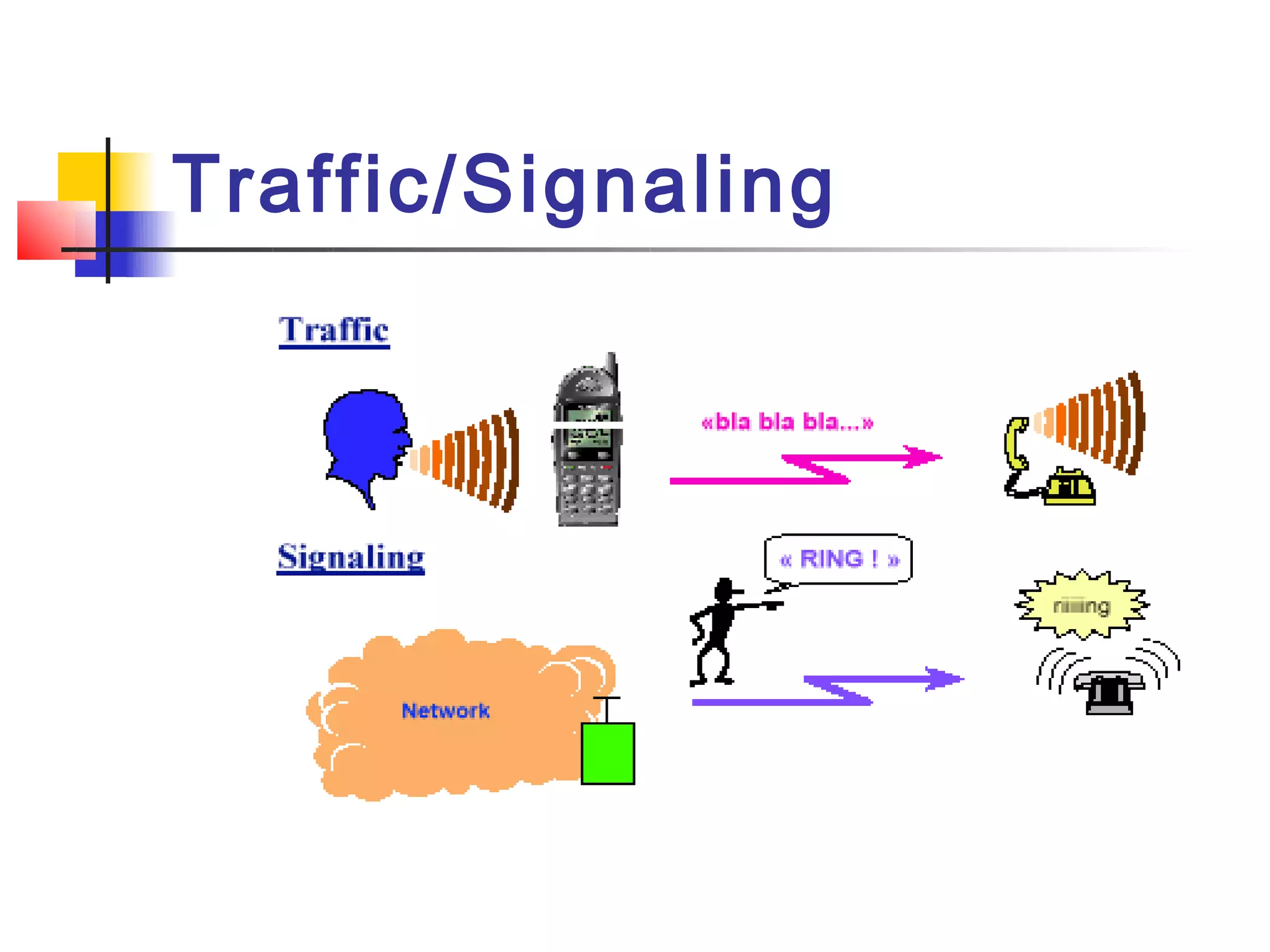
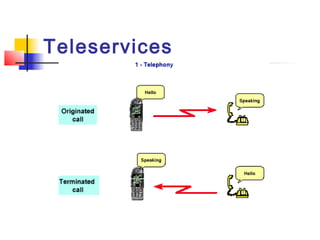
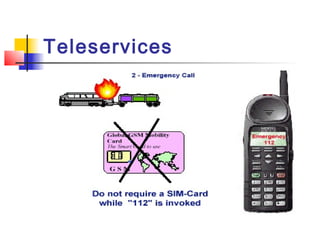
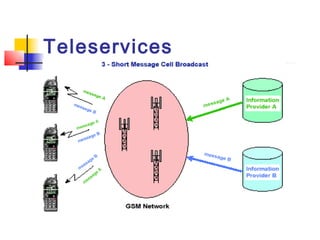
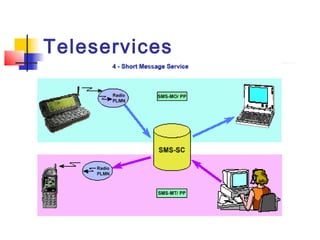
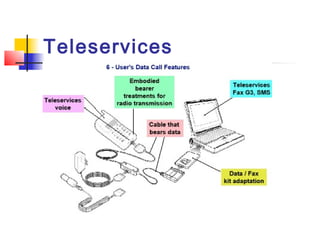
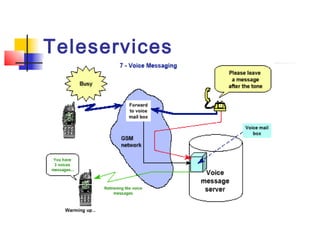
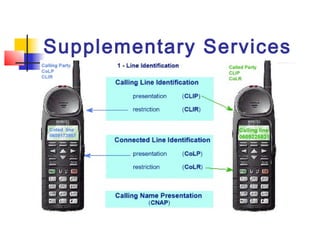
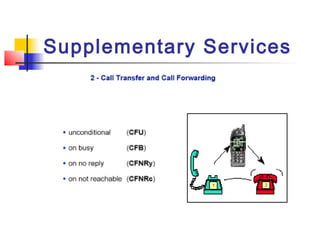
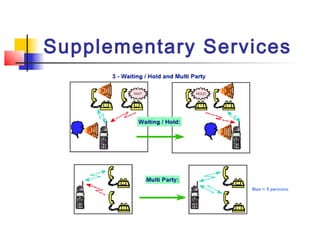
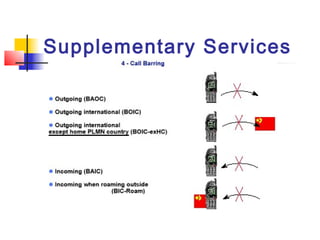
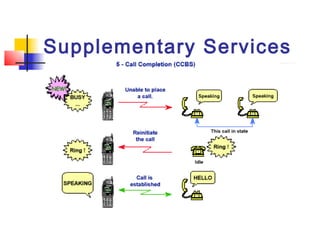
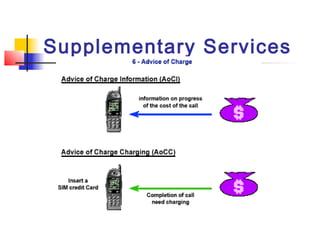
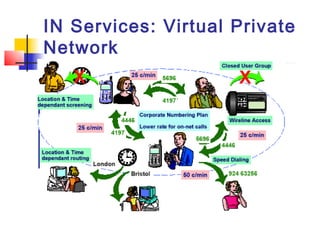
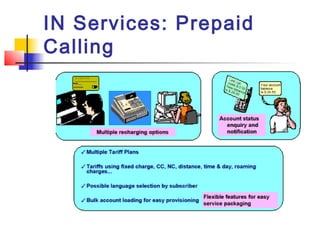
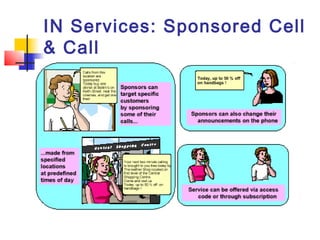
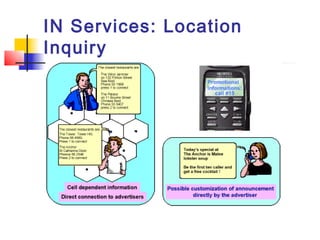
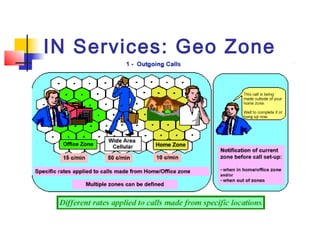
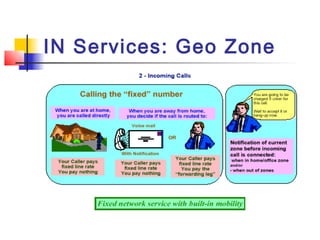
The document discusses teleservices and supplementary services provided by GSM networks. It describes the main teleservices which include regular telephony, emergency calls, voice messaging, and short message handling. It also explains several supplementary services such as calling line identification, call forwarding, call waiting, call barring, and advice of charge features. The document further discusses intelligent network services including virtual private networks, prepaid calling, and sponsored cell and call services.