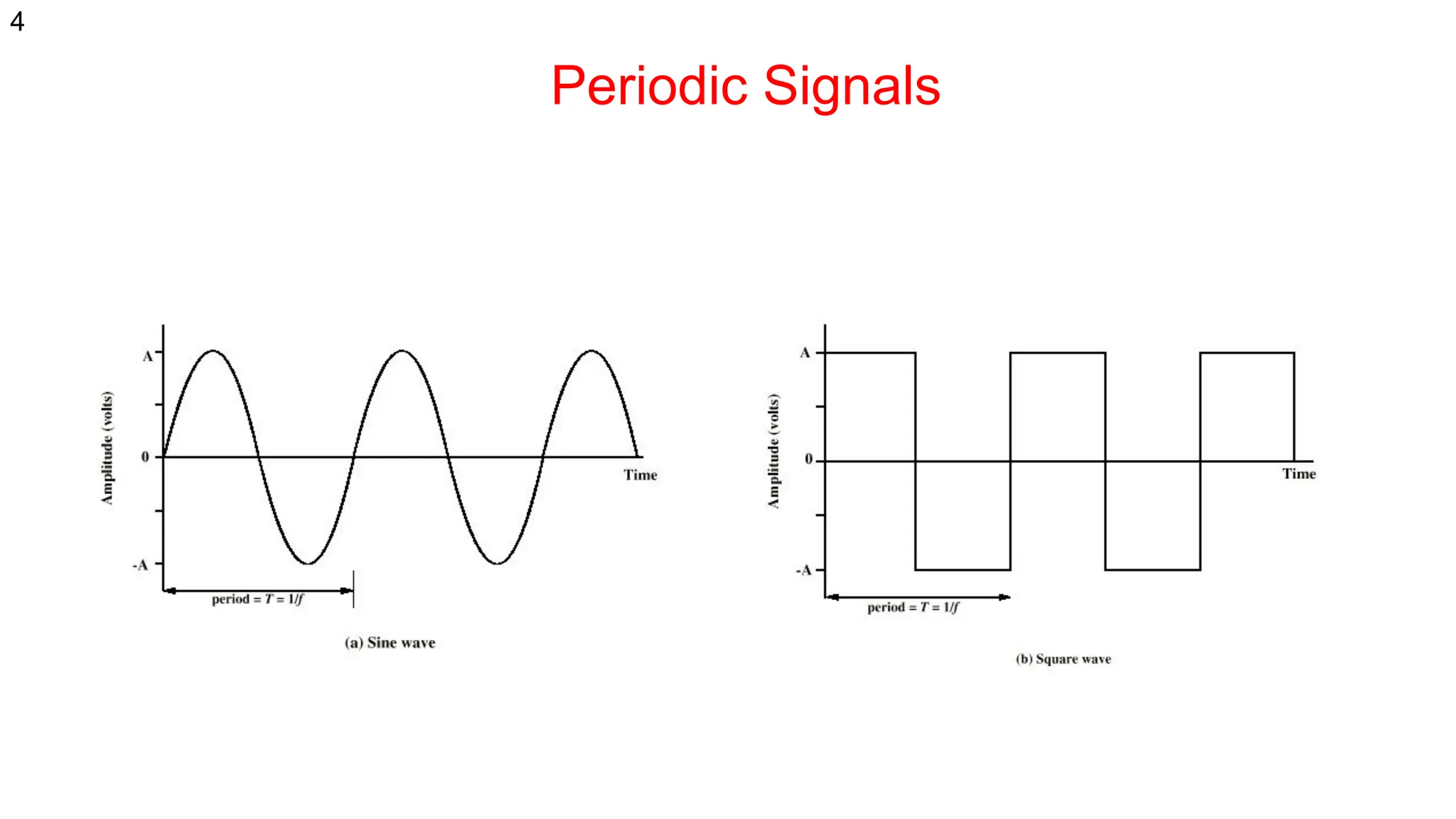
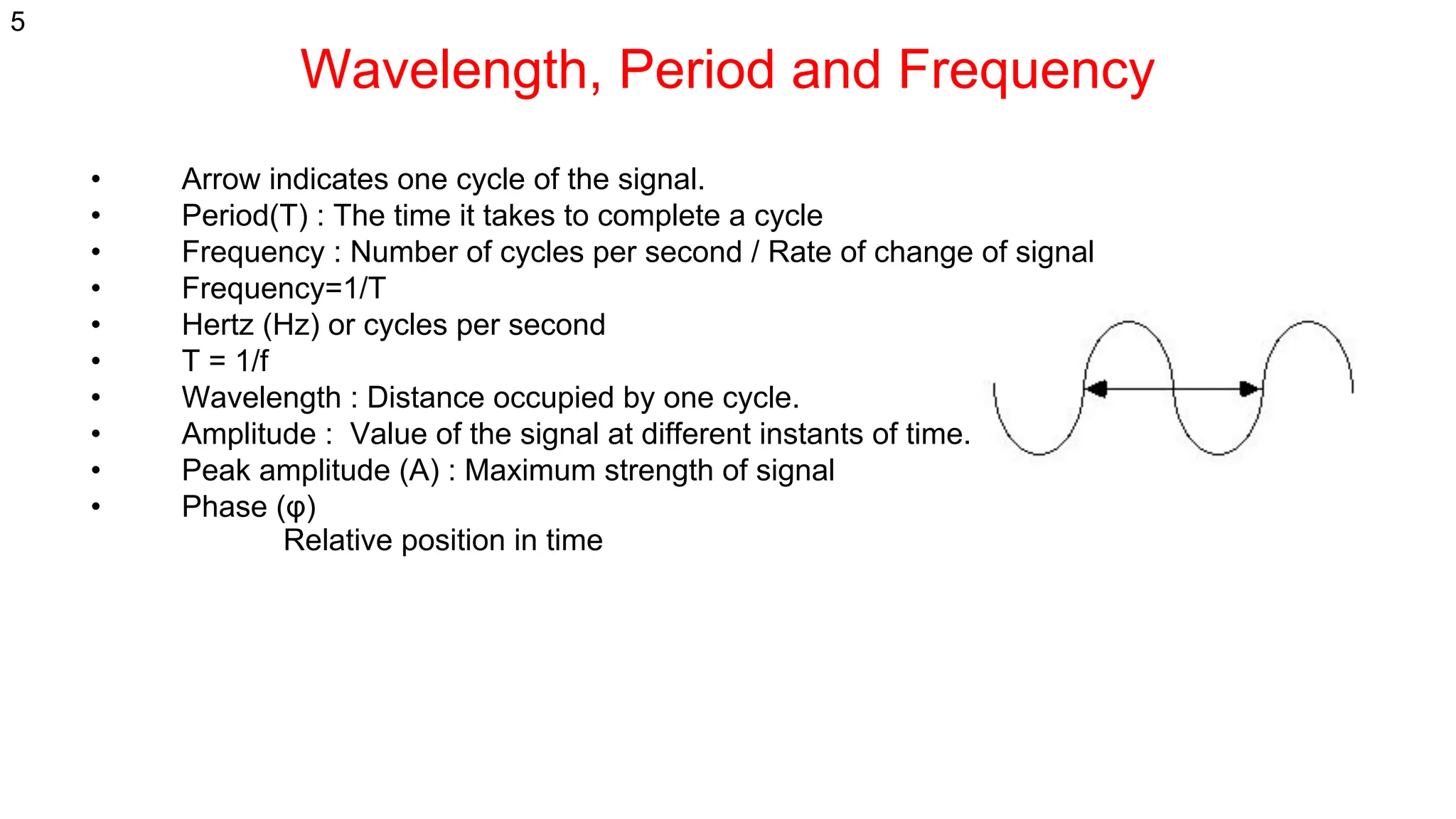
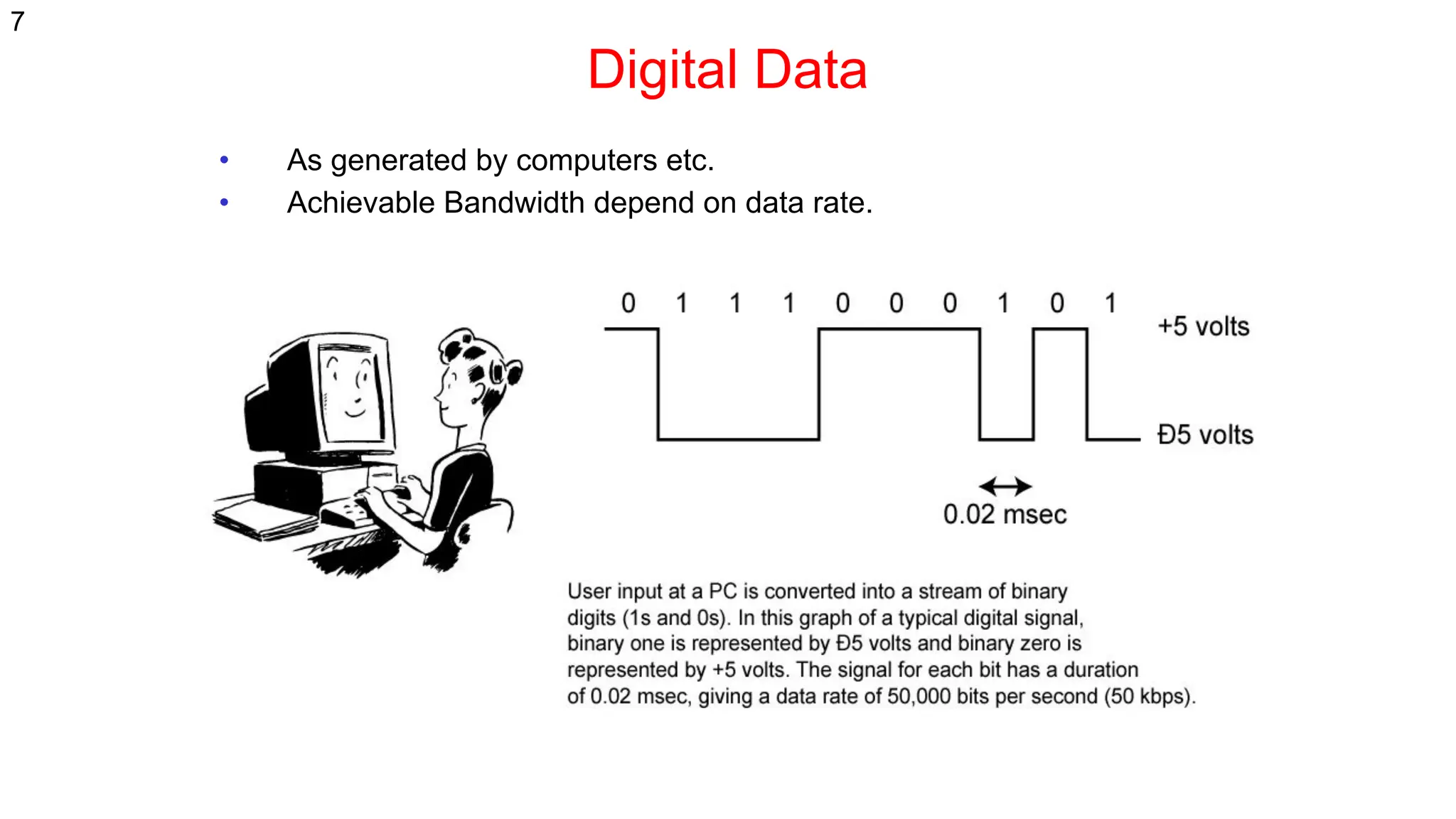
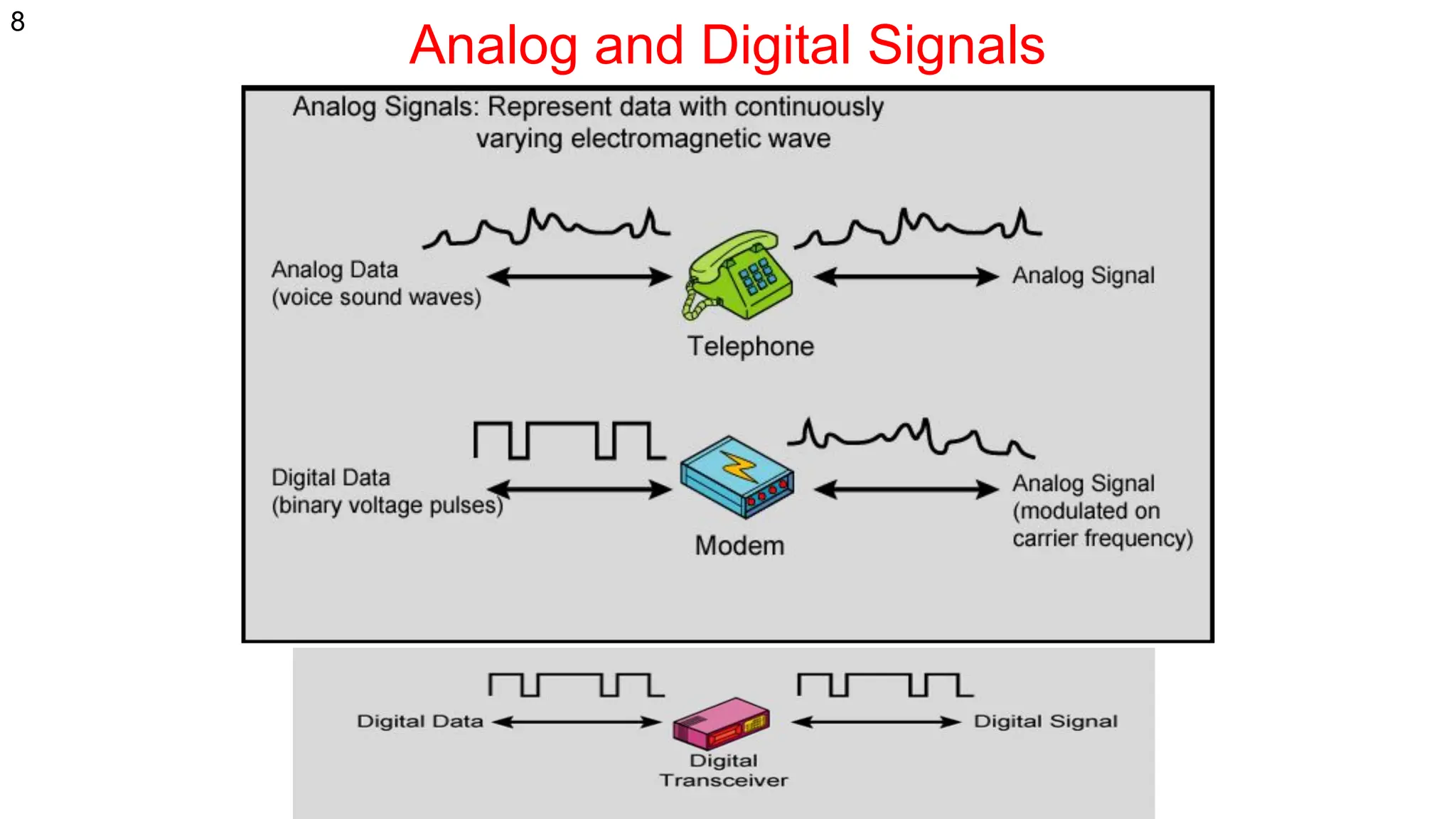
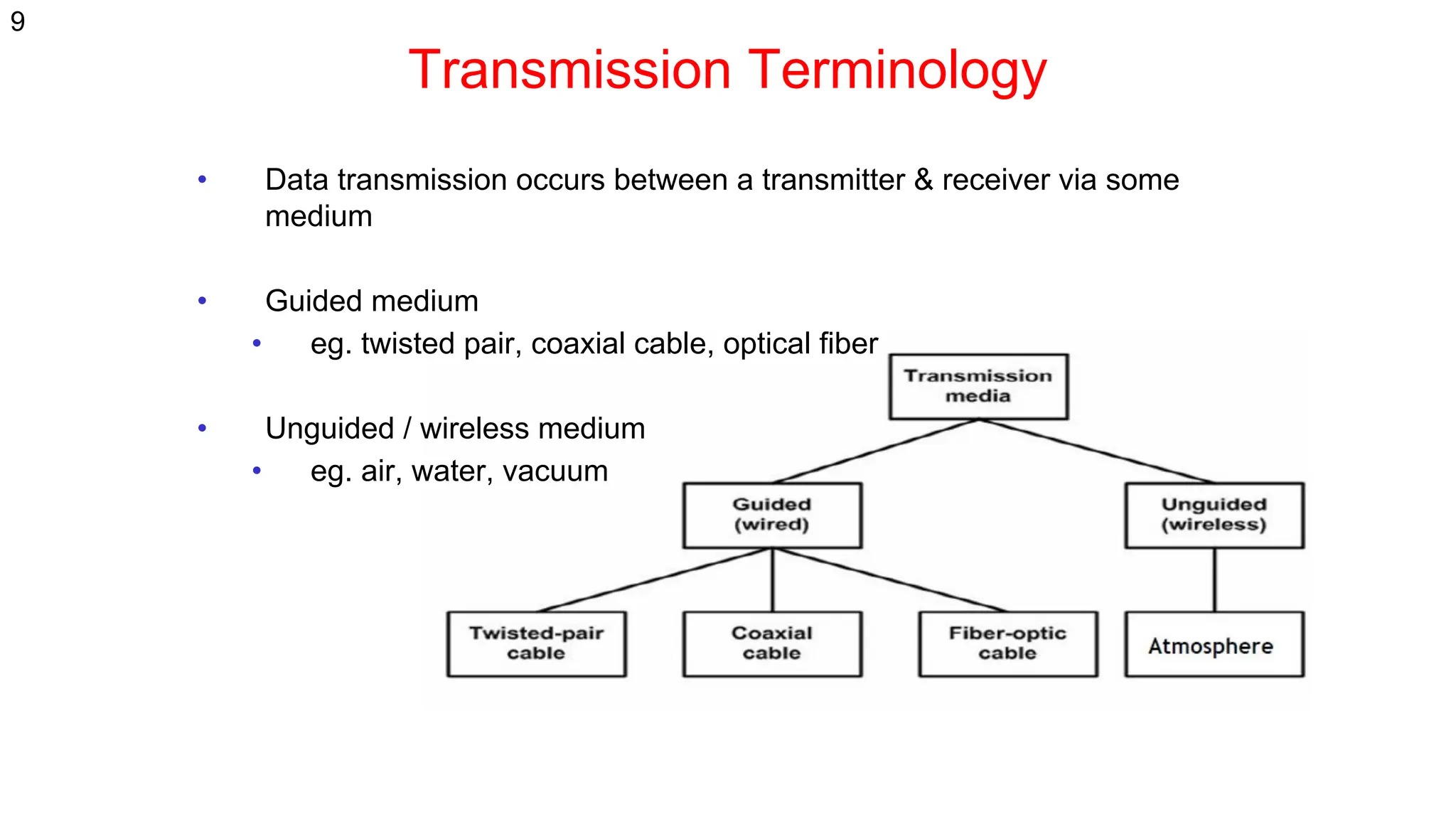
