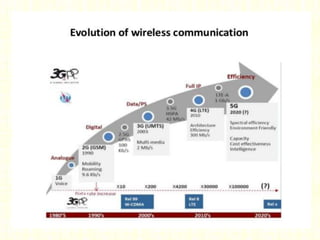
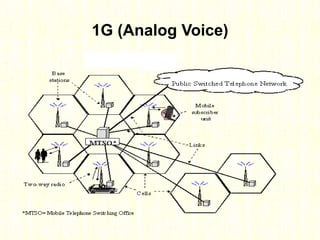
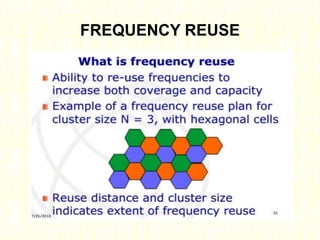
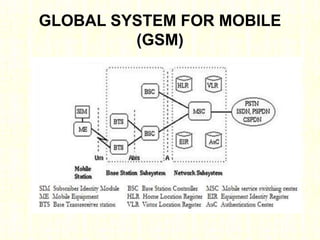
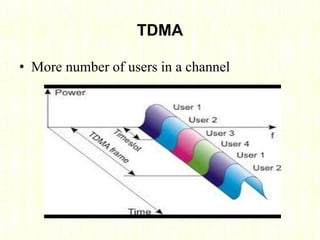
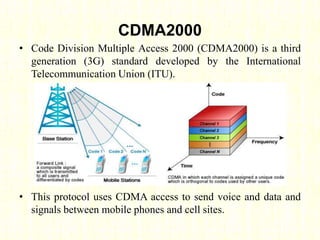
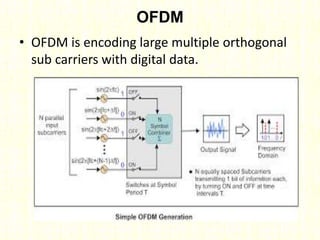
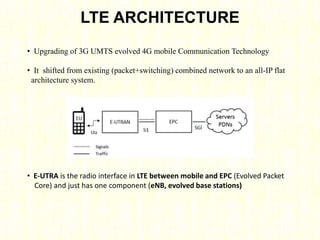
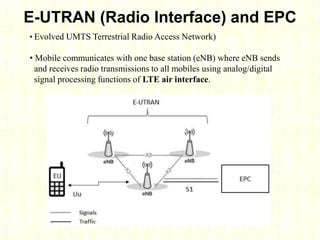
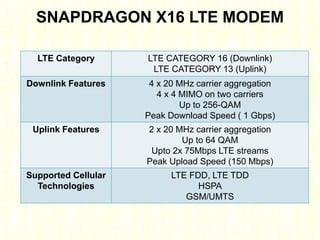
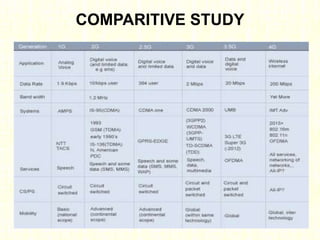
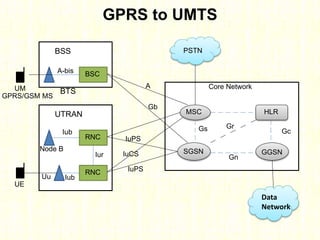
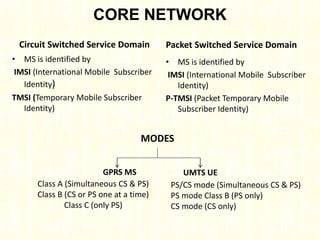
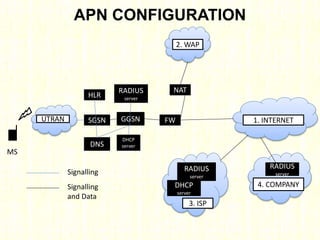
The document outlines the evolution of mobile technologies from 1G to 4G, highlighting key advancements such as increased voice capacity in 2G, enhanced throughput in 3G with CDMA2000 and HSPA, and the integration of existing technologies in 4G LTE. It details the architecture of these technologies, particularly the transition to an all-IP system with LTE, and compares different mobile communication protocols and structures. Additionally, it provides technical specifications related to the Snapdragon 835 mobile platform and various cellular technology features.