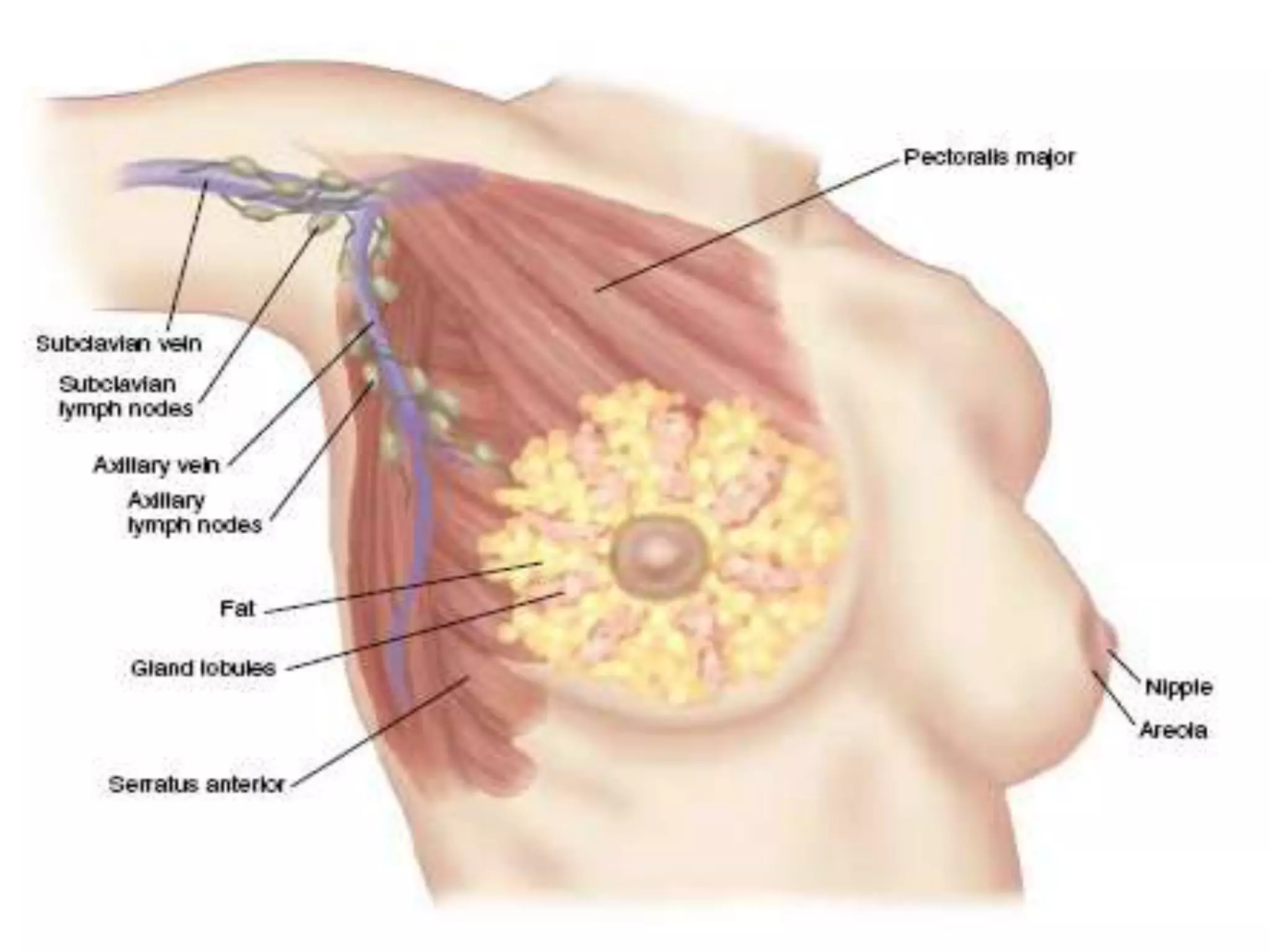
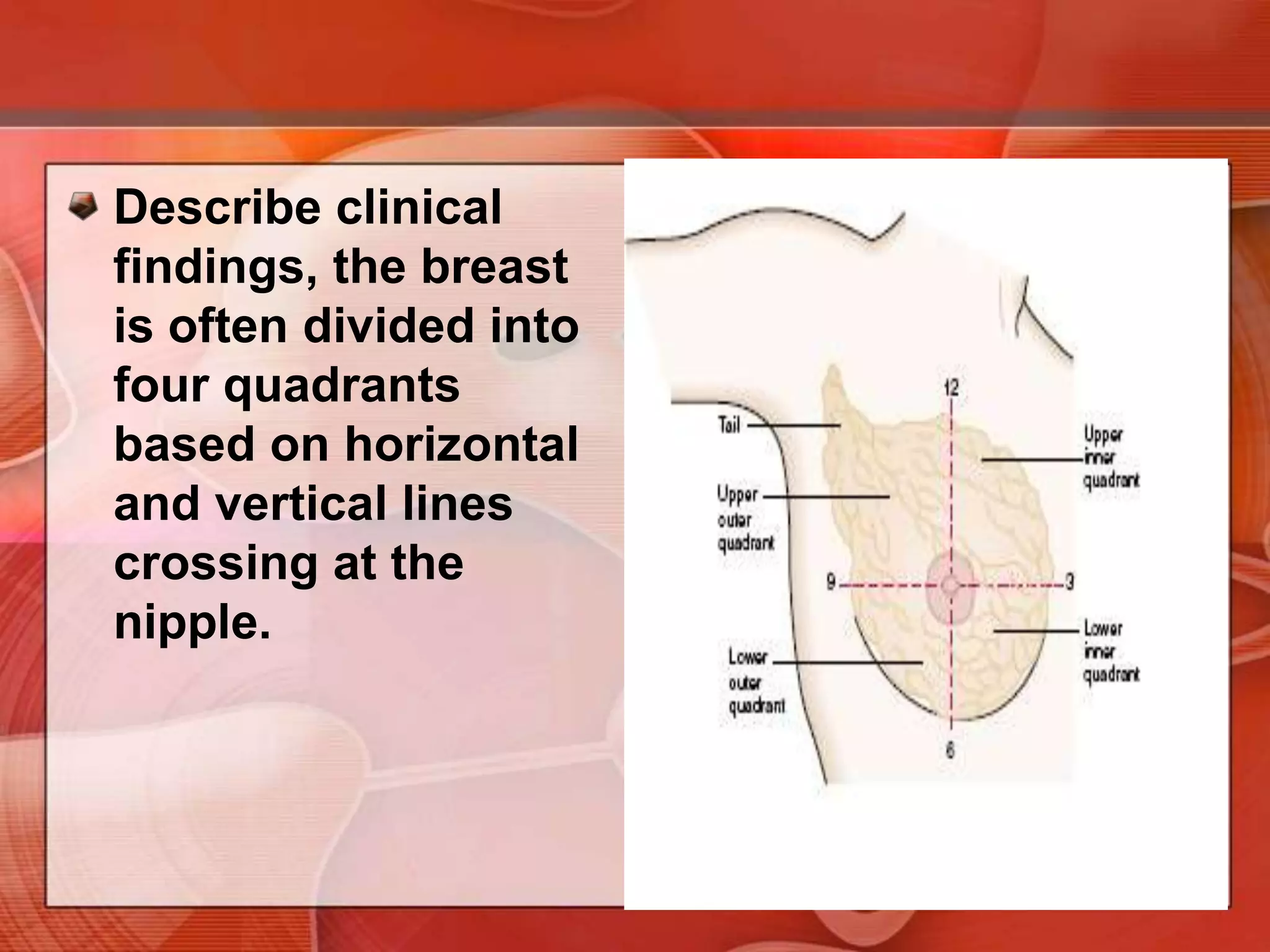
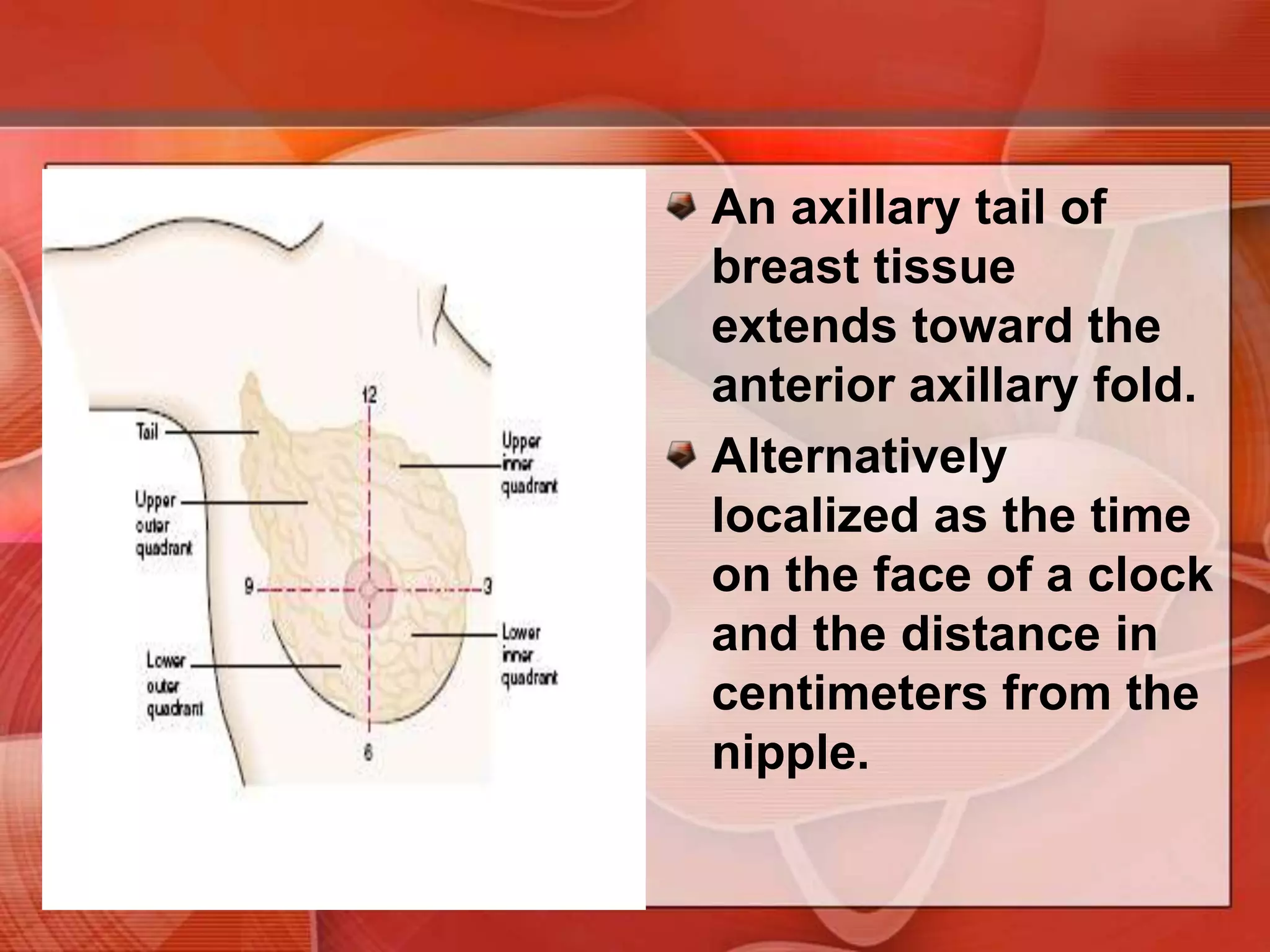