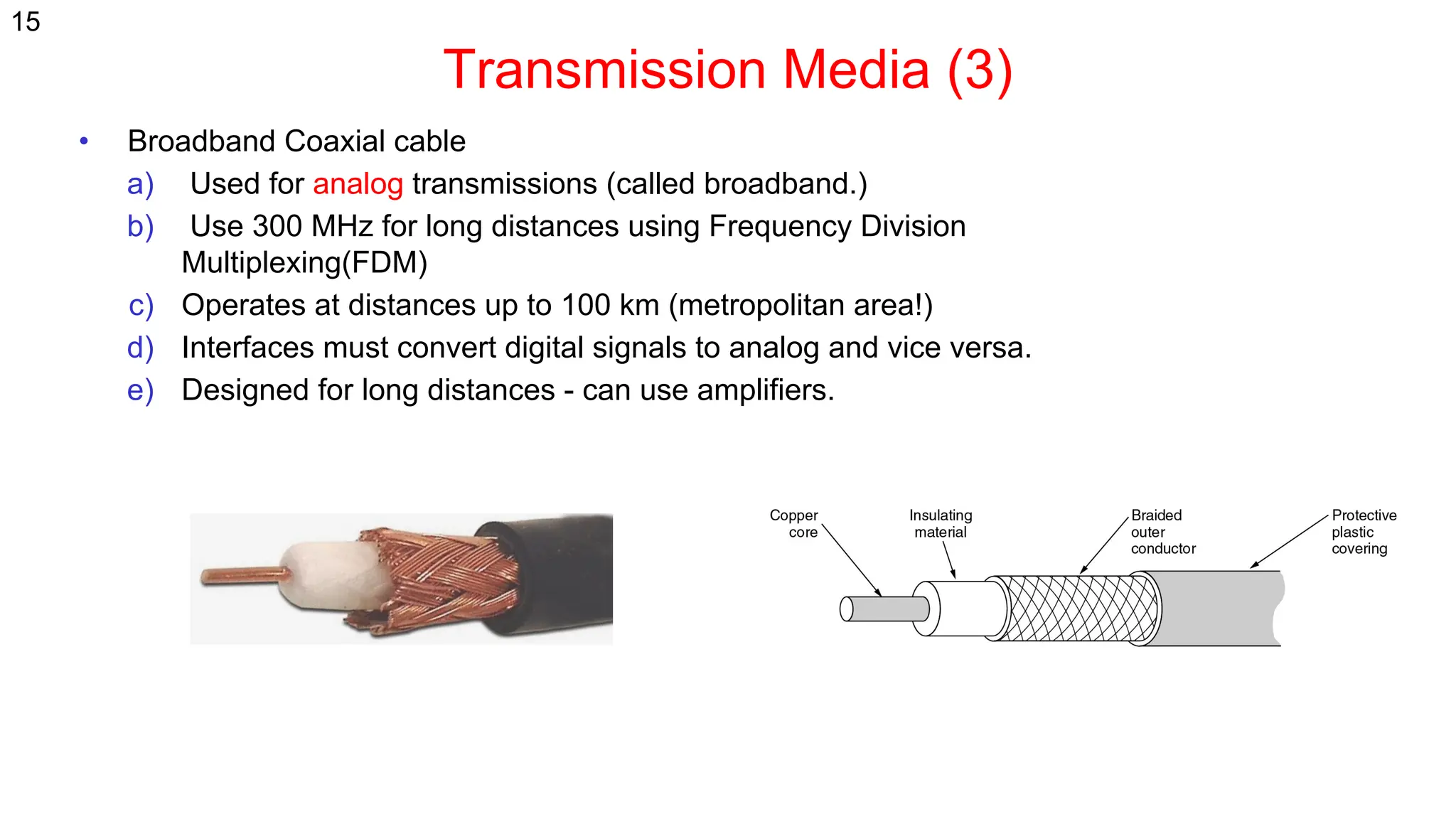
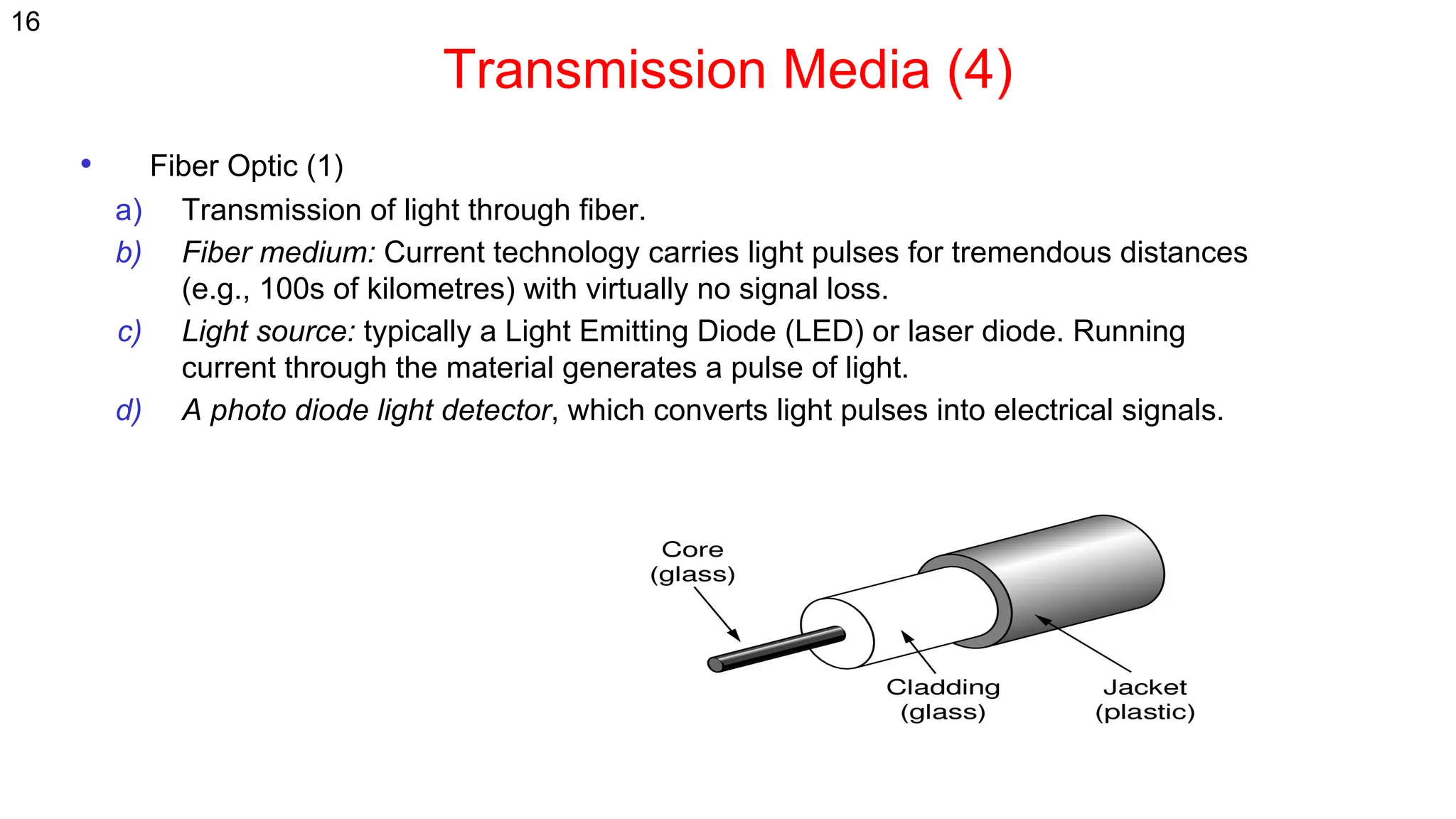
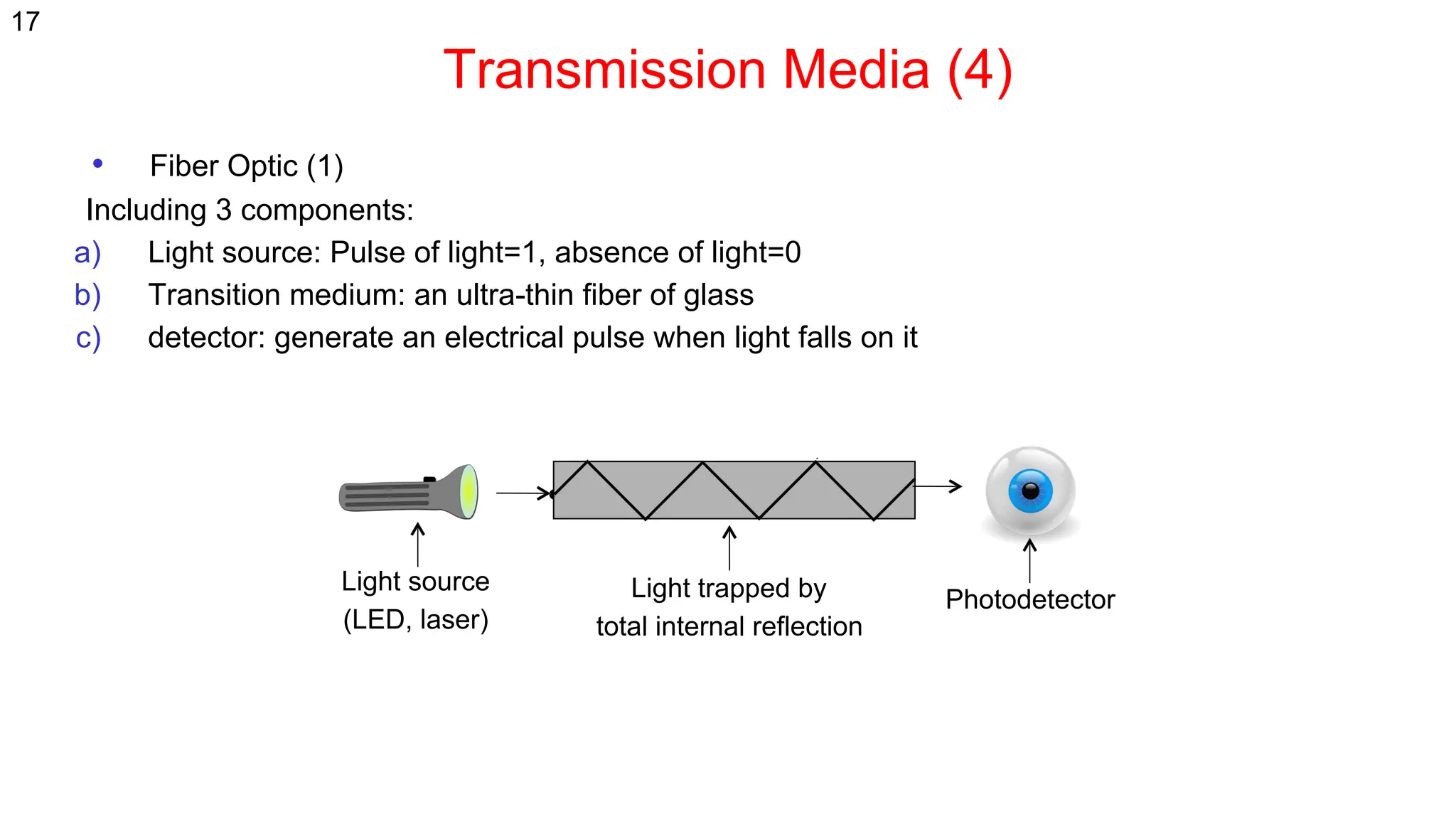
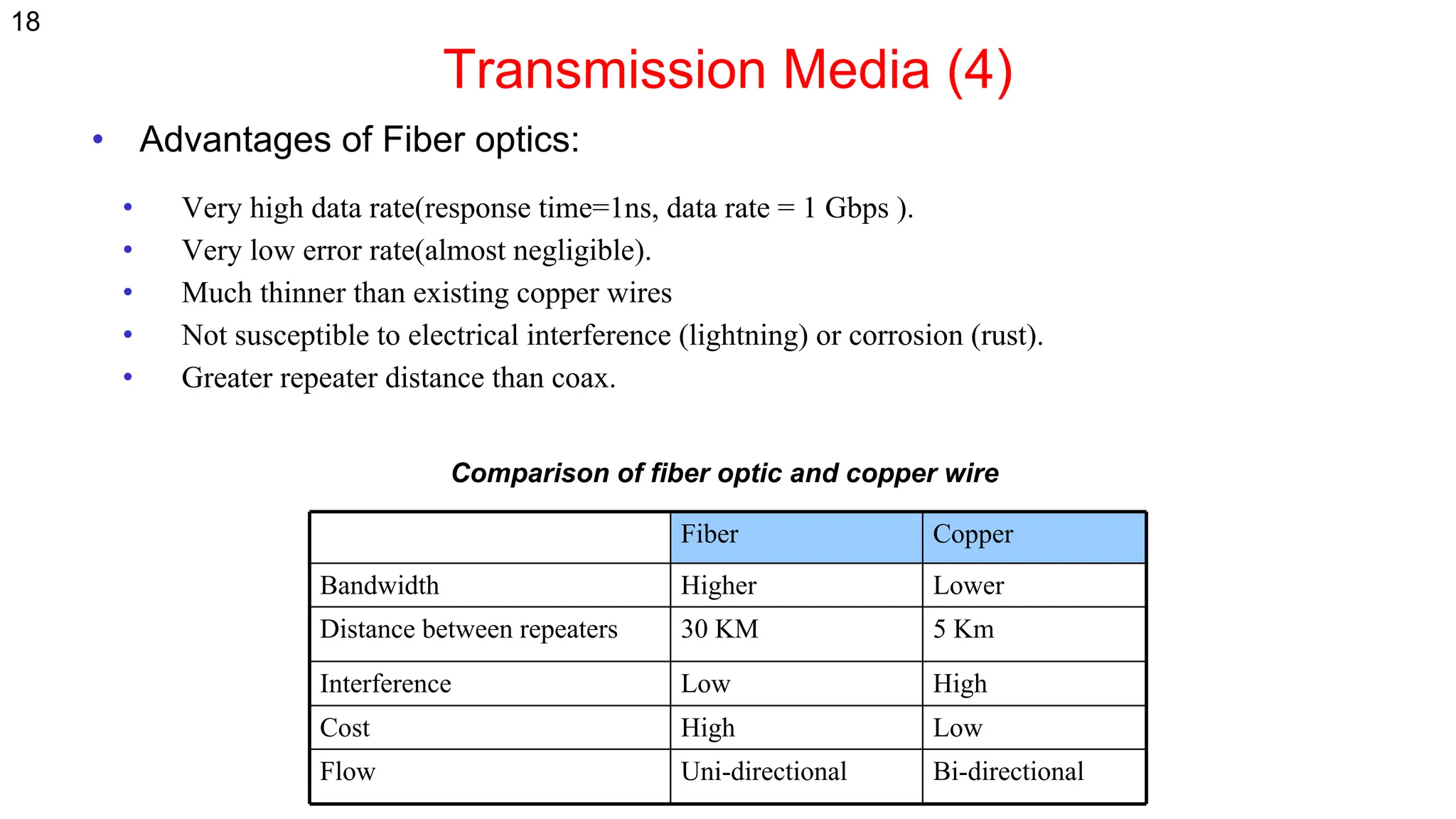
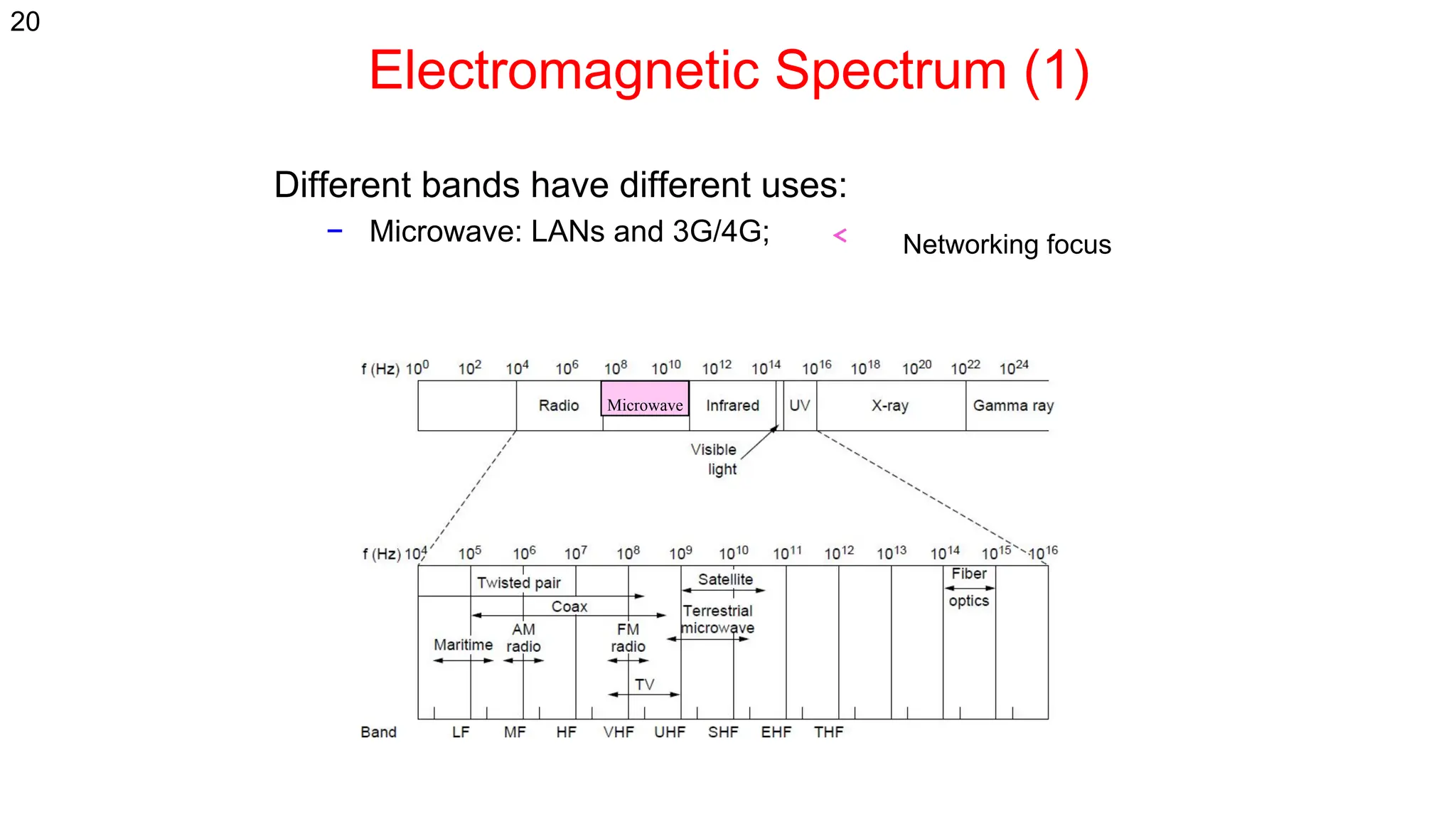
