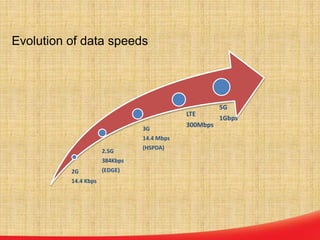
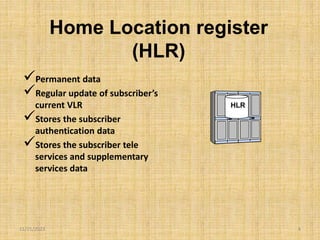
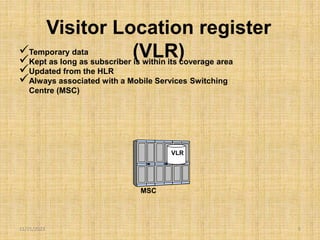
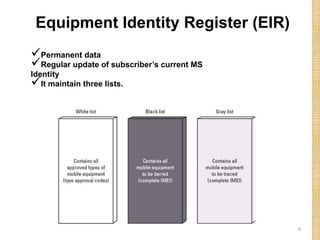
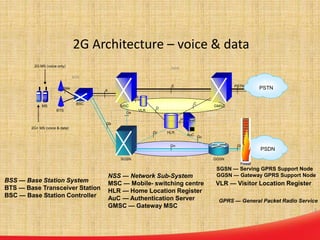
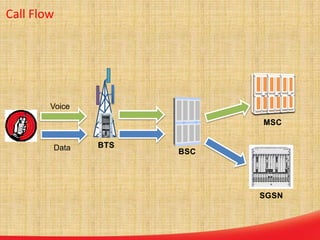
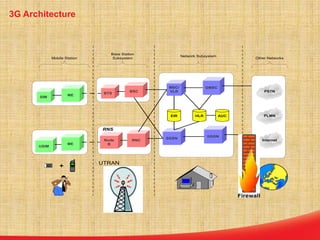
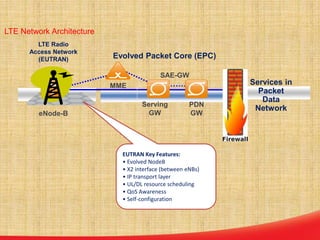
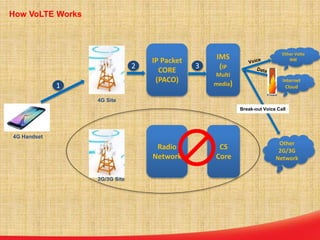
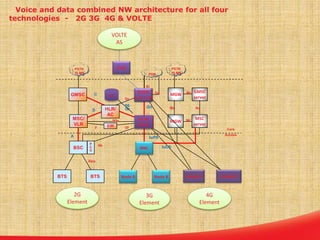
This document discusses the evolution of mobile network architecture from 2G to 5G. It describes the increasing data speeds over time from 2G's 14.4 Kbps to 5G's potential for 1 Gbps. It also outlines the key components of a mobile network including the mobile station, base station, switching centers, and registers that store location and authentication data. Finally, it provides an overview of 4G LTE architecture and the transition to an all-IP network as well as steps taken for secure mobile data networks.