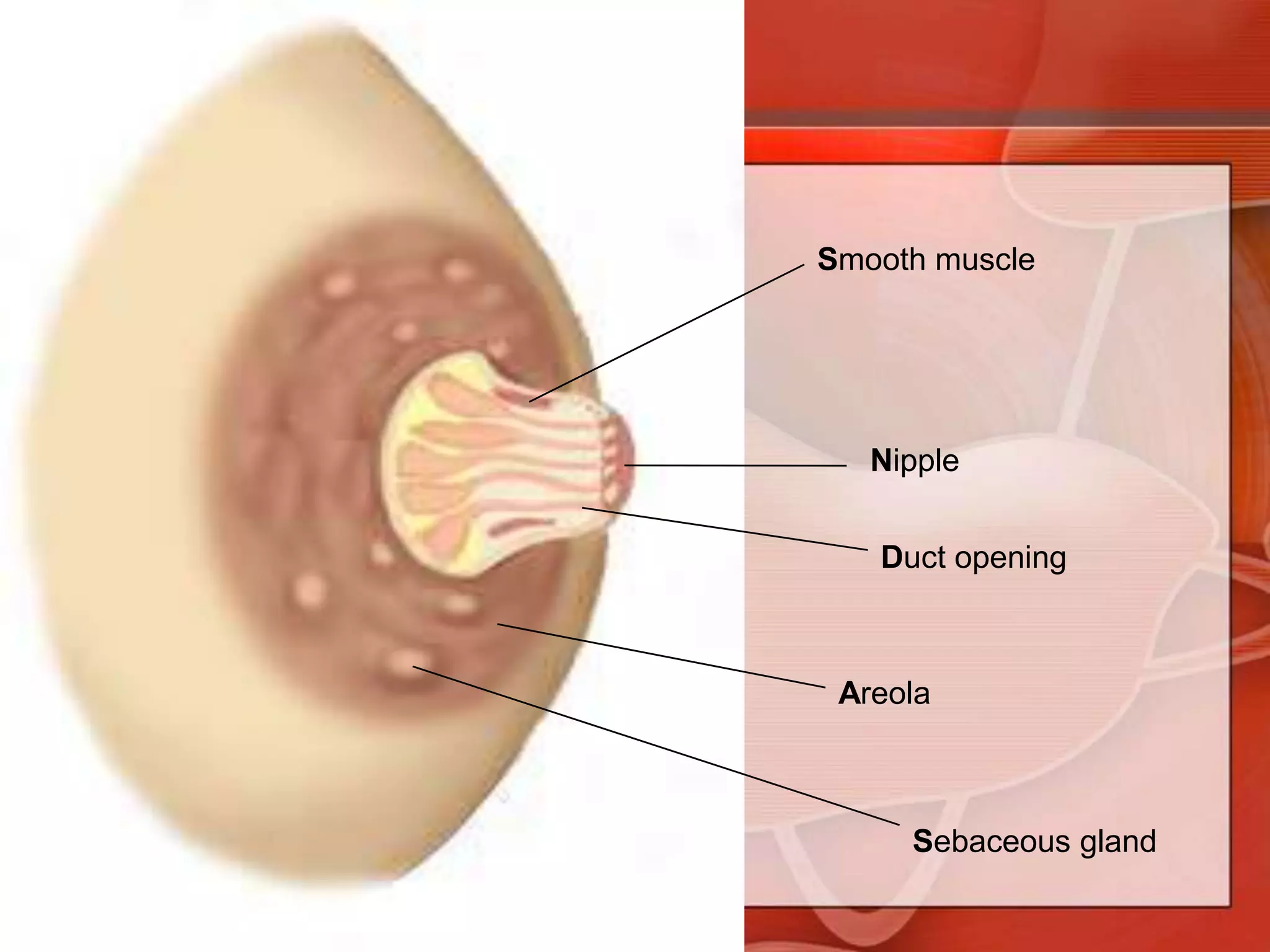
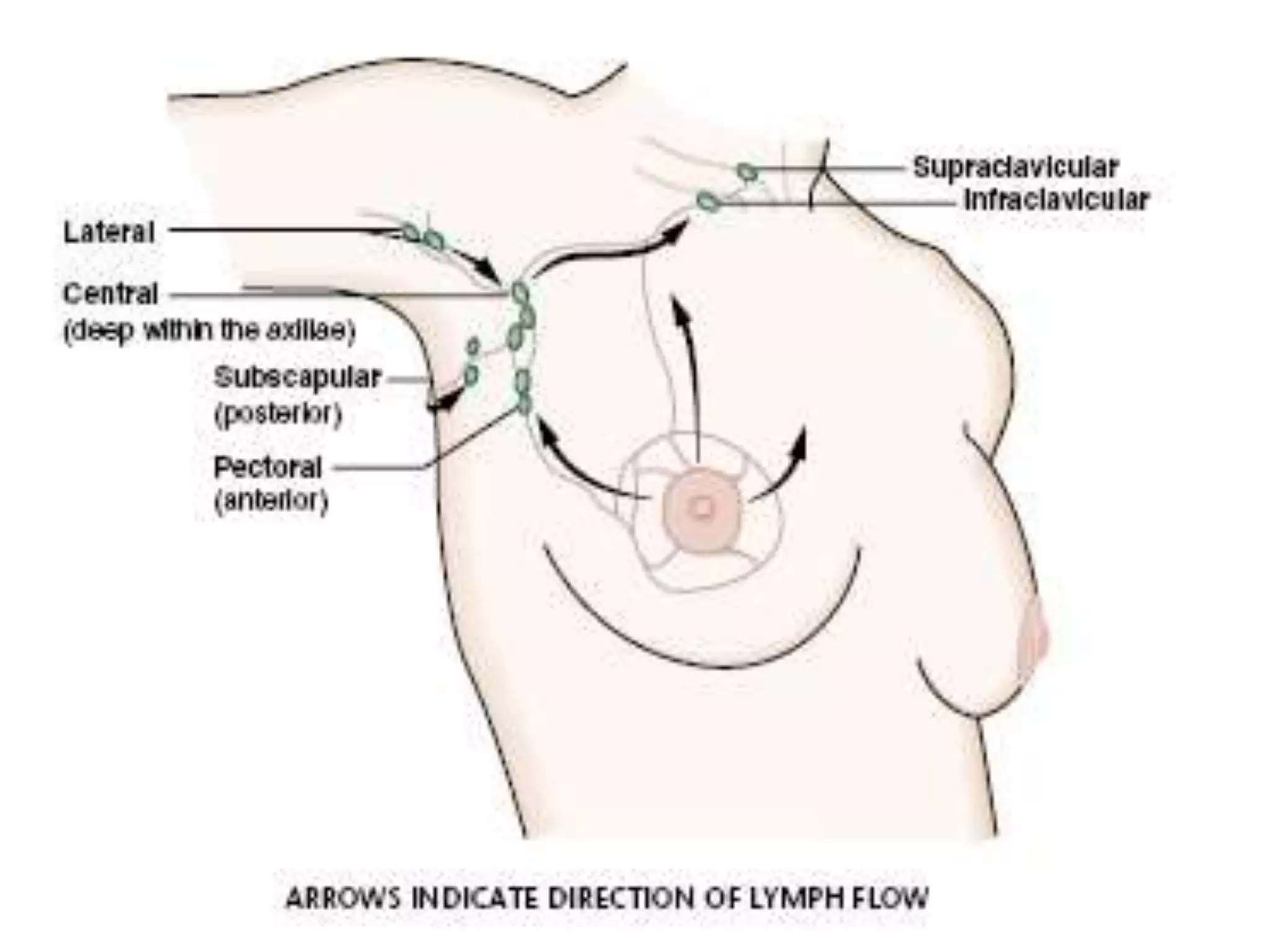
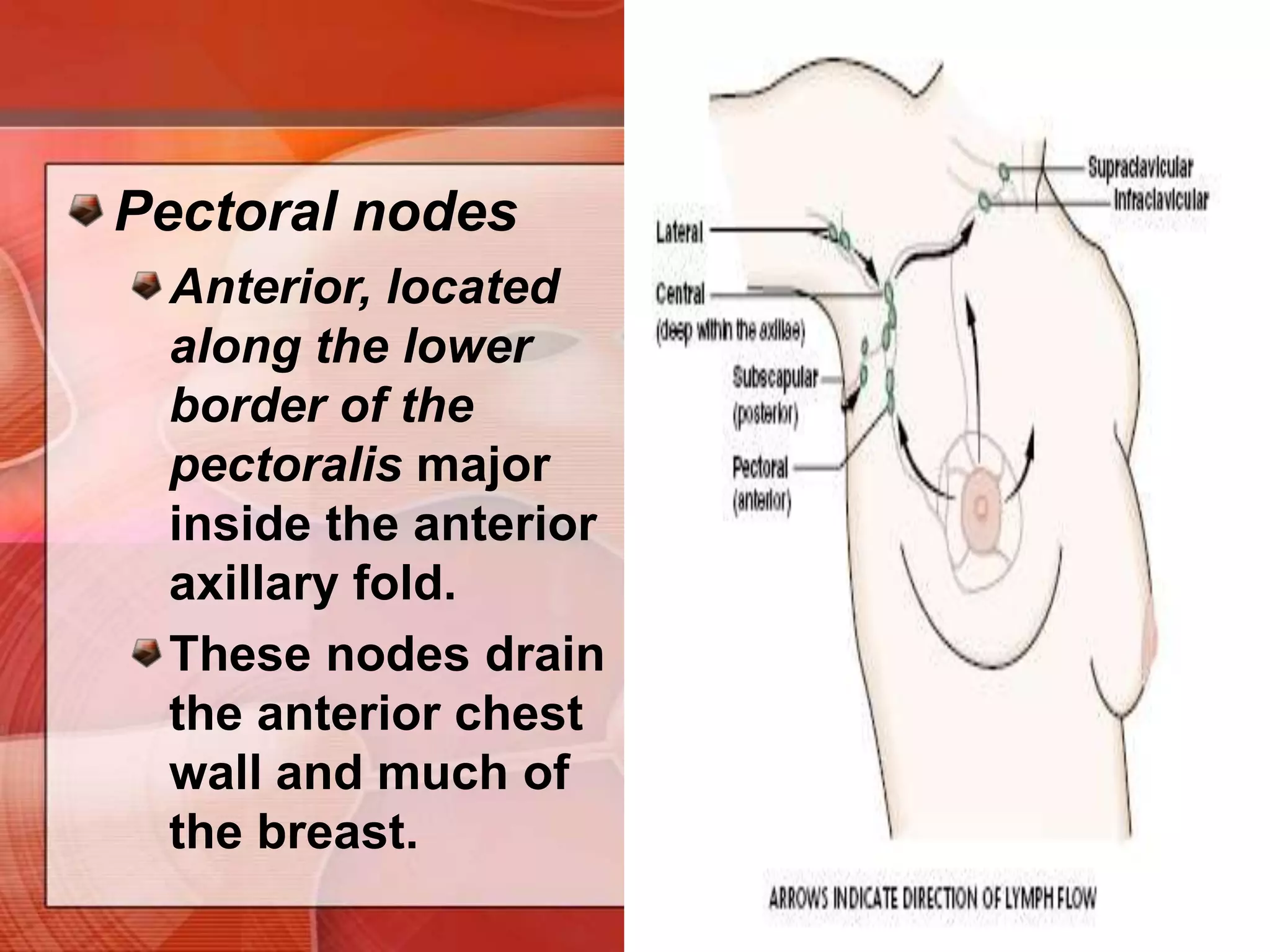
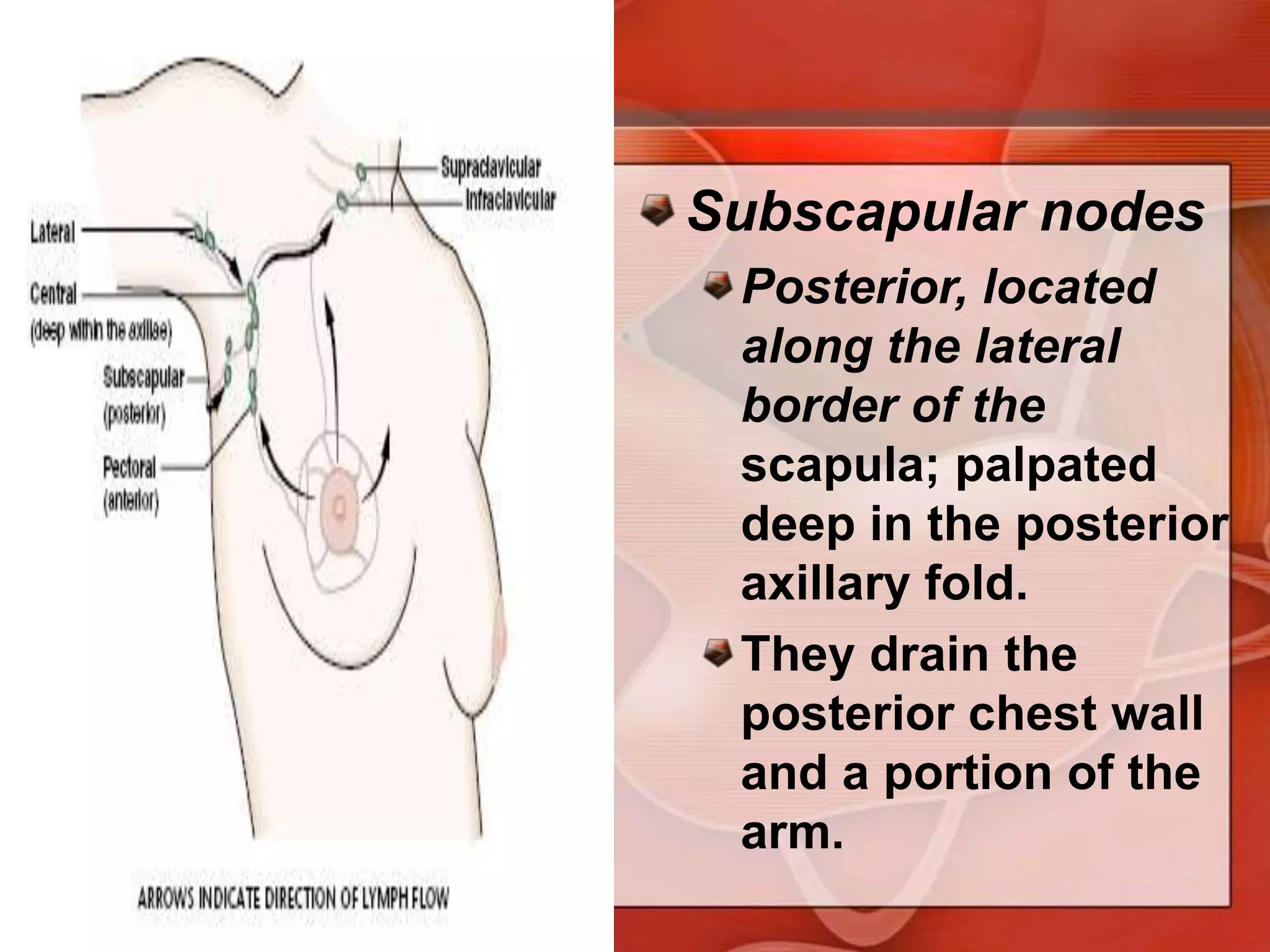
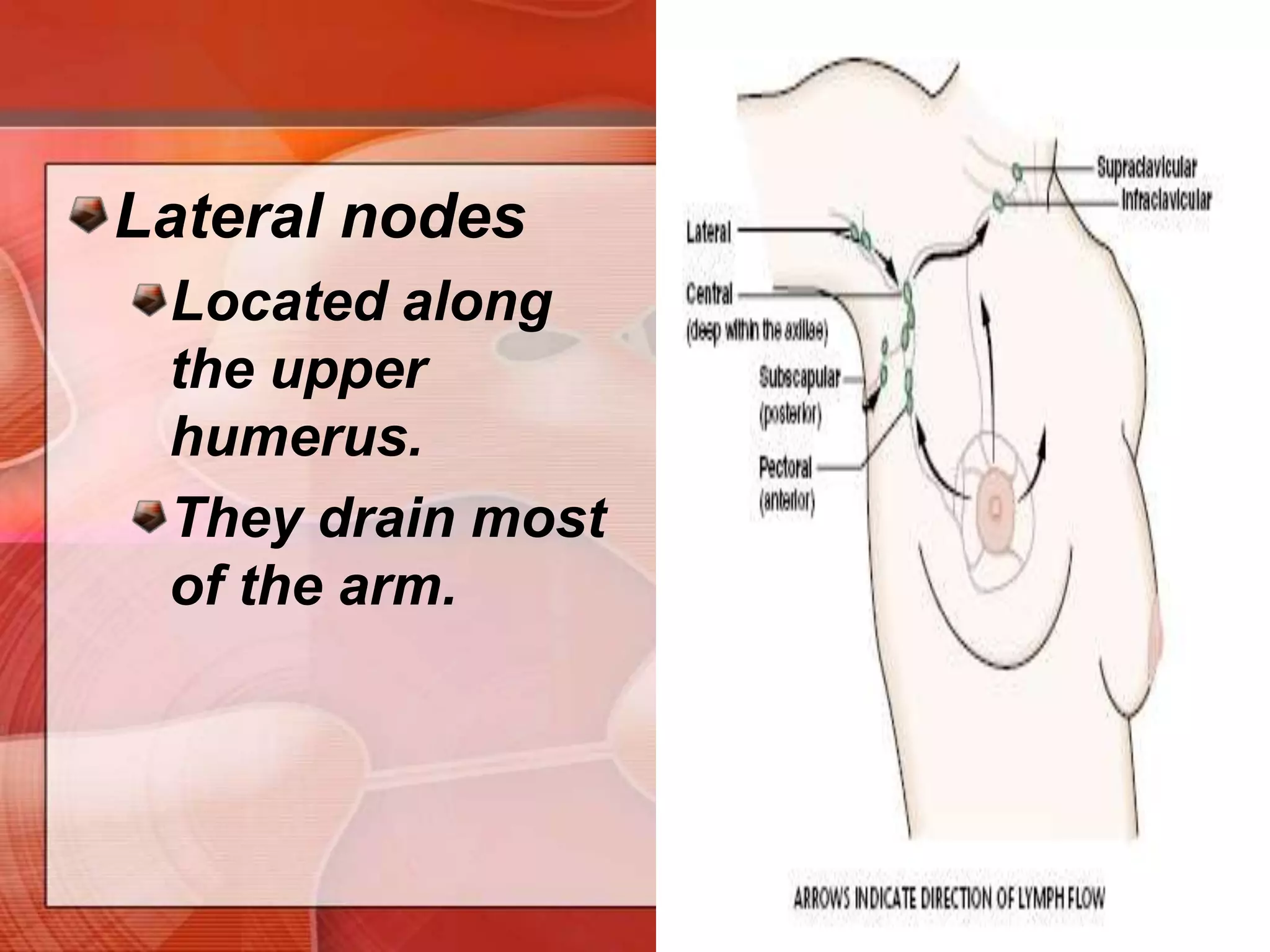
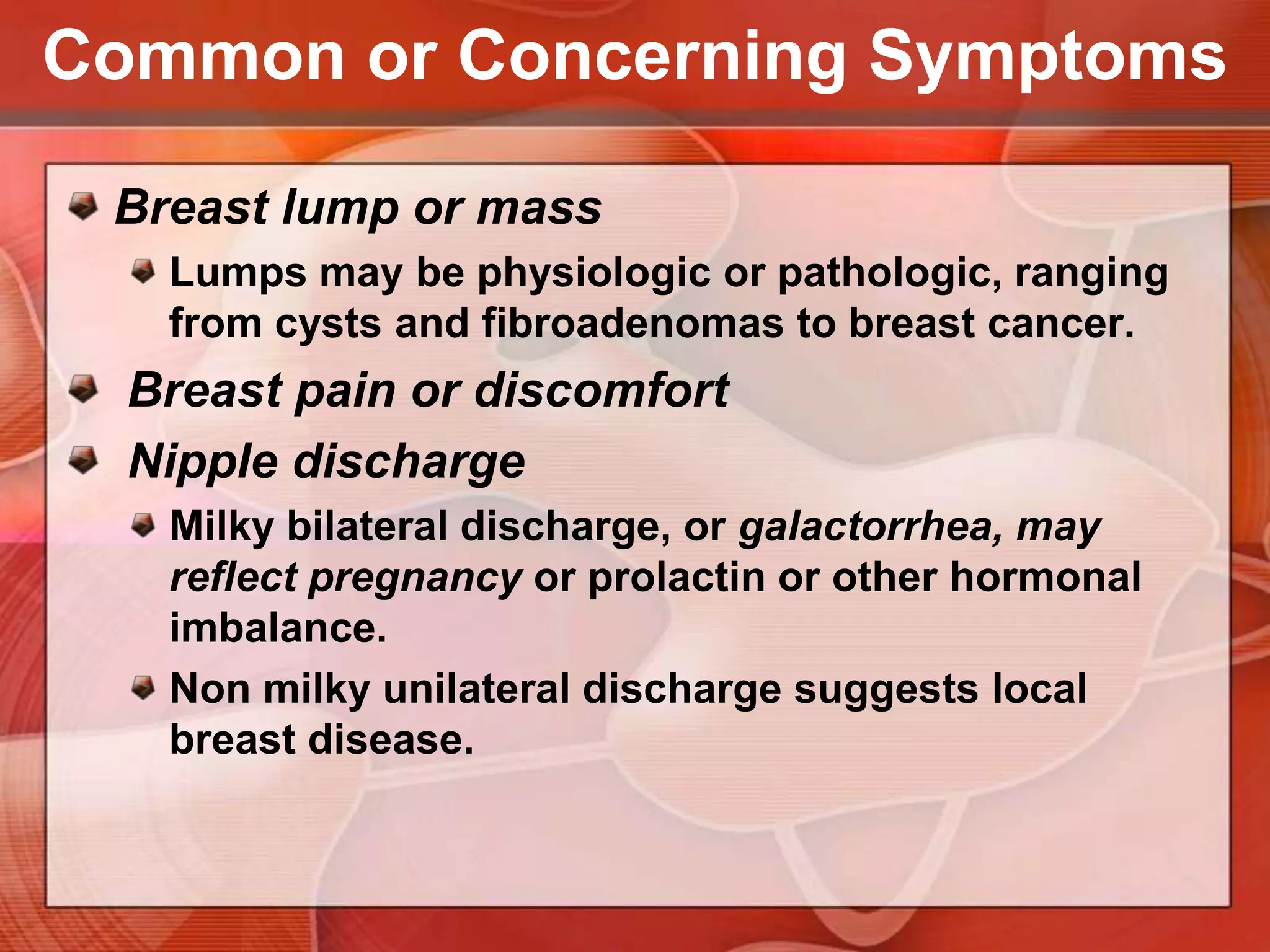