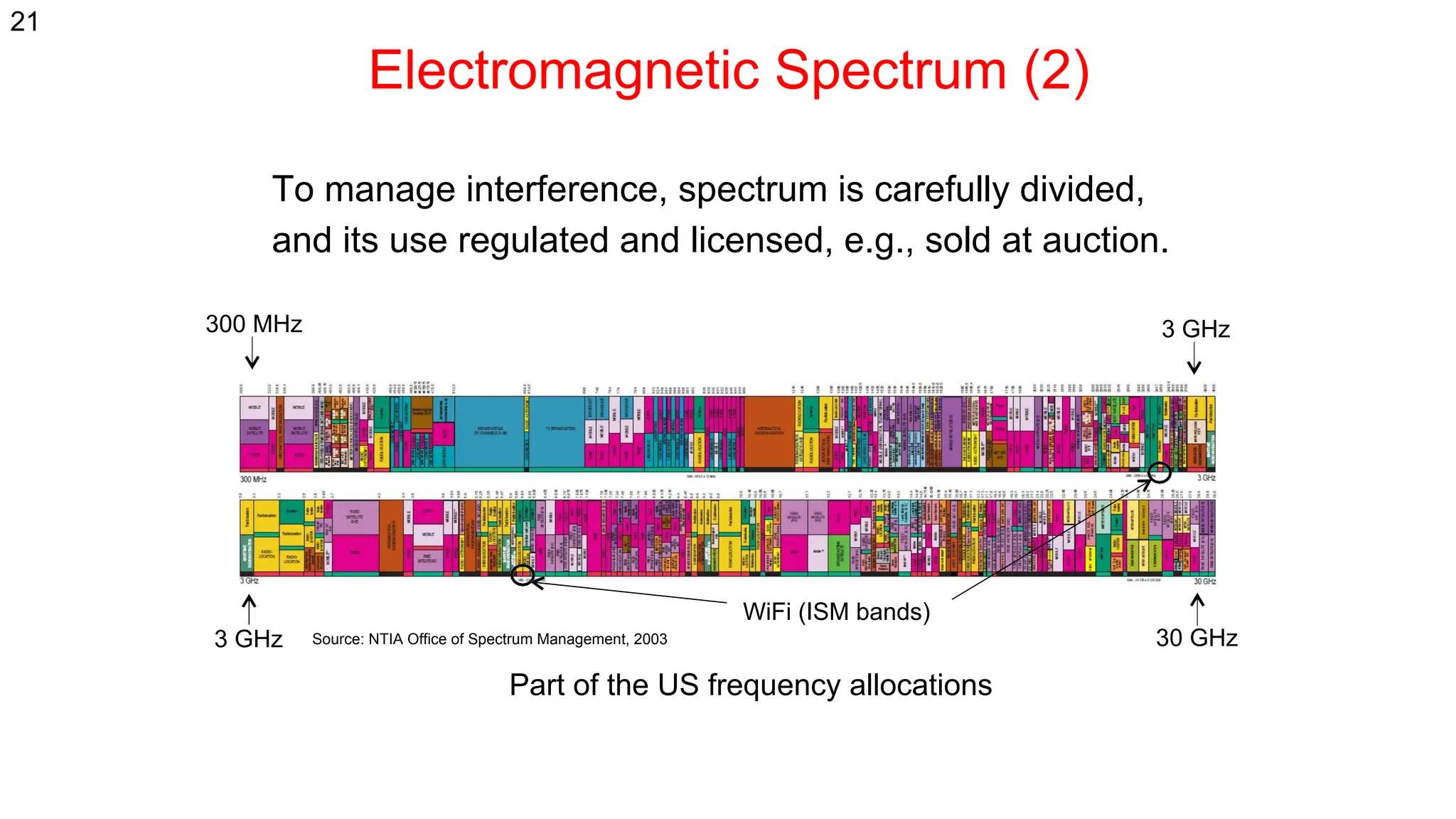
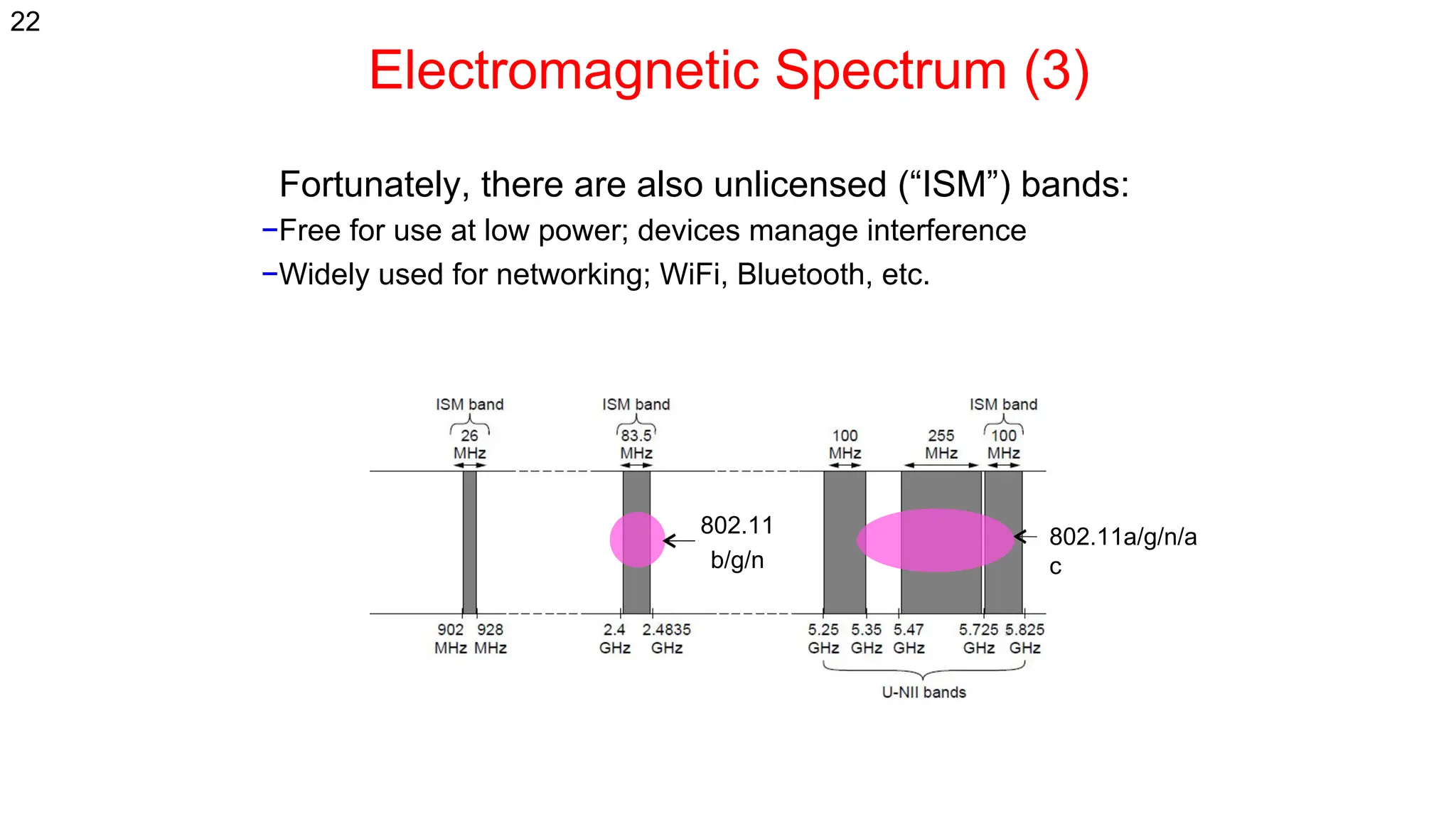
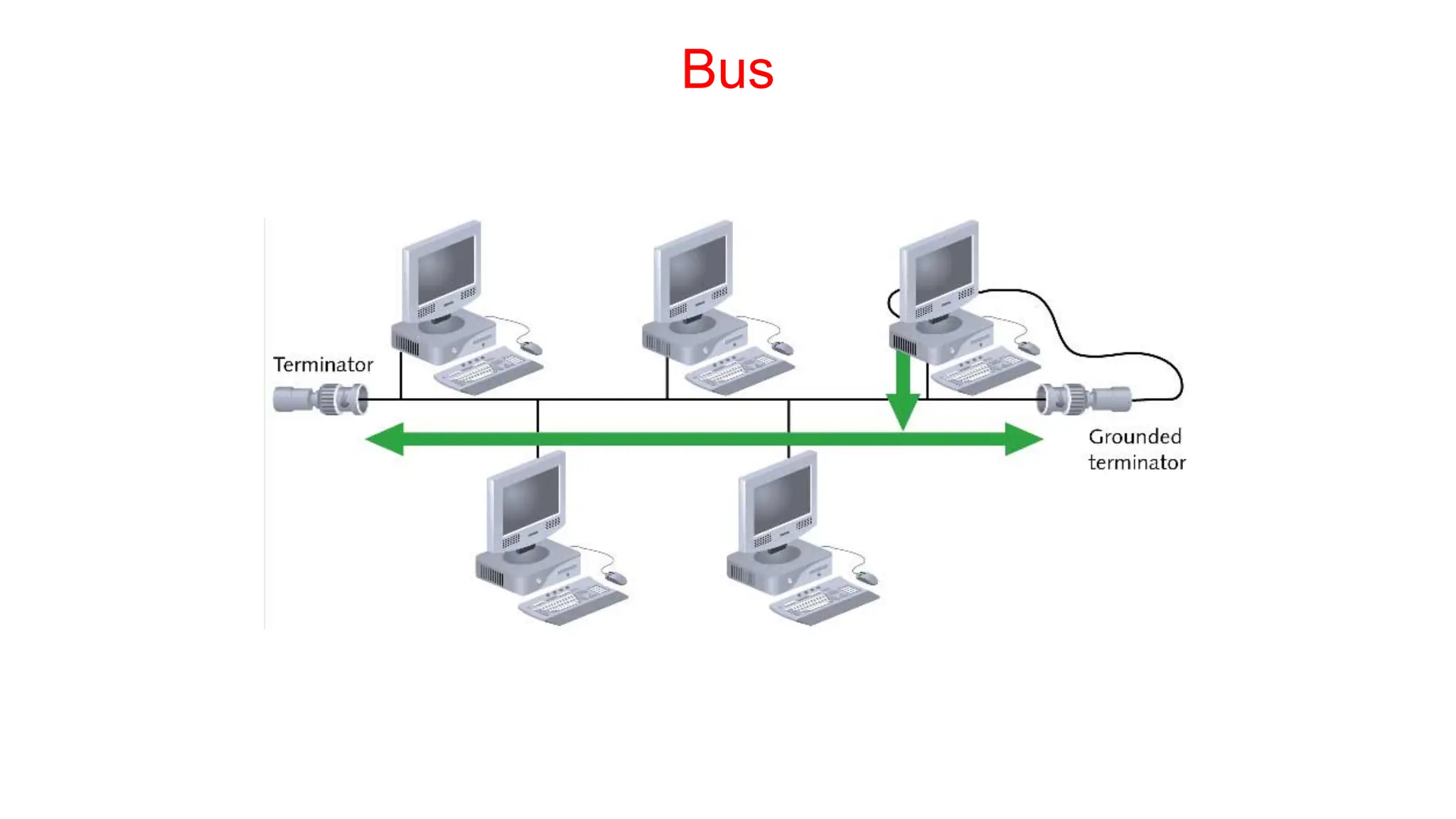
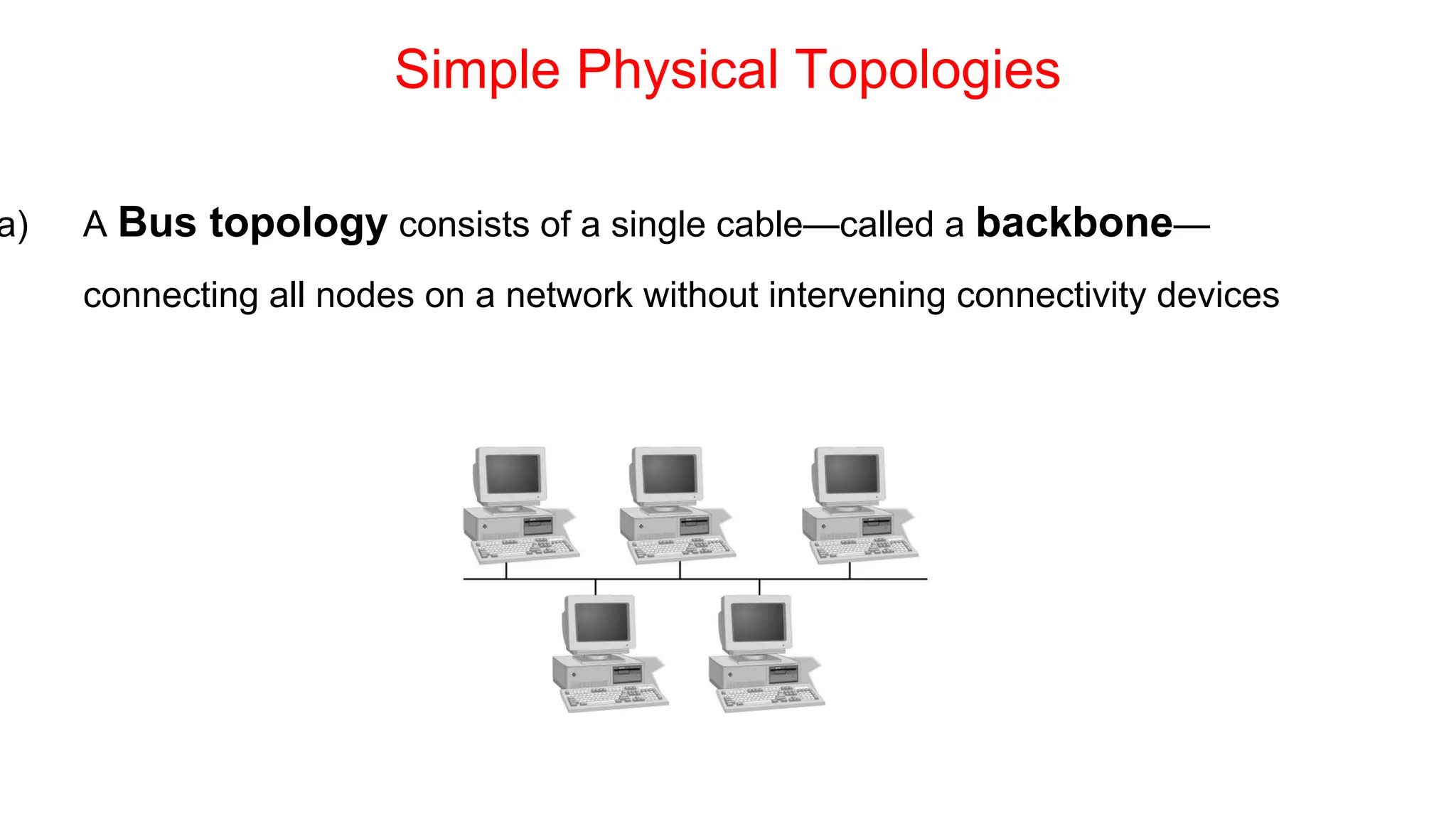
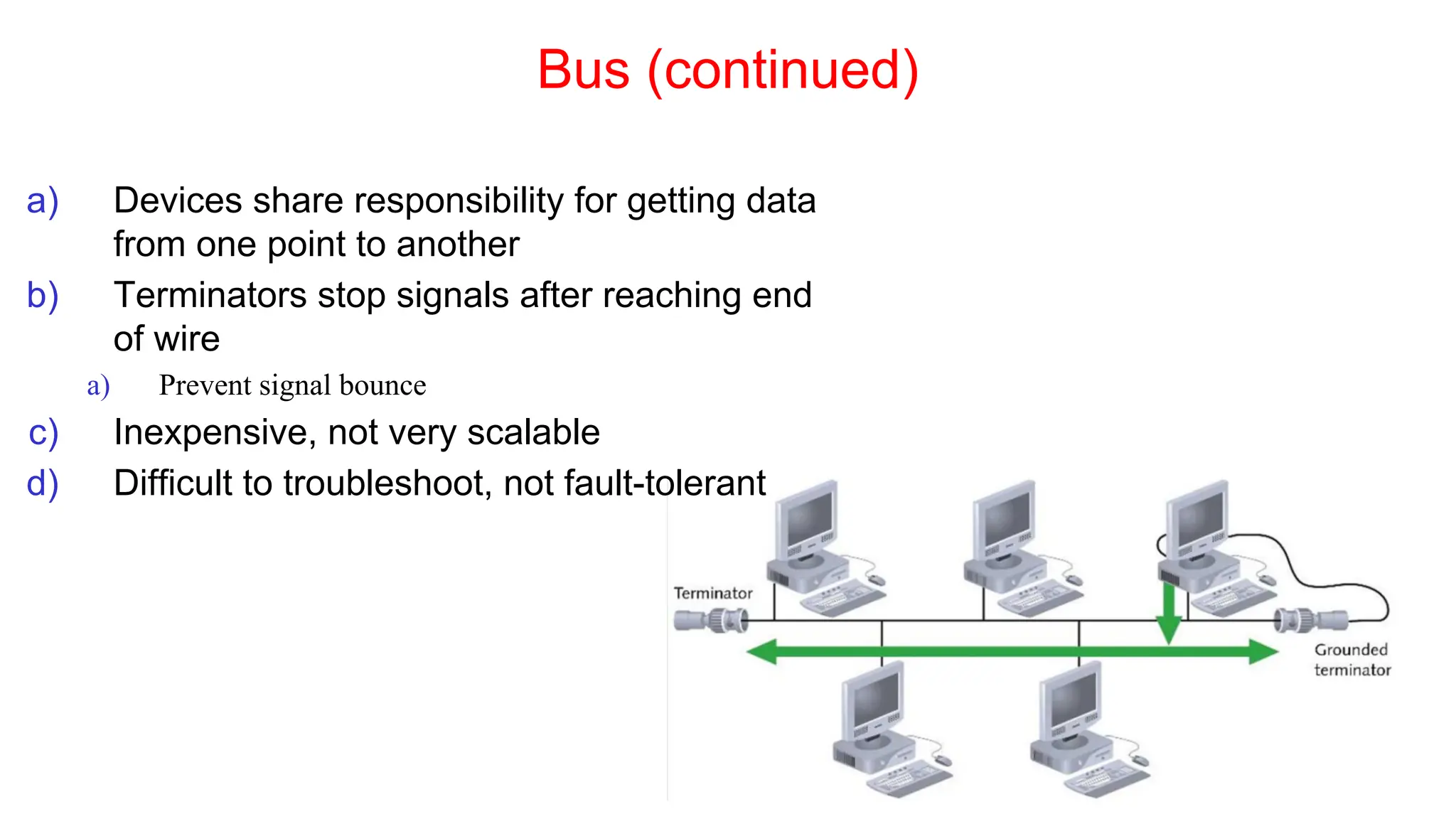
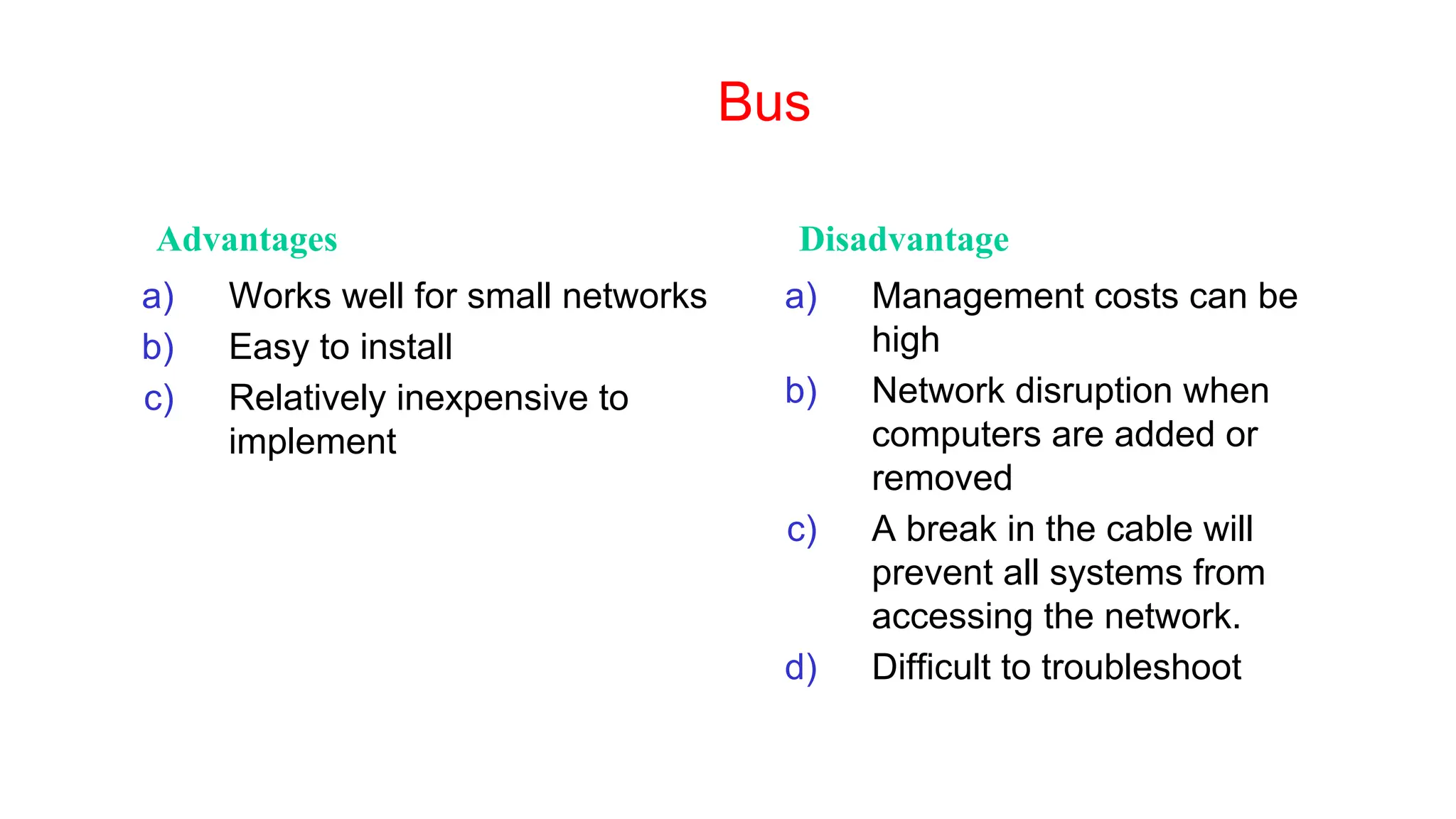
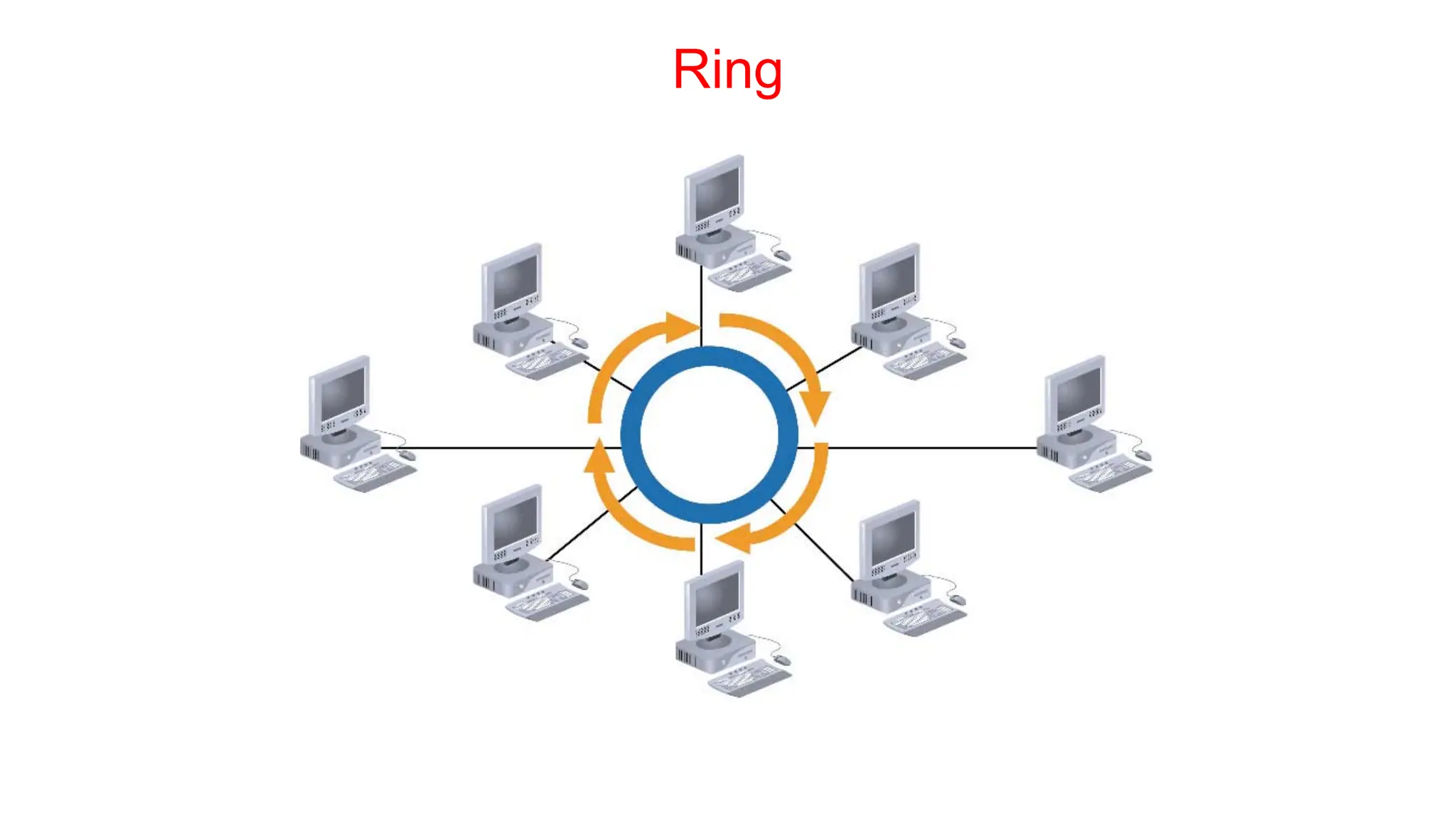
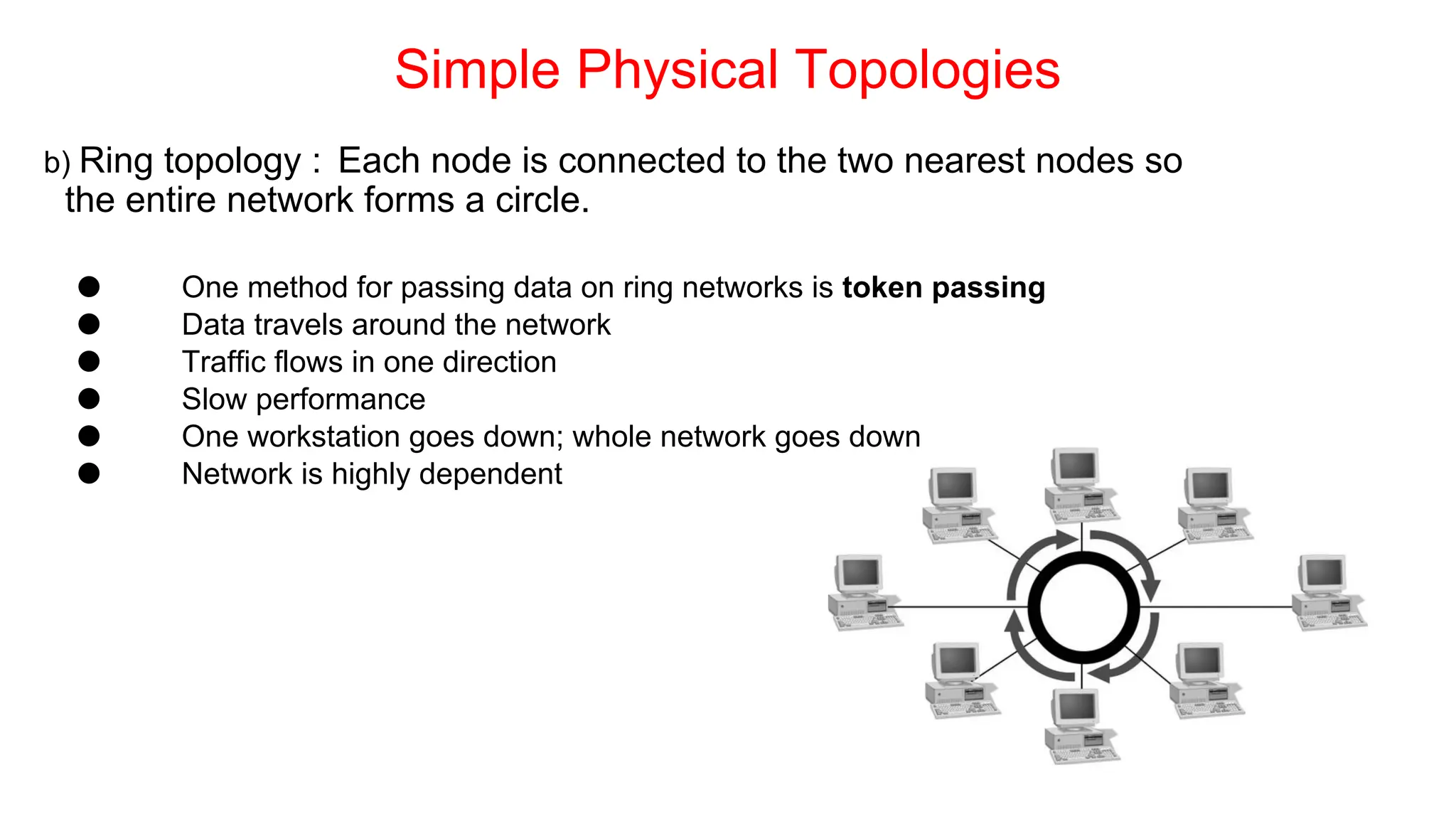
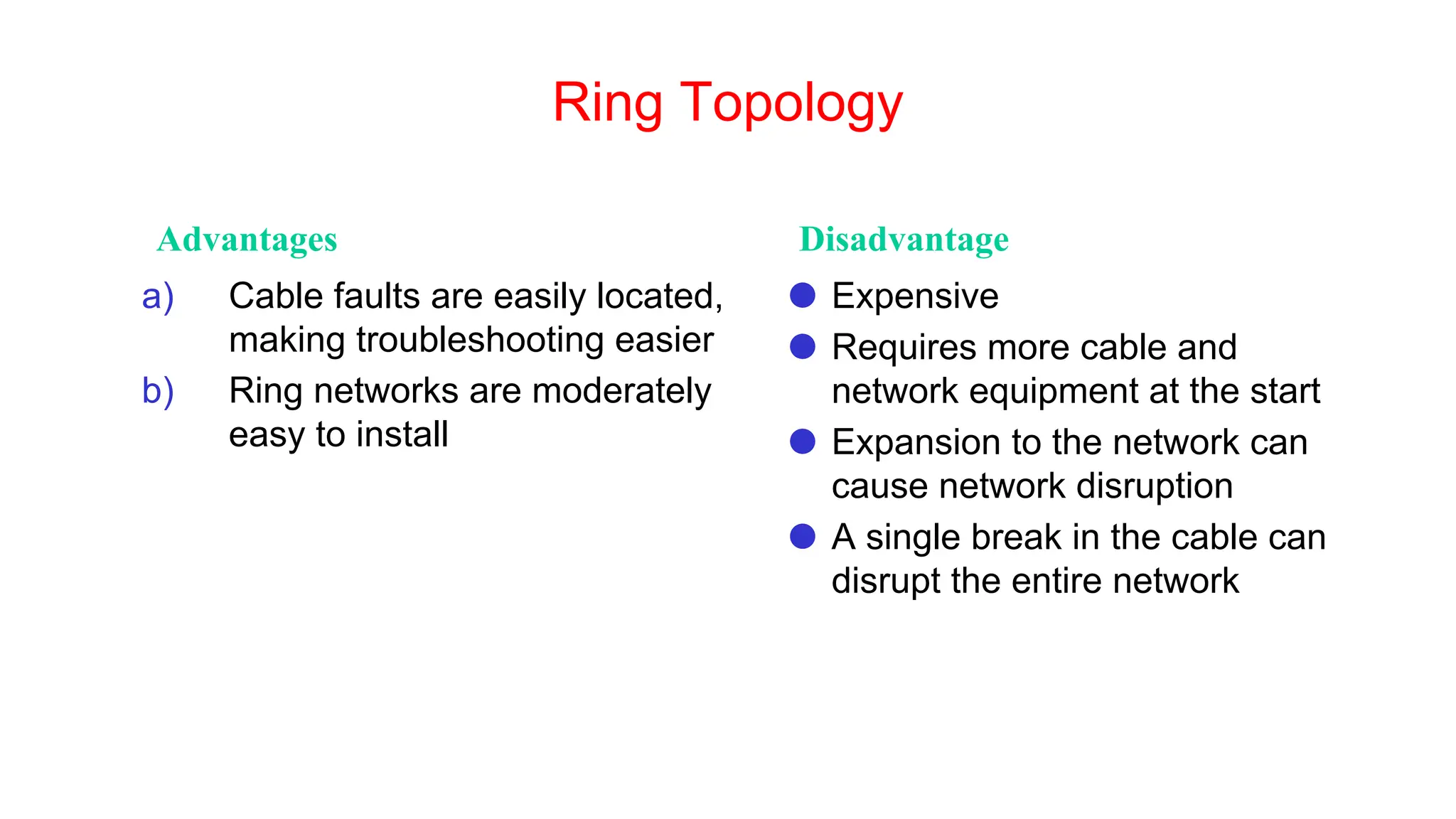
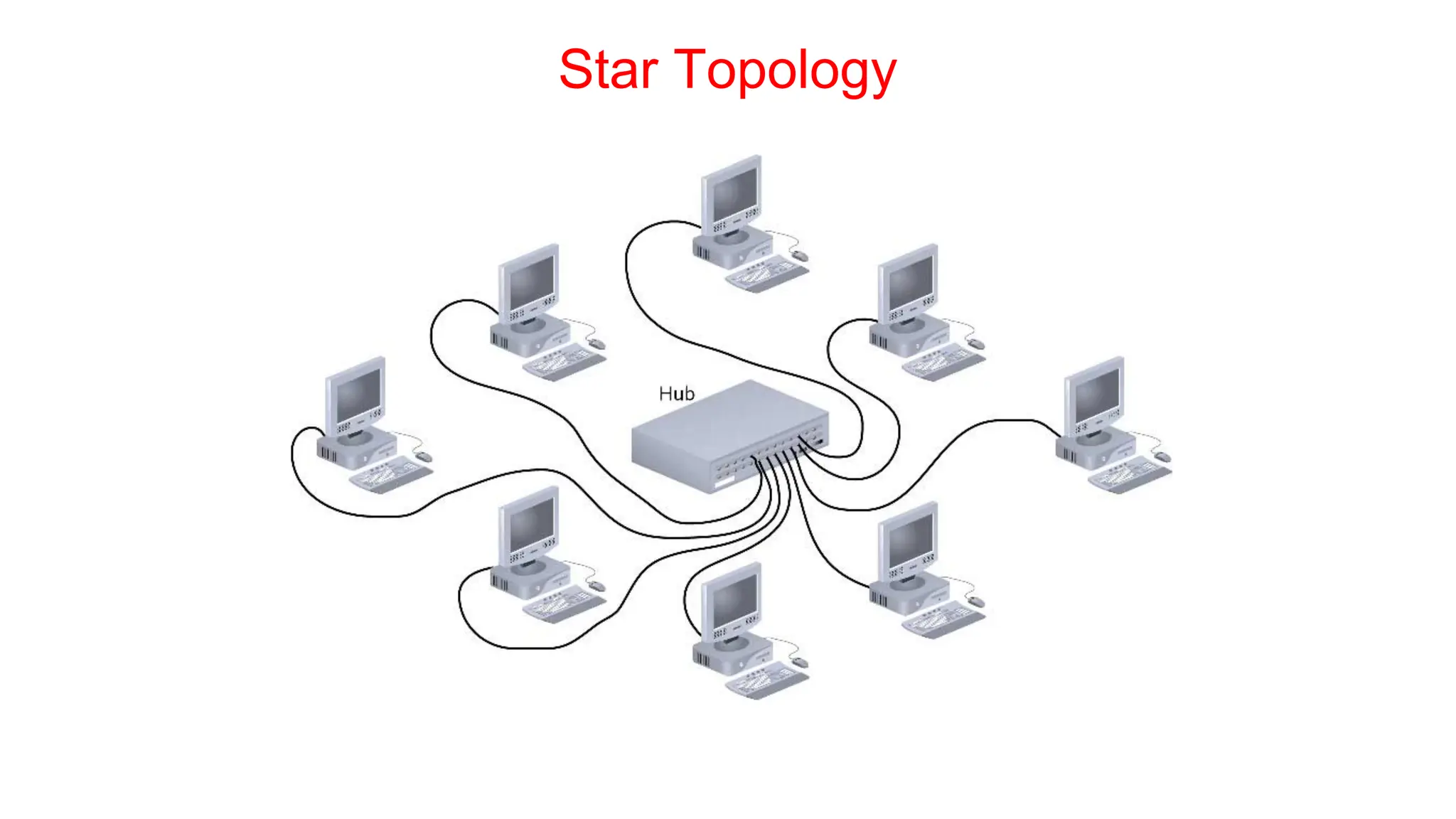