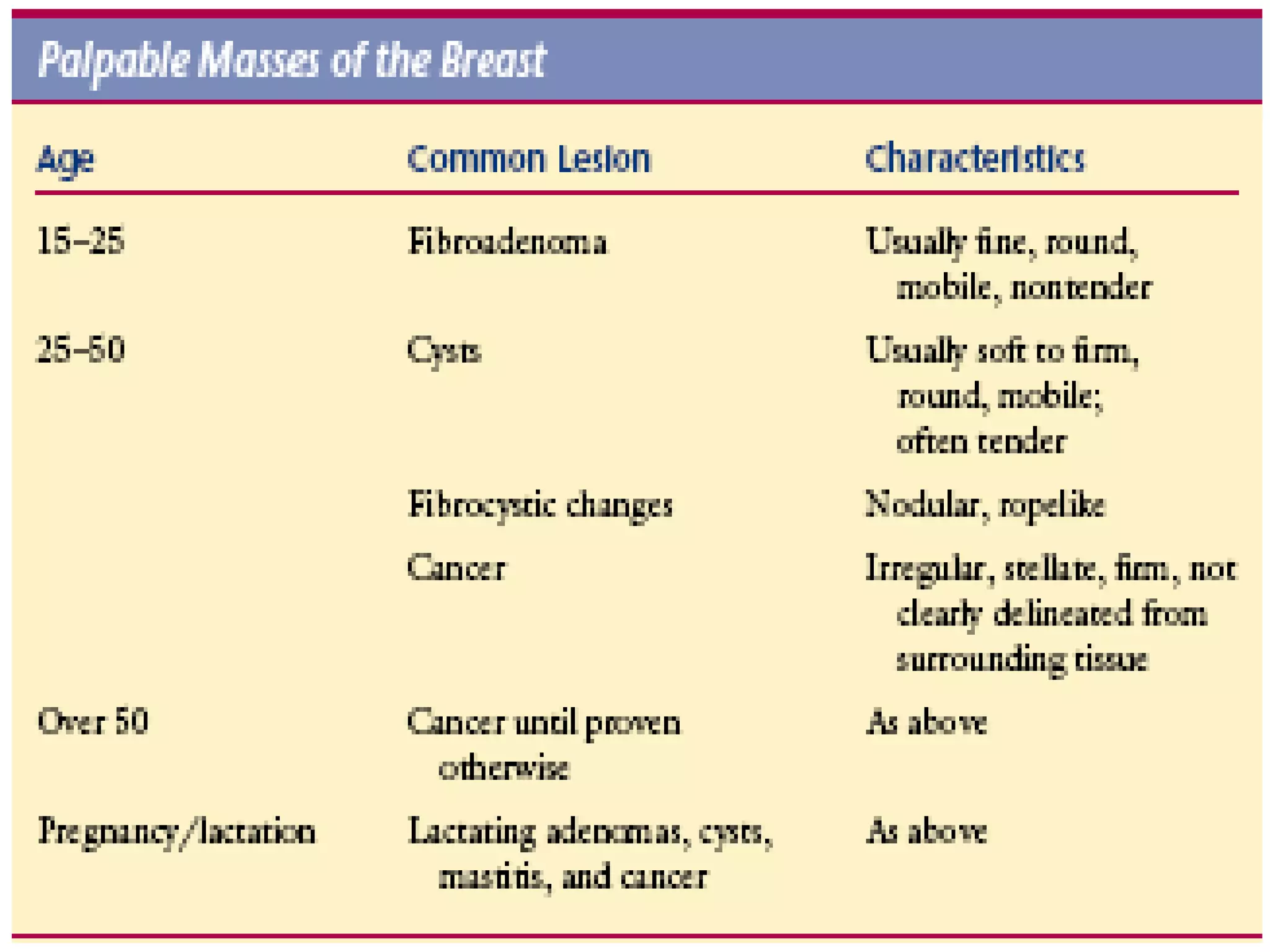
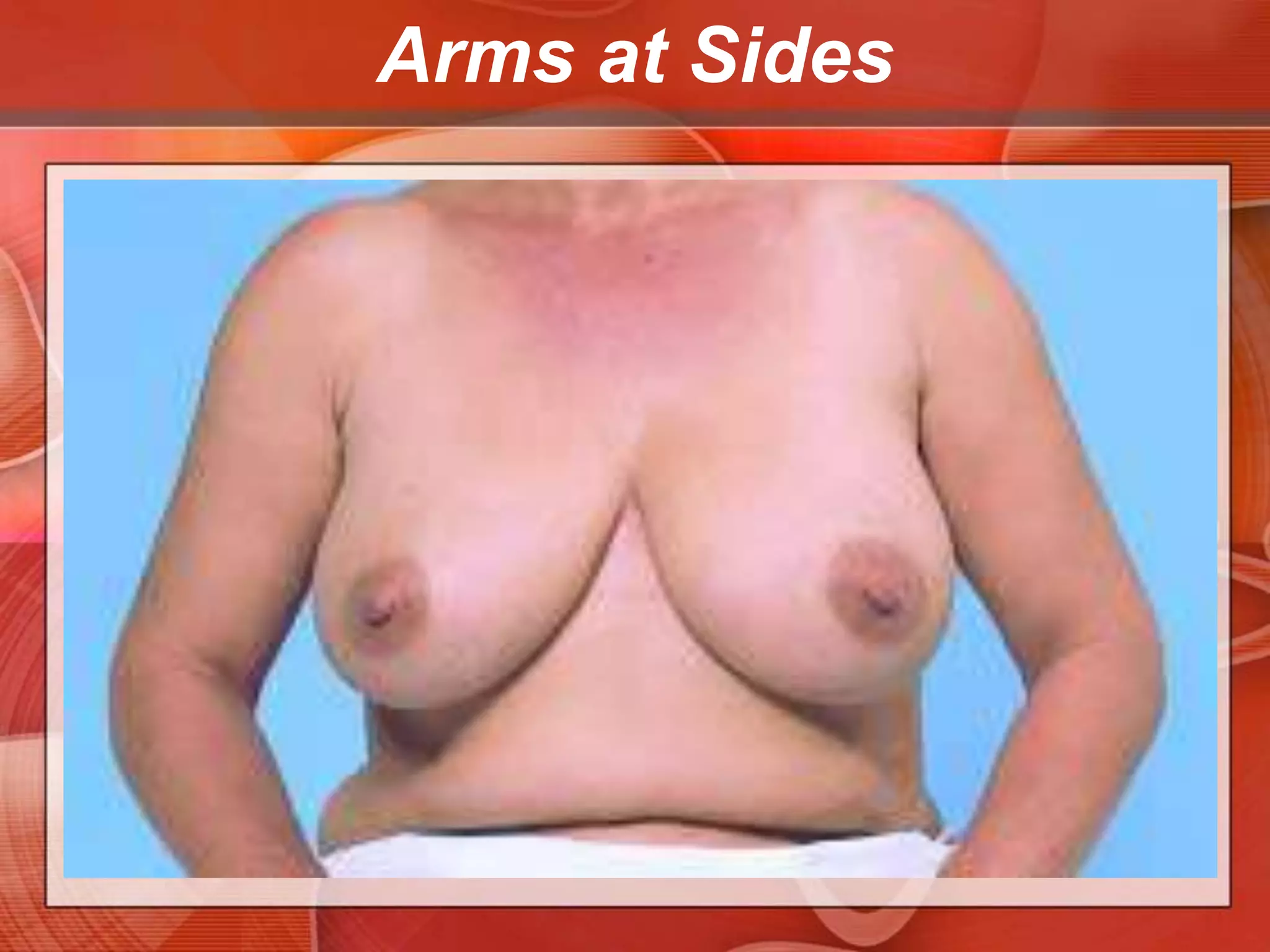
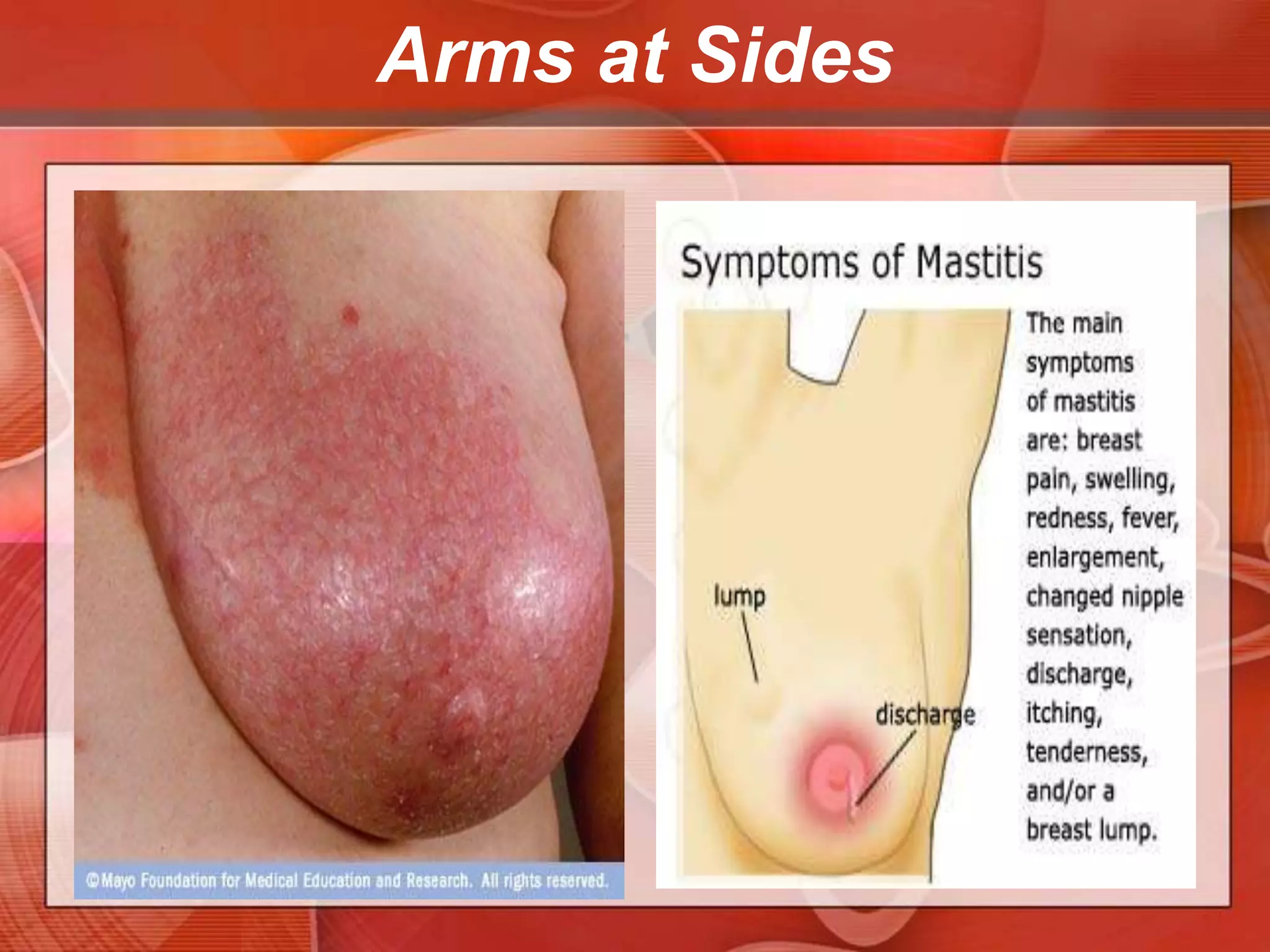