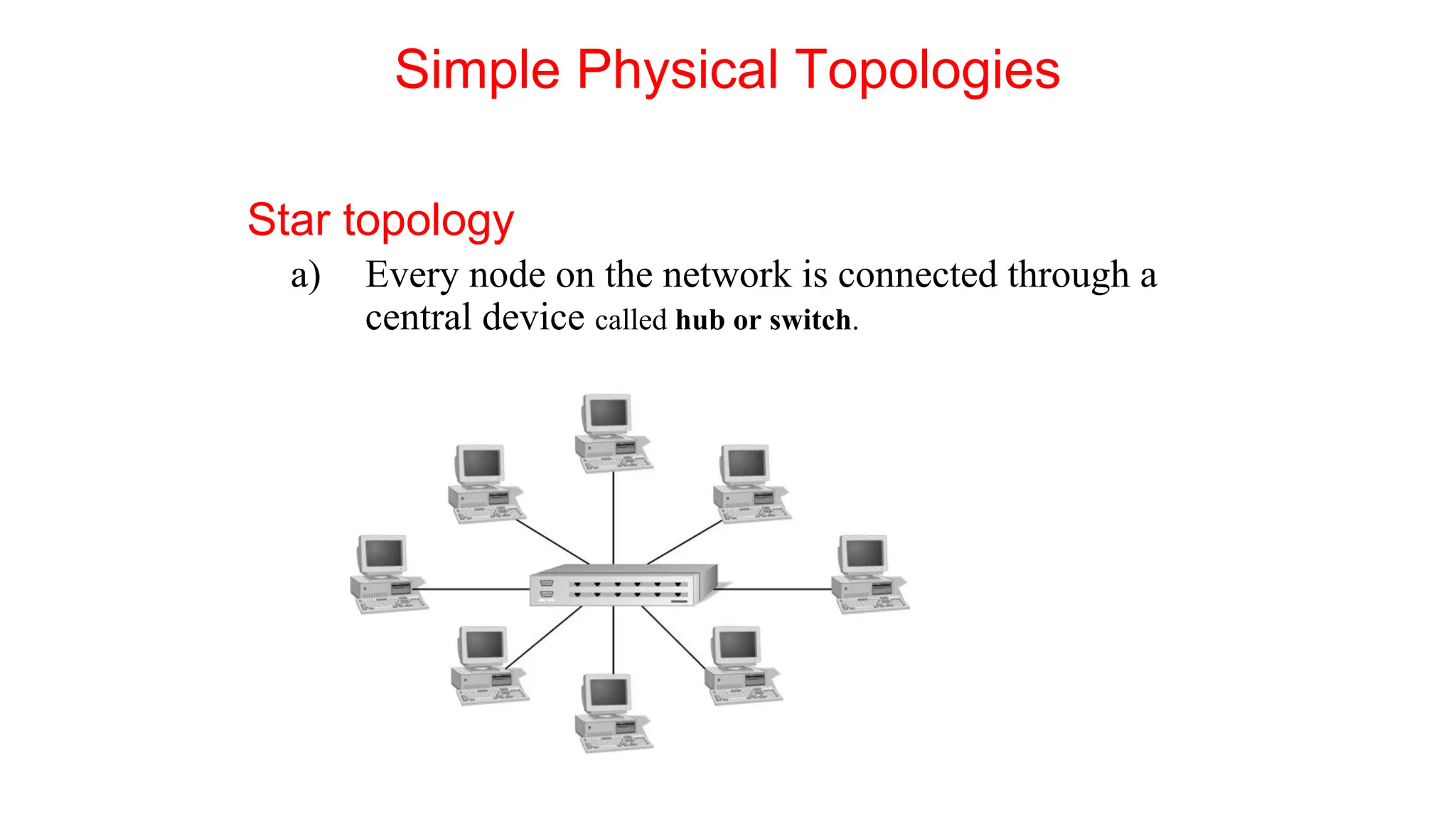
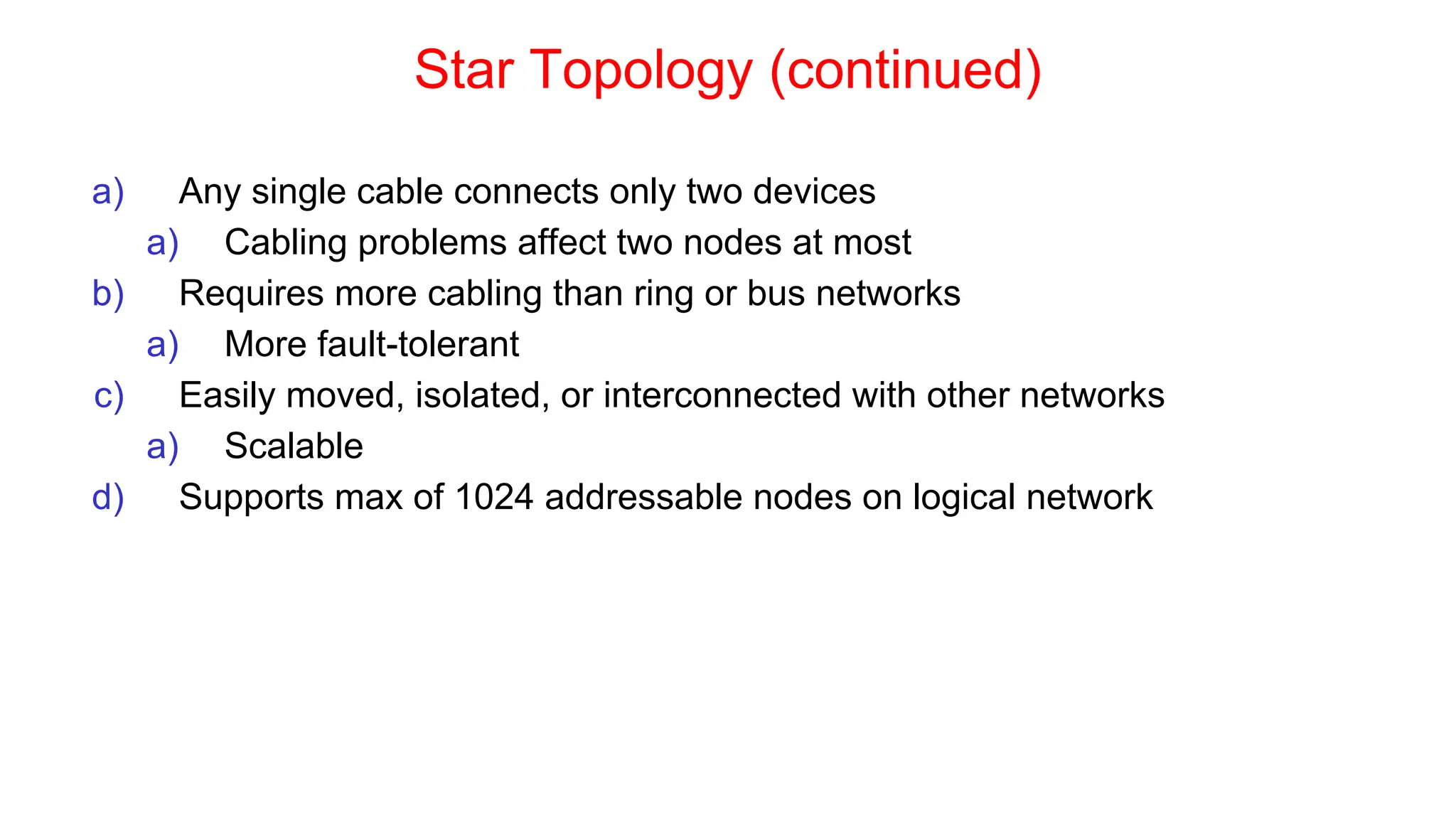
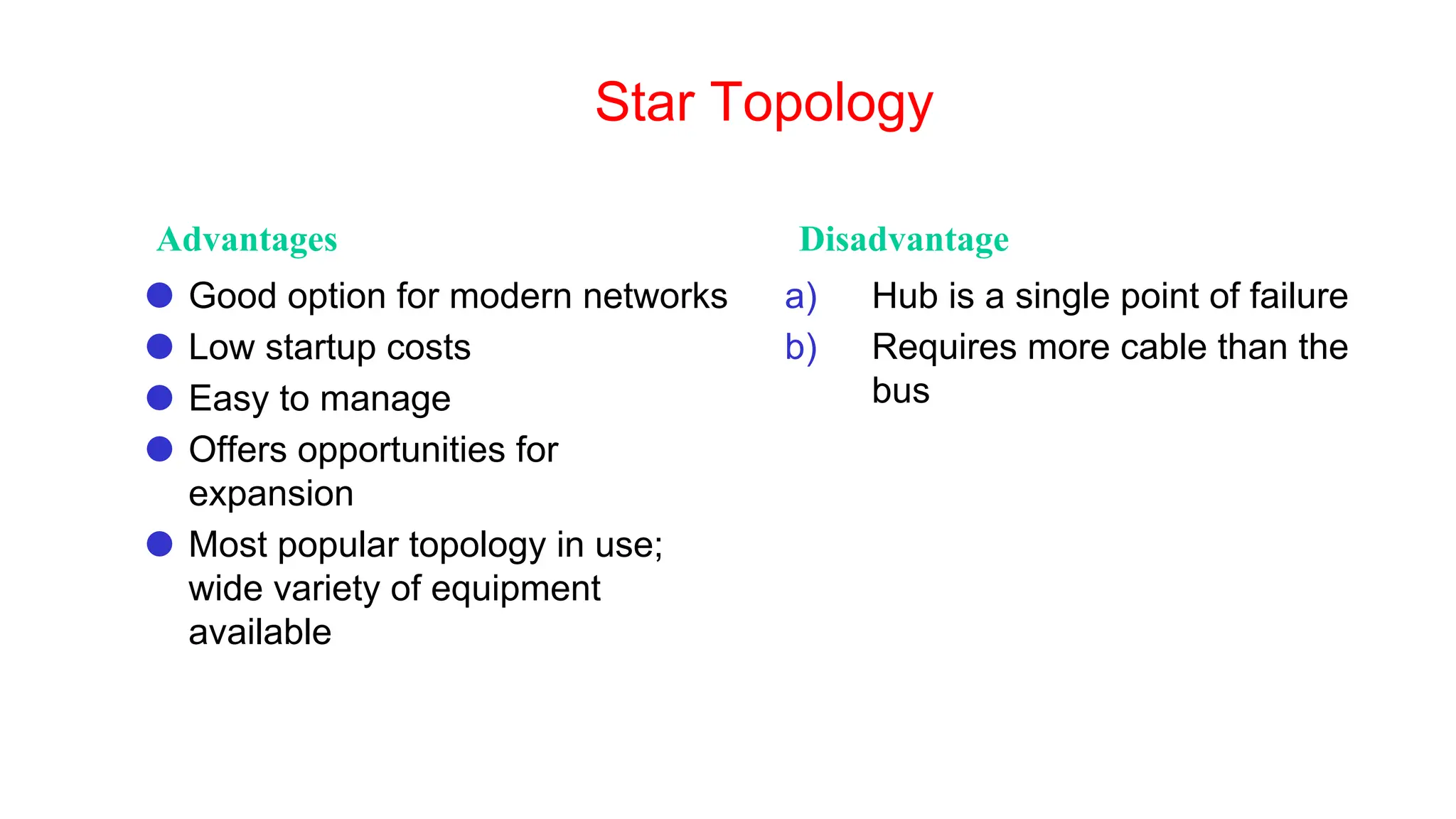
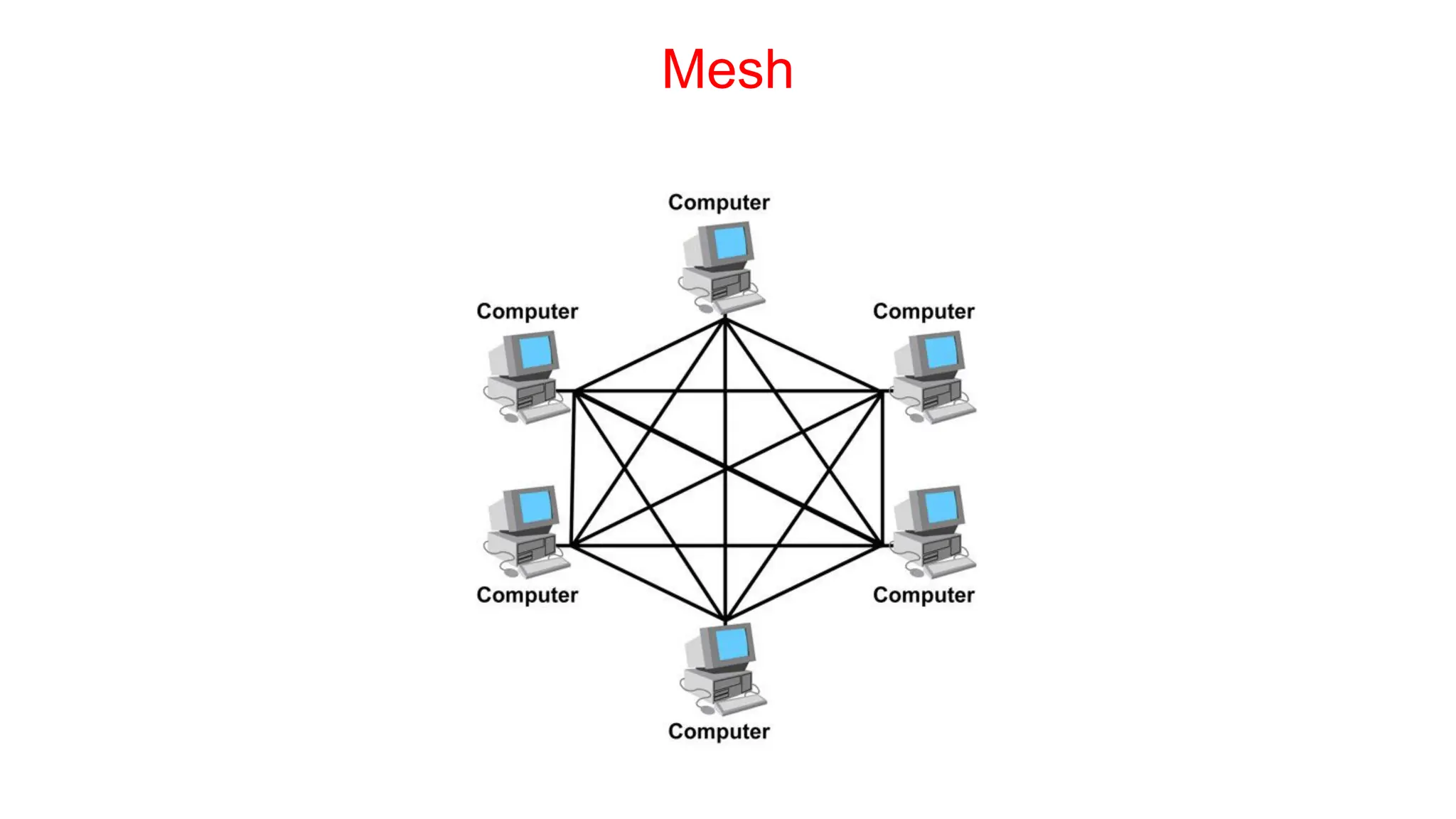
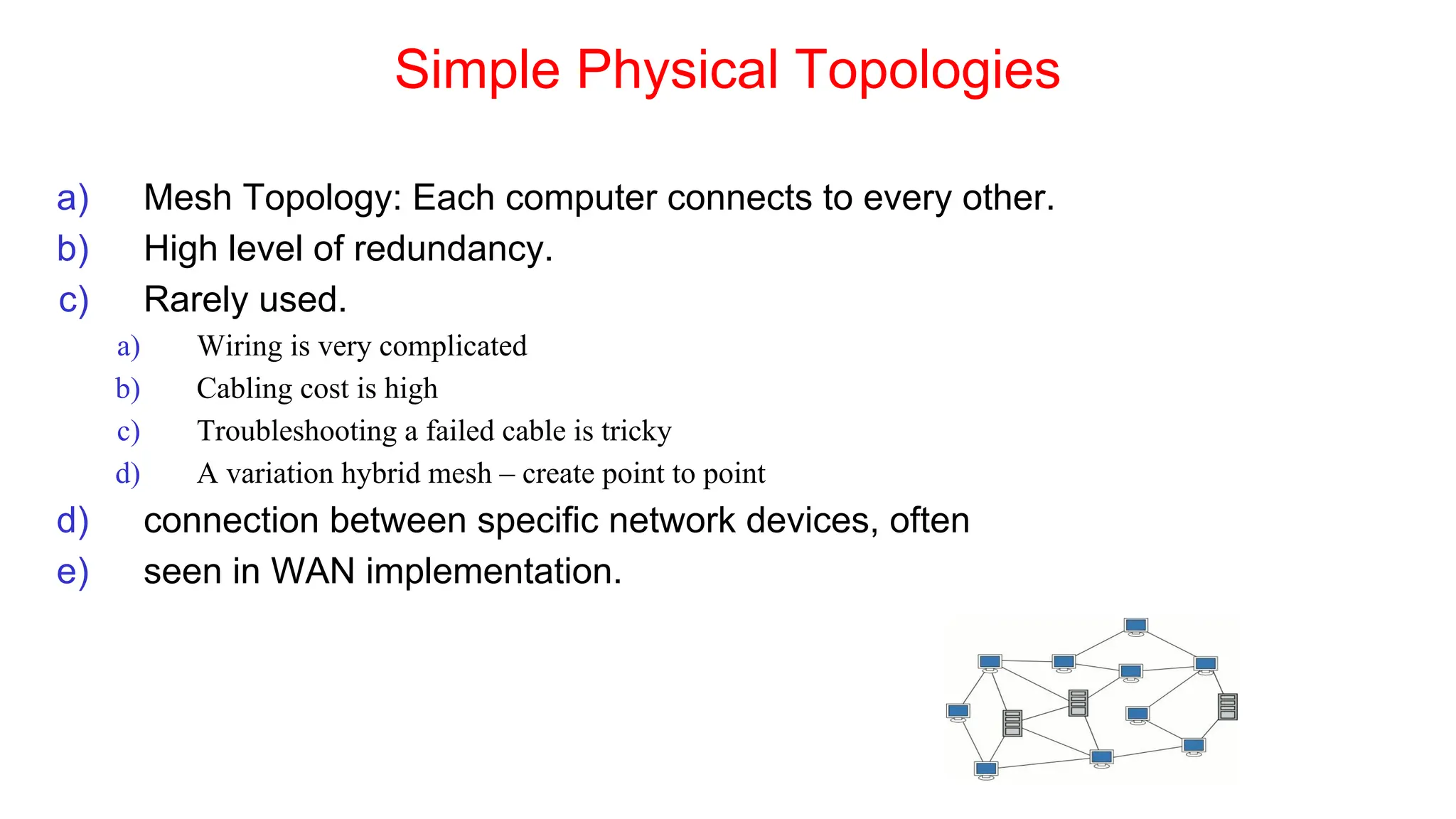