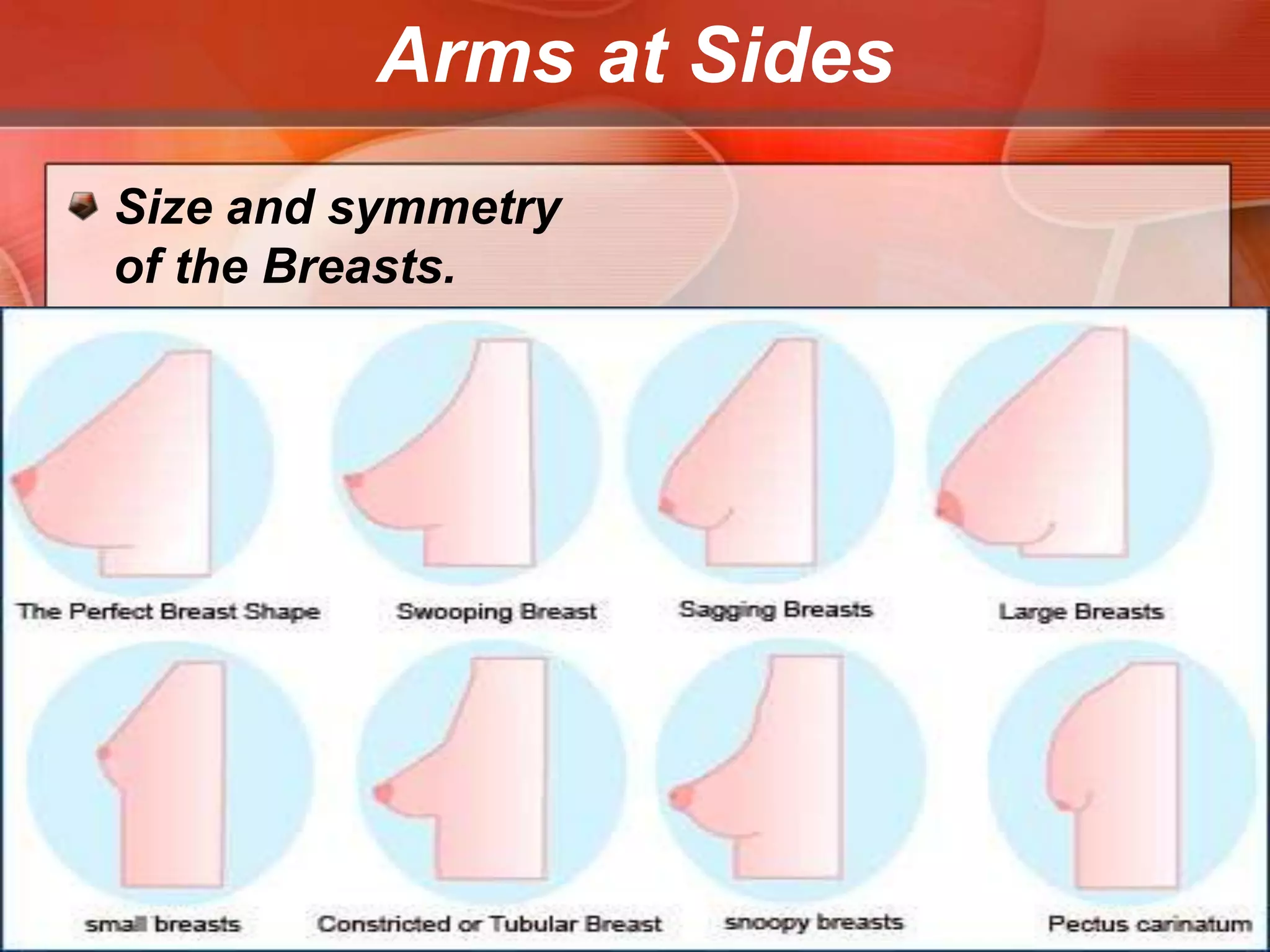
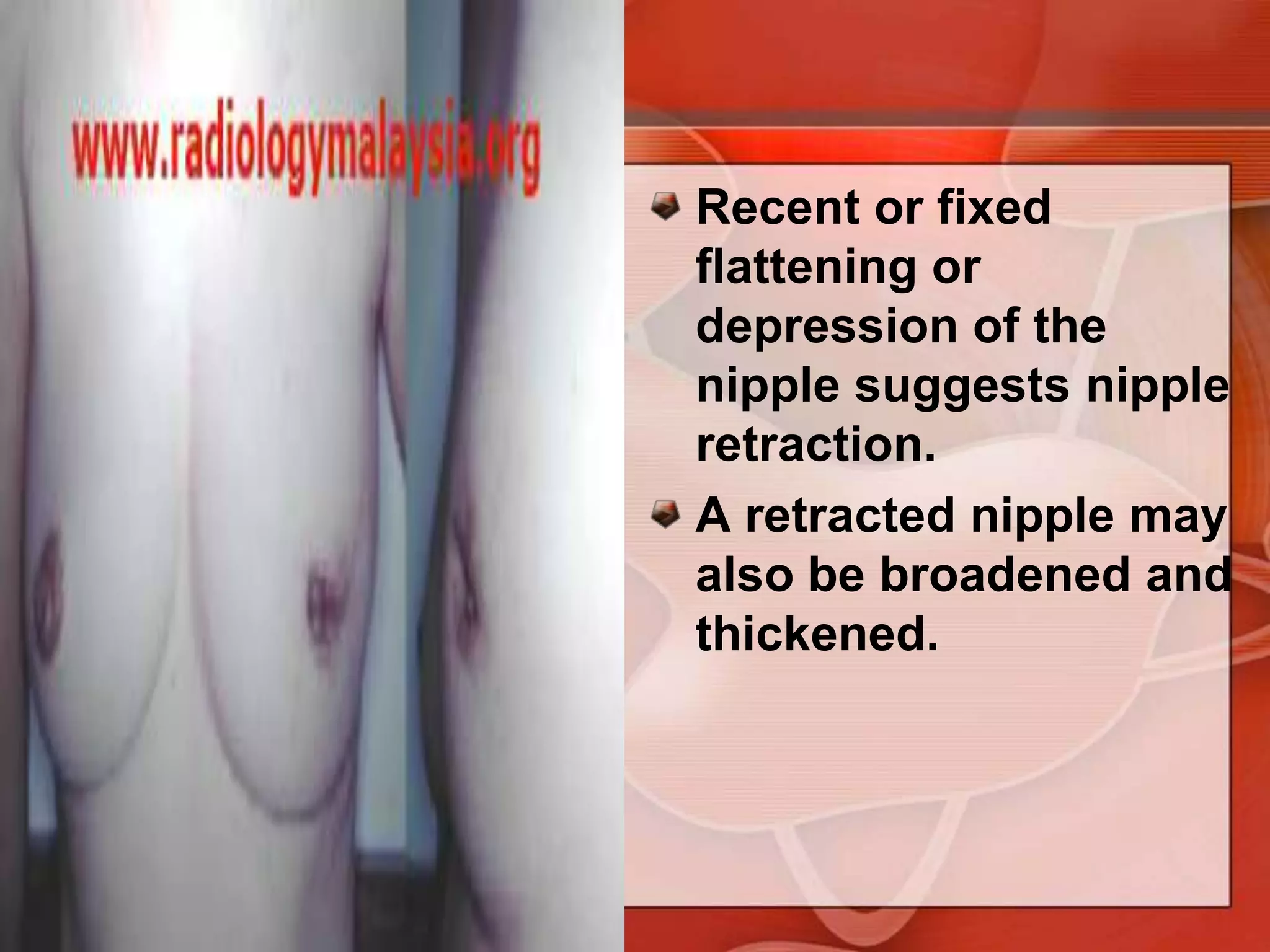
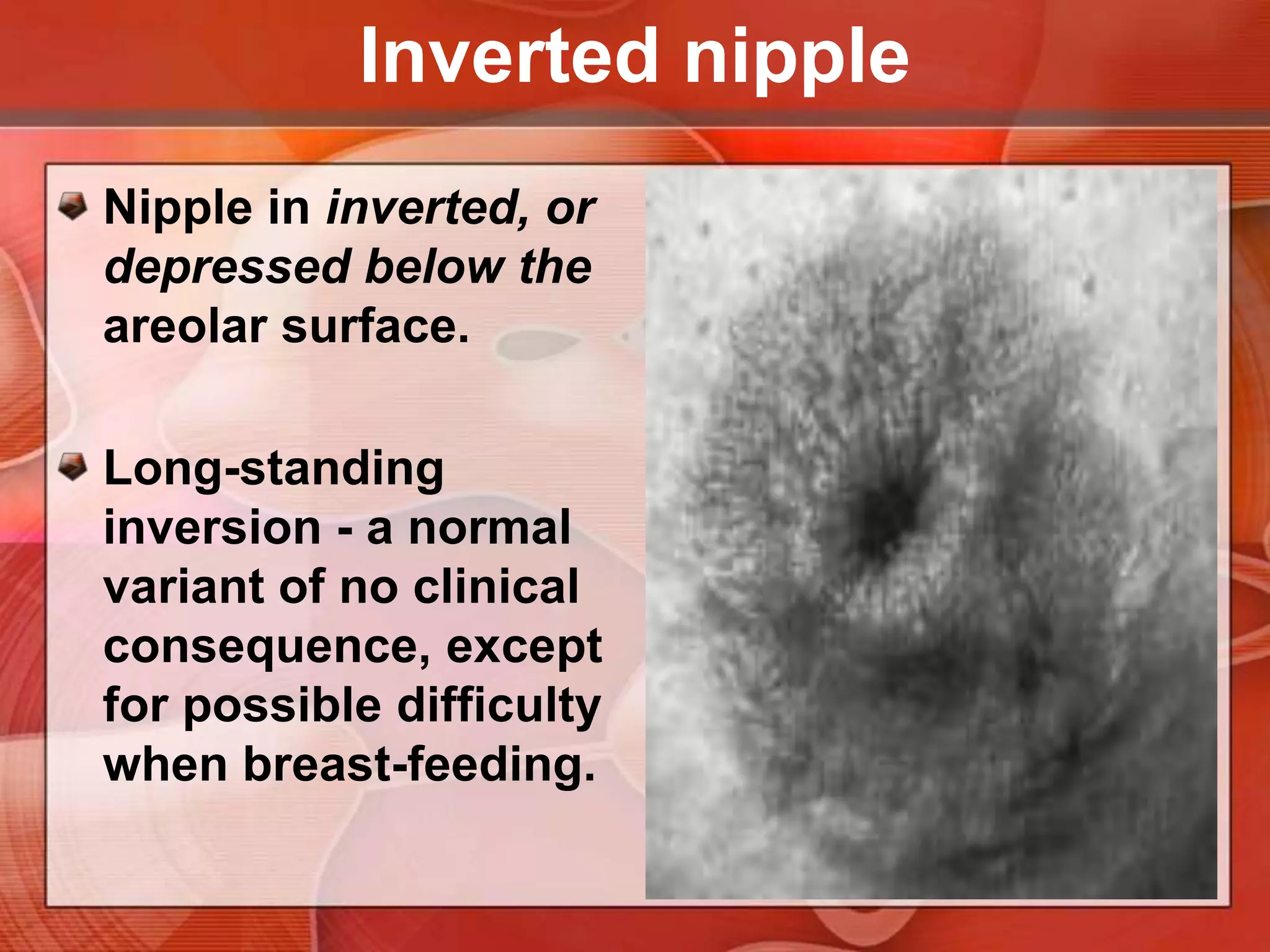
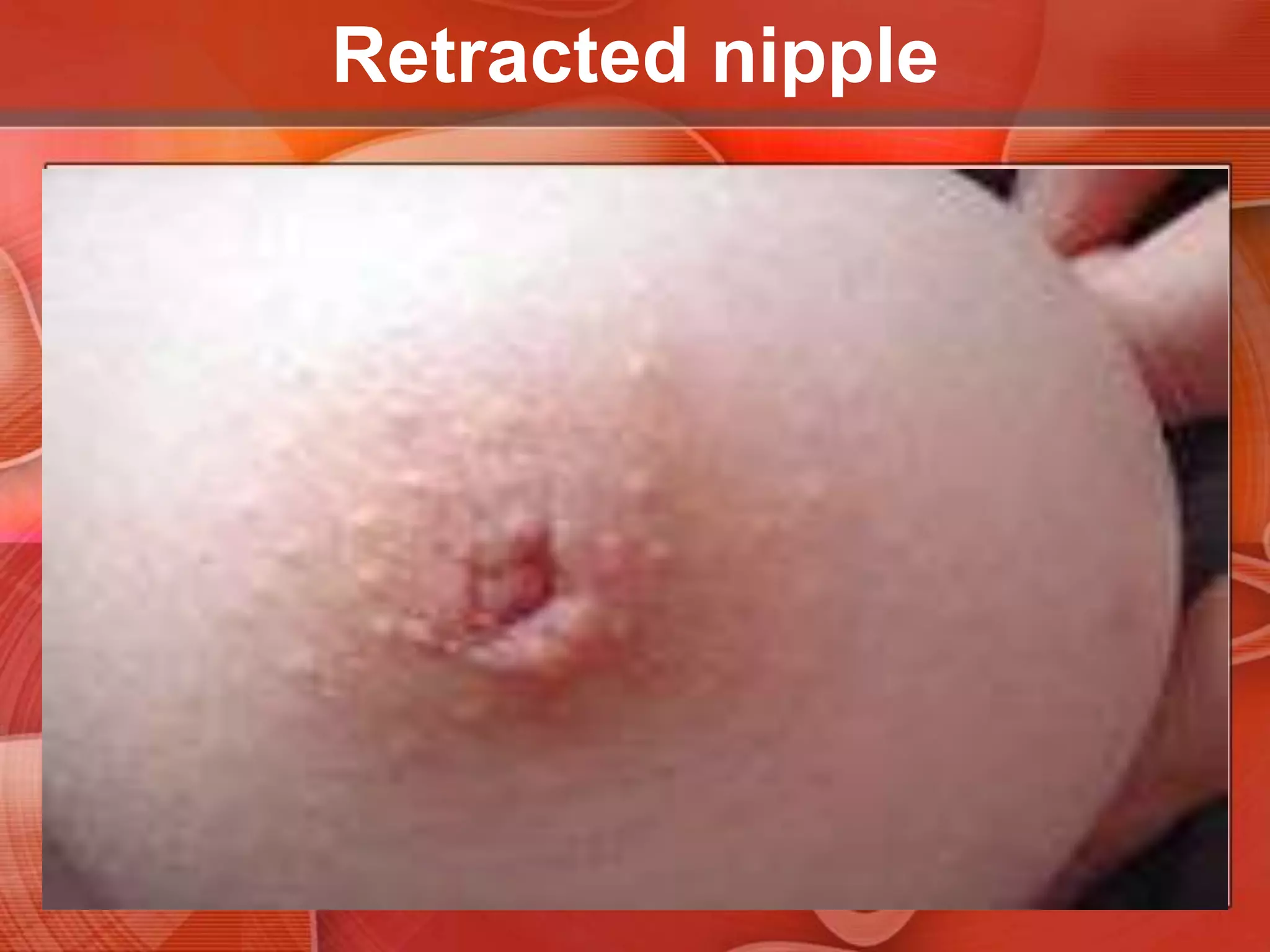
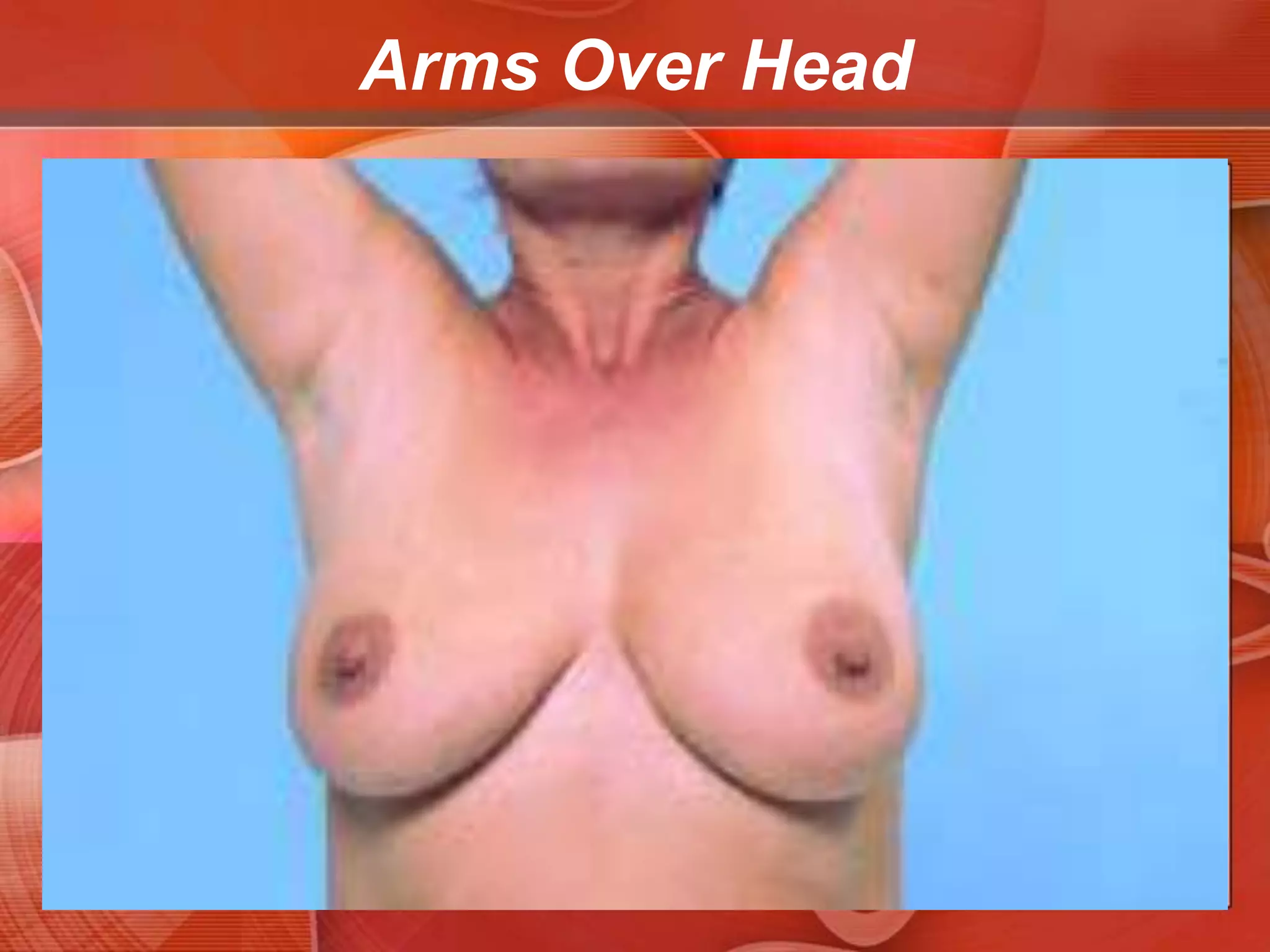
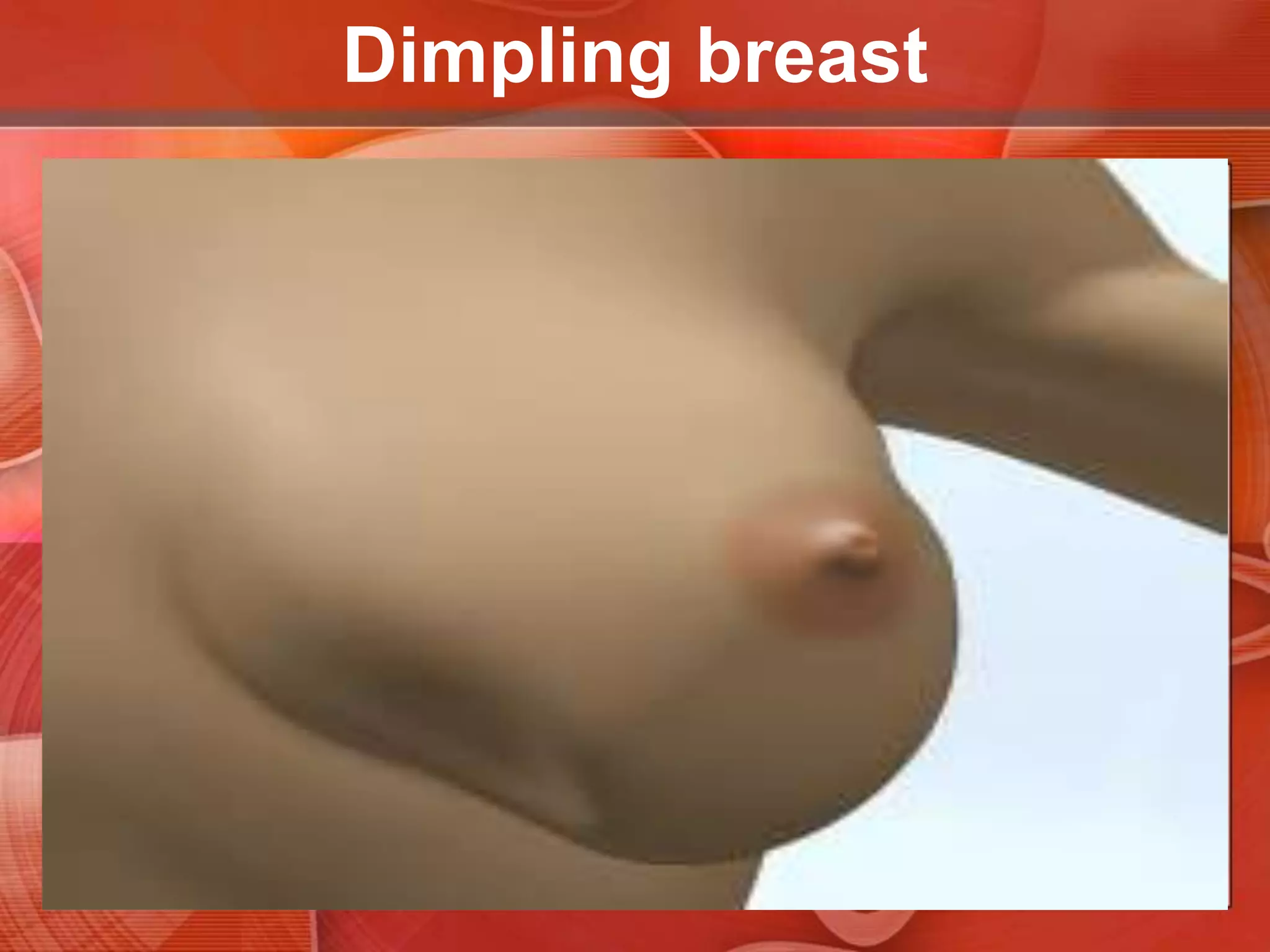
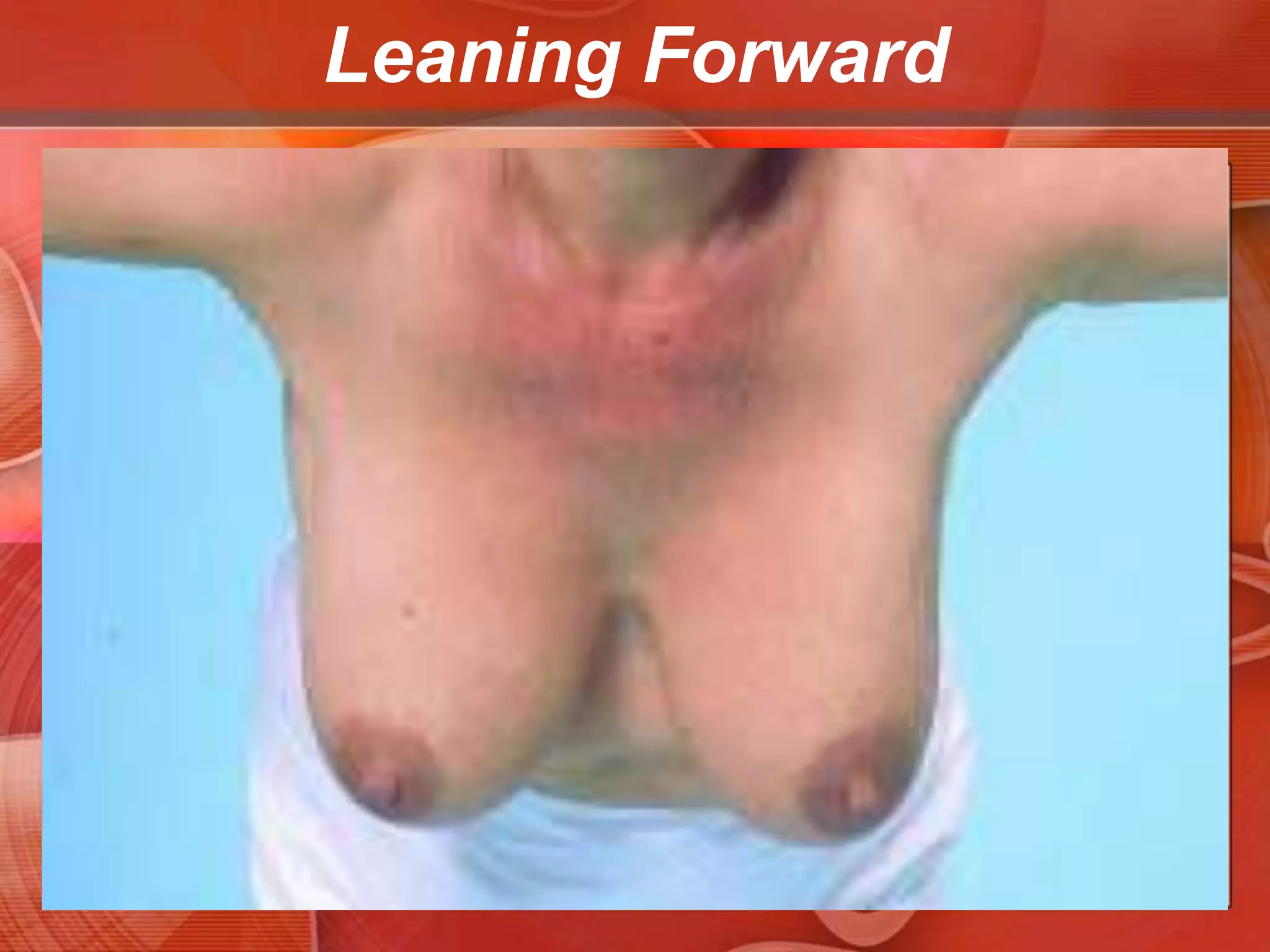
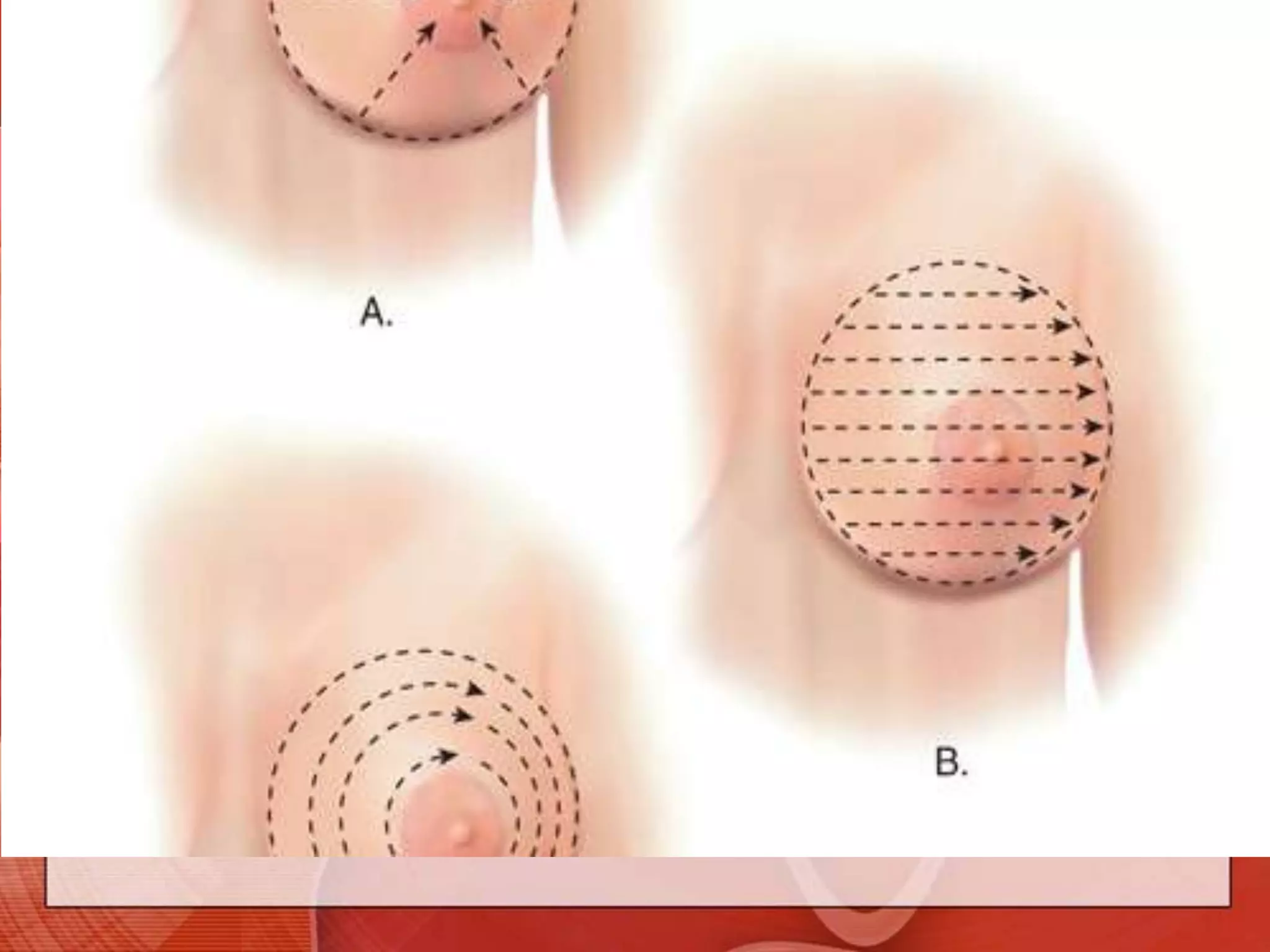
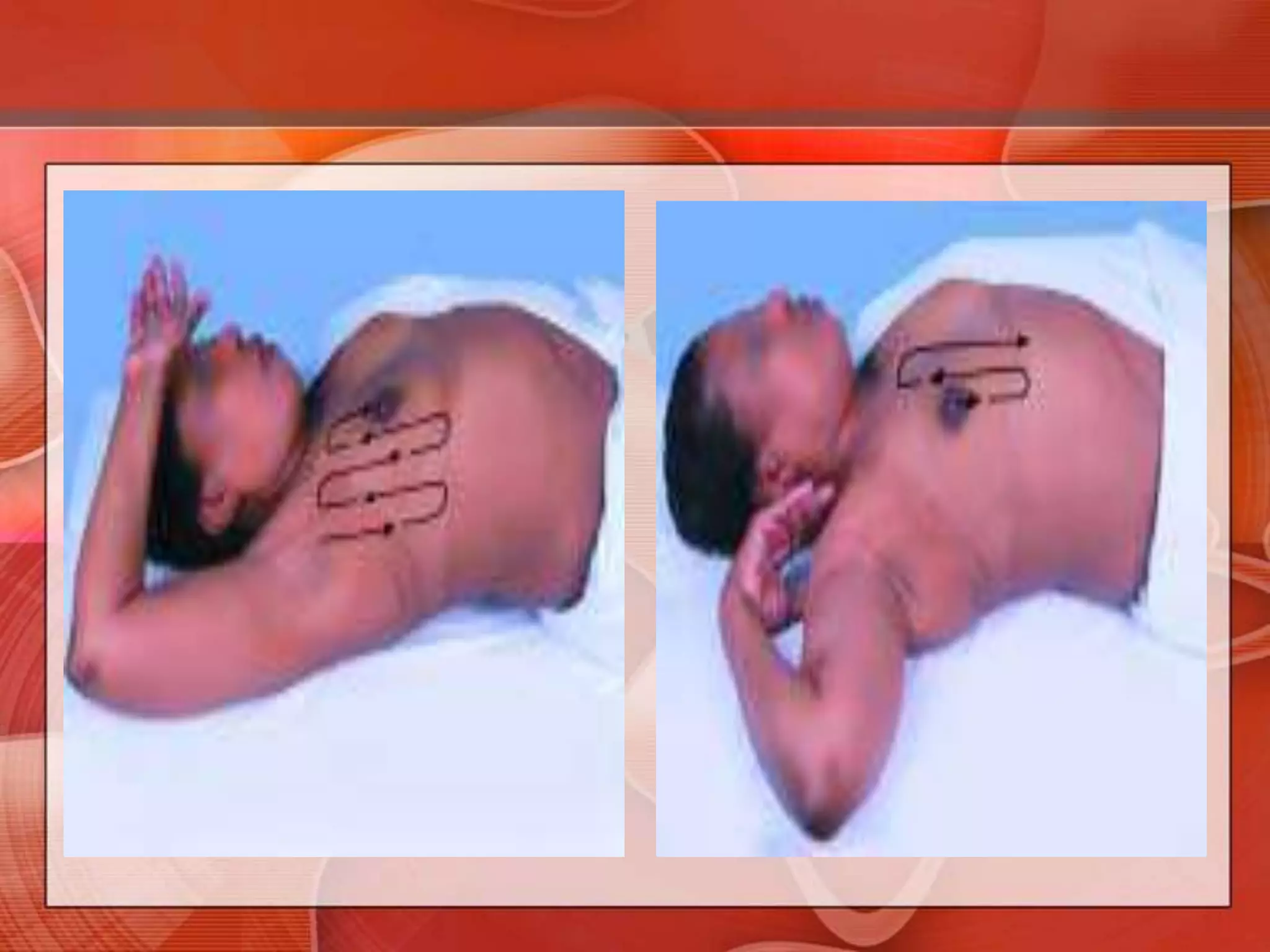
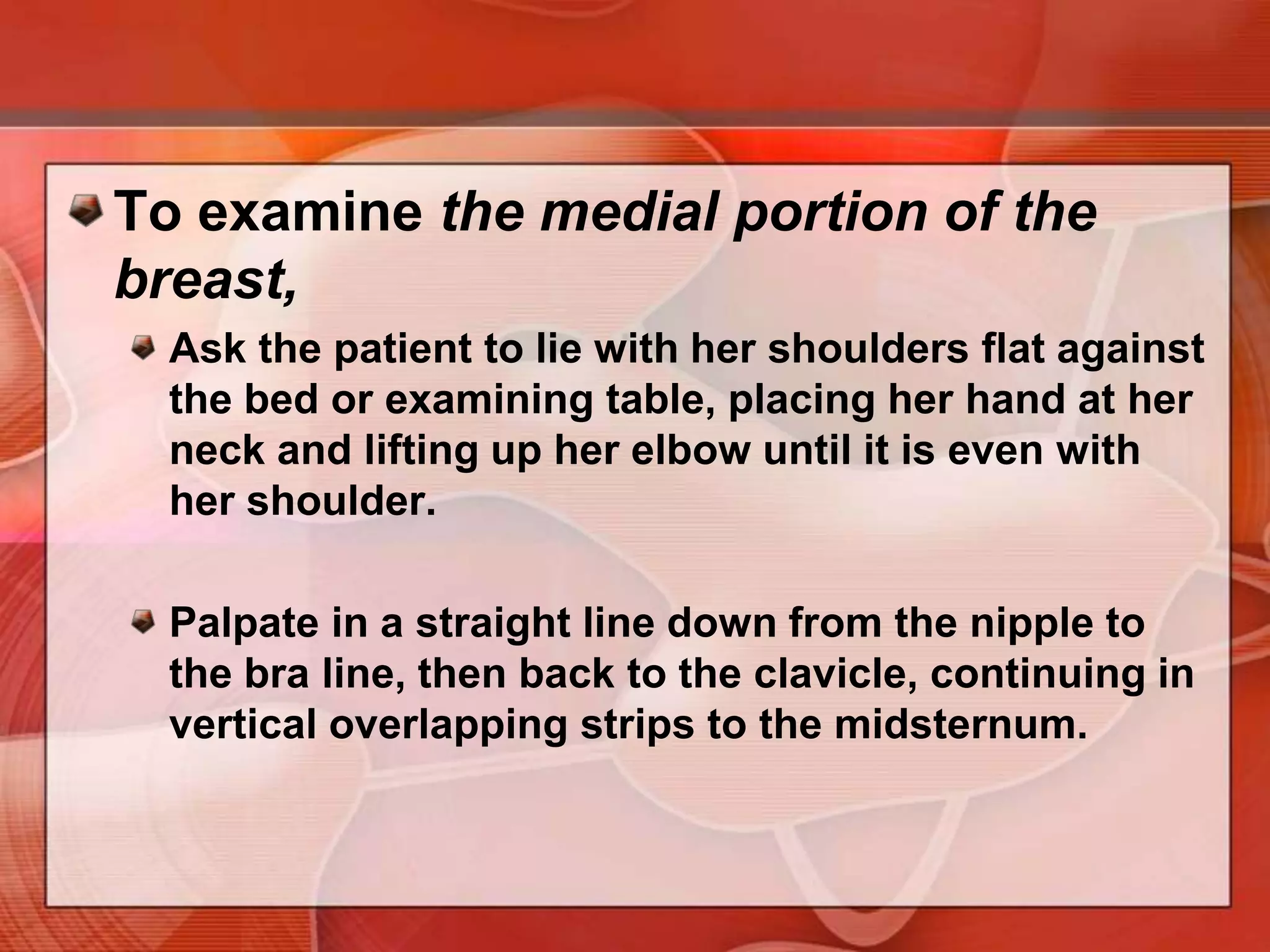
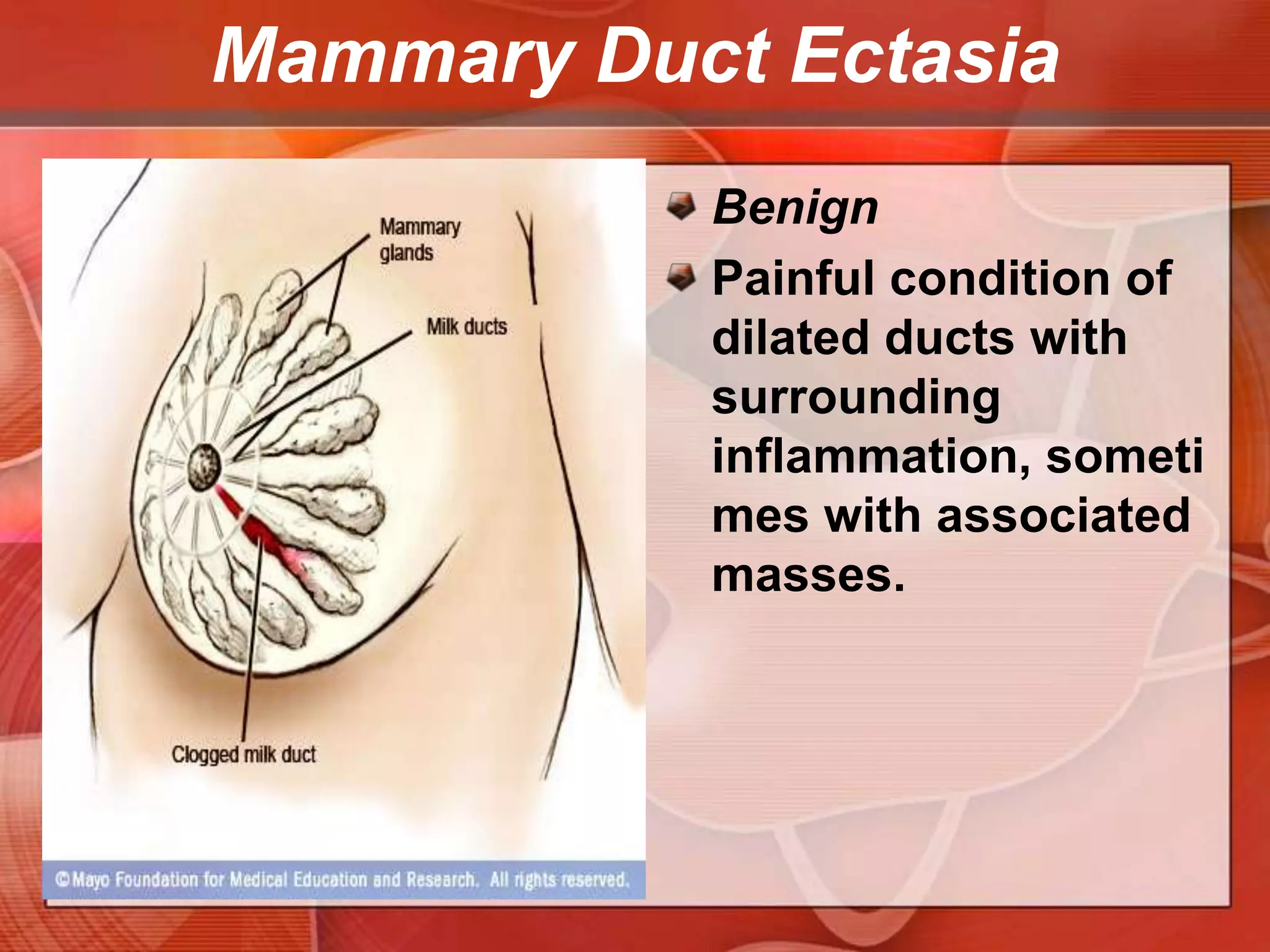
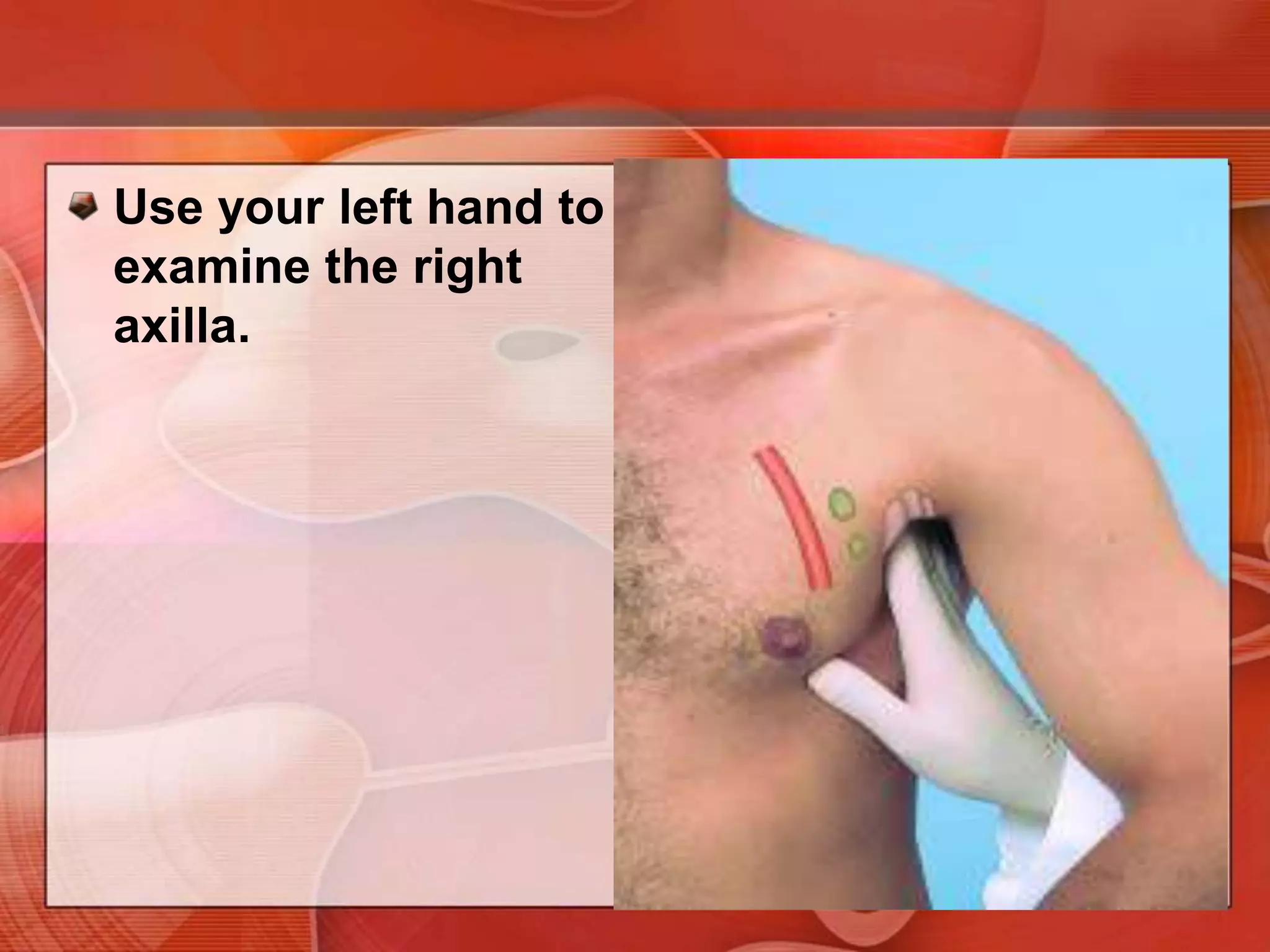
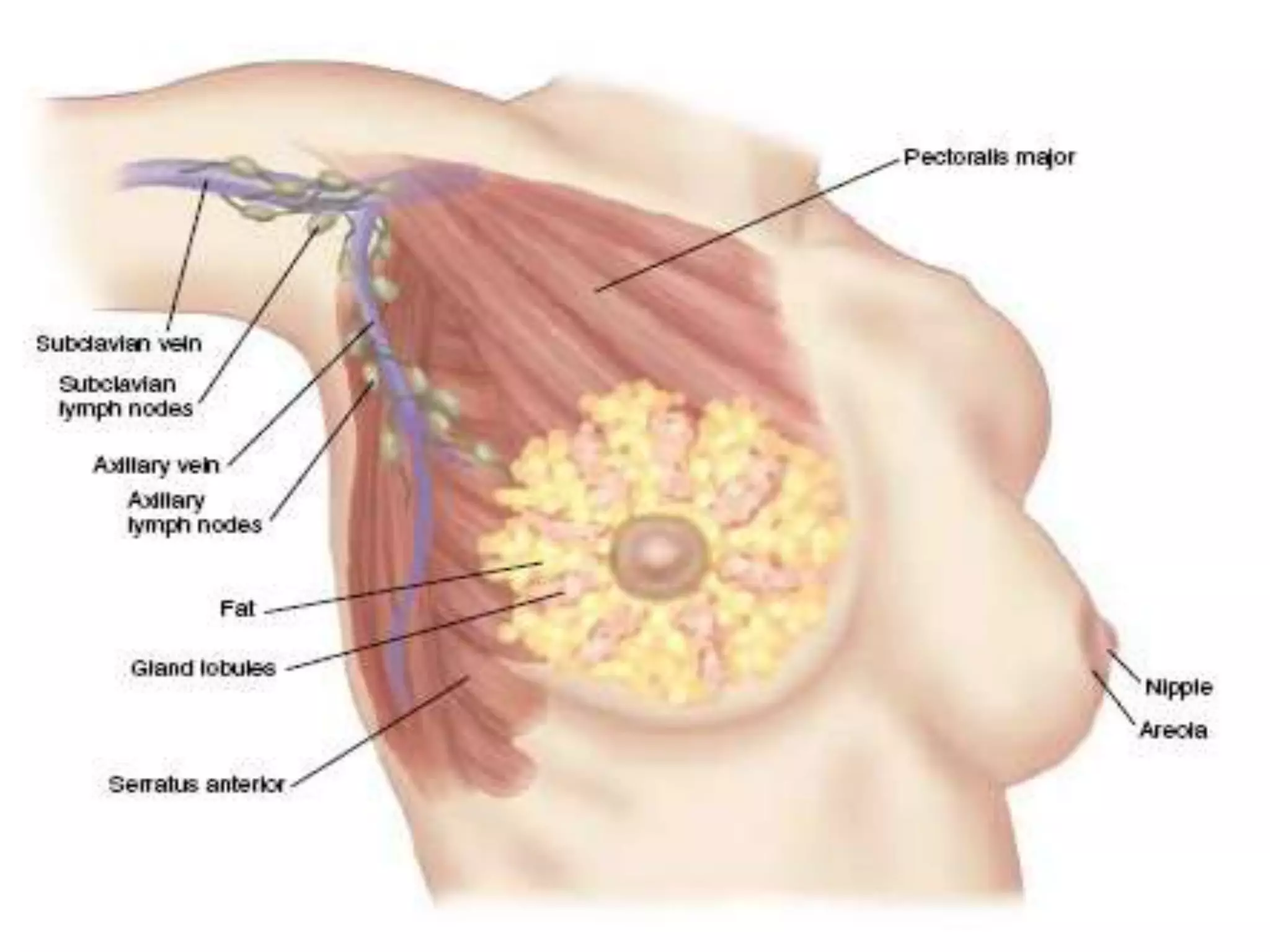