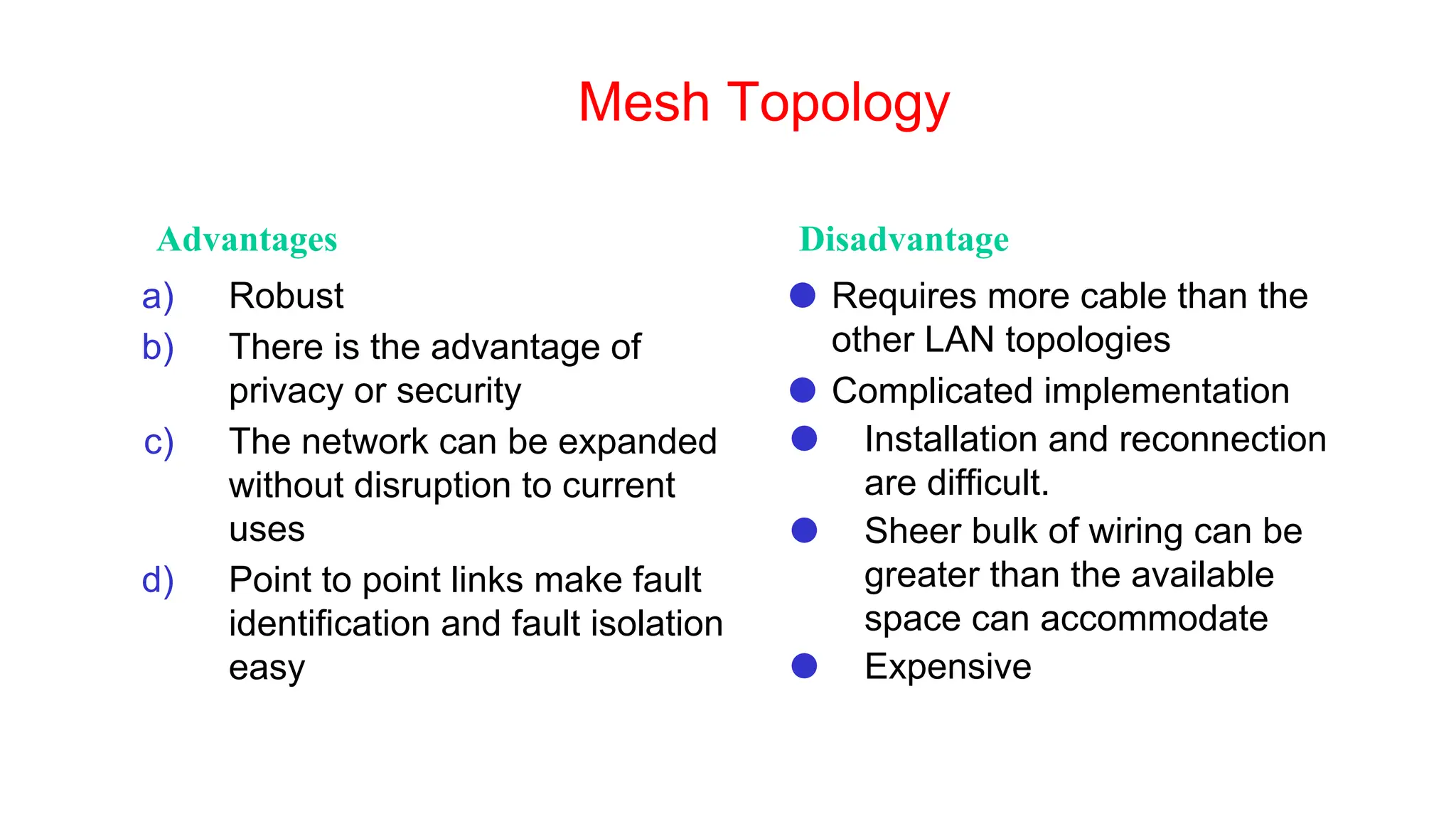
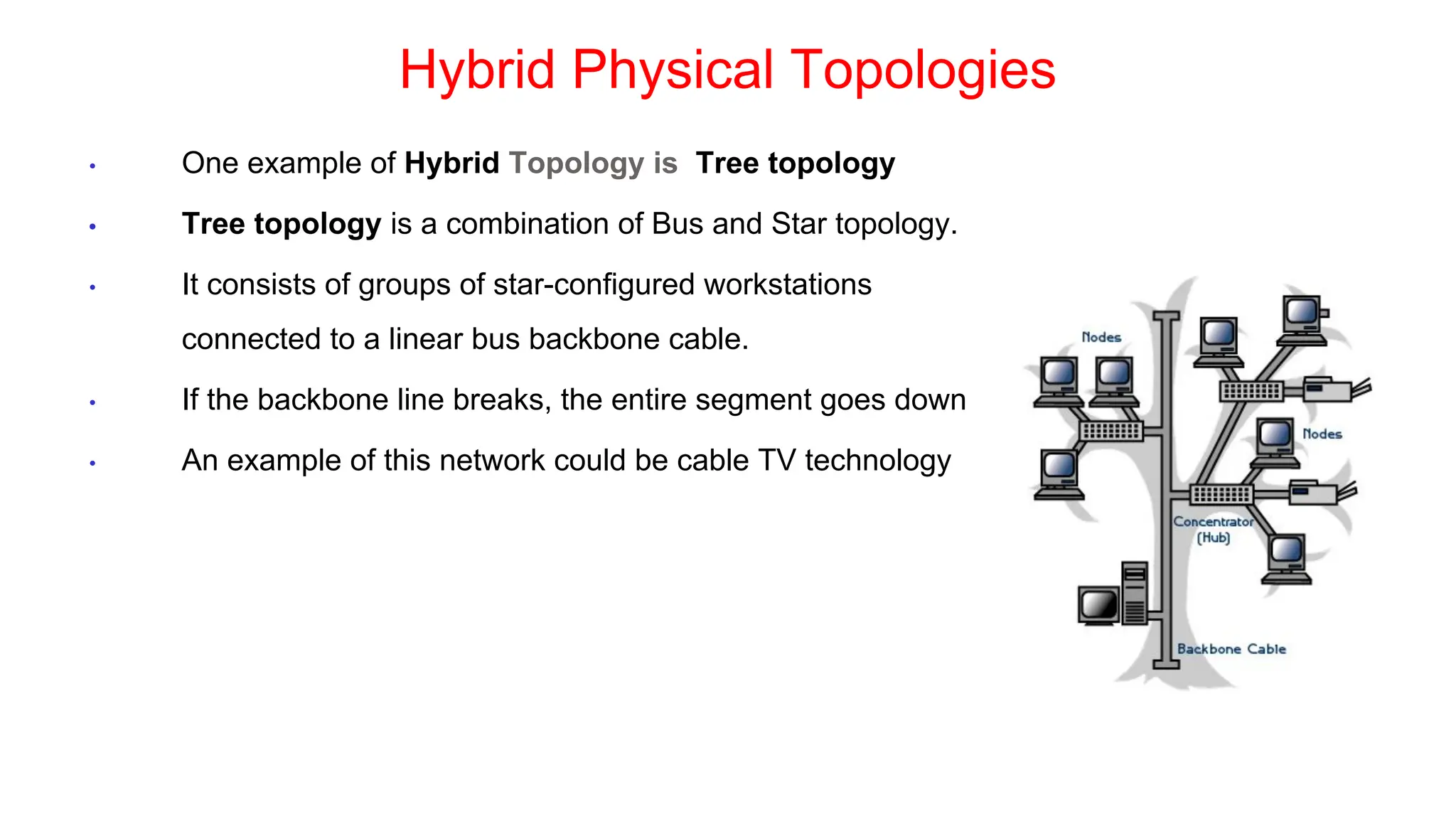
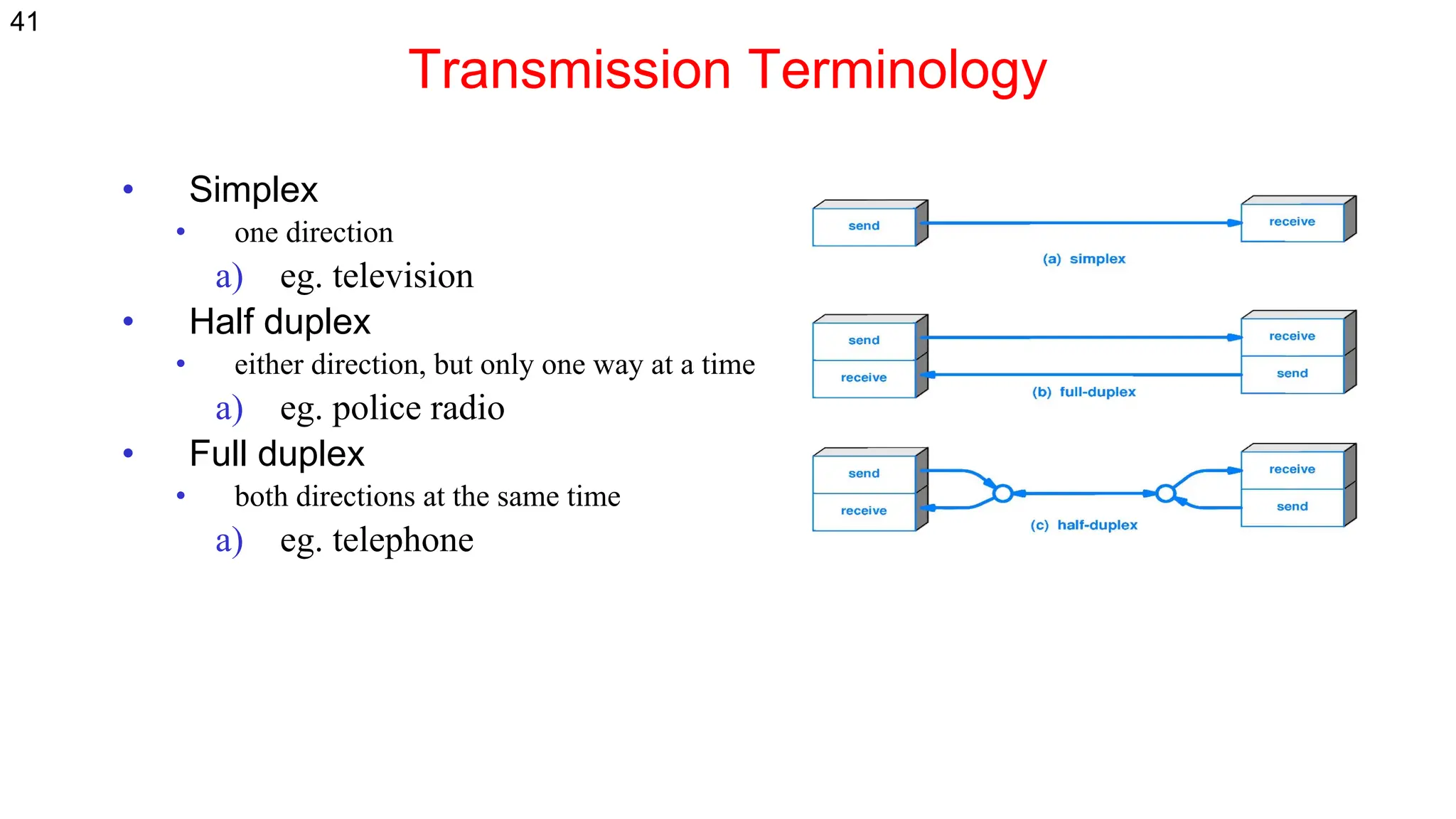
The document discusses the physical layer concepts of computer networks, covering key topics such as signal types (analog and digital), transmission media (twisted pair, coaxial, fiber optics), and various network topologies (bus, ring, star, mesh). It explains the properties of periodic signals, data transmission methods, and the advantages and disadvantages of different transmission mediums. Additionally, it highlights the importance of topology choice in network management and expansion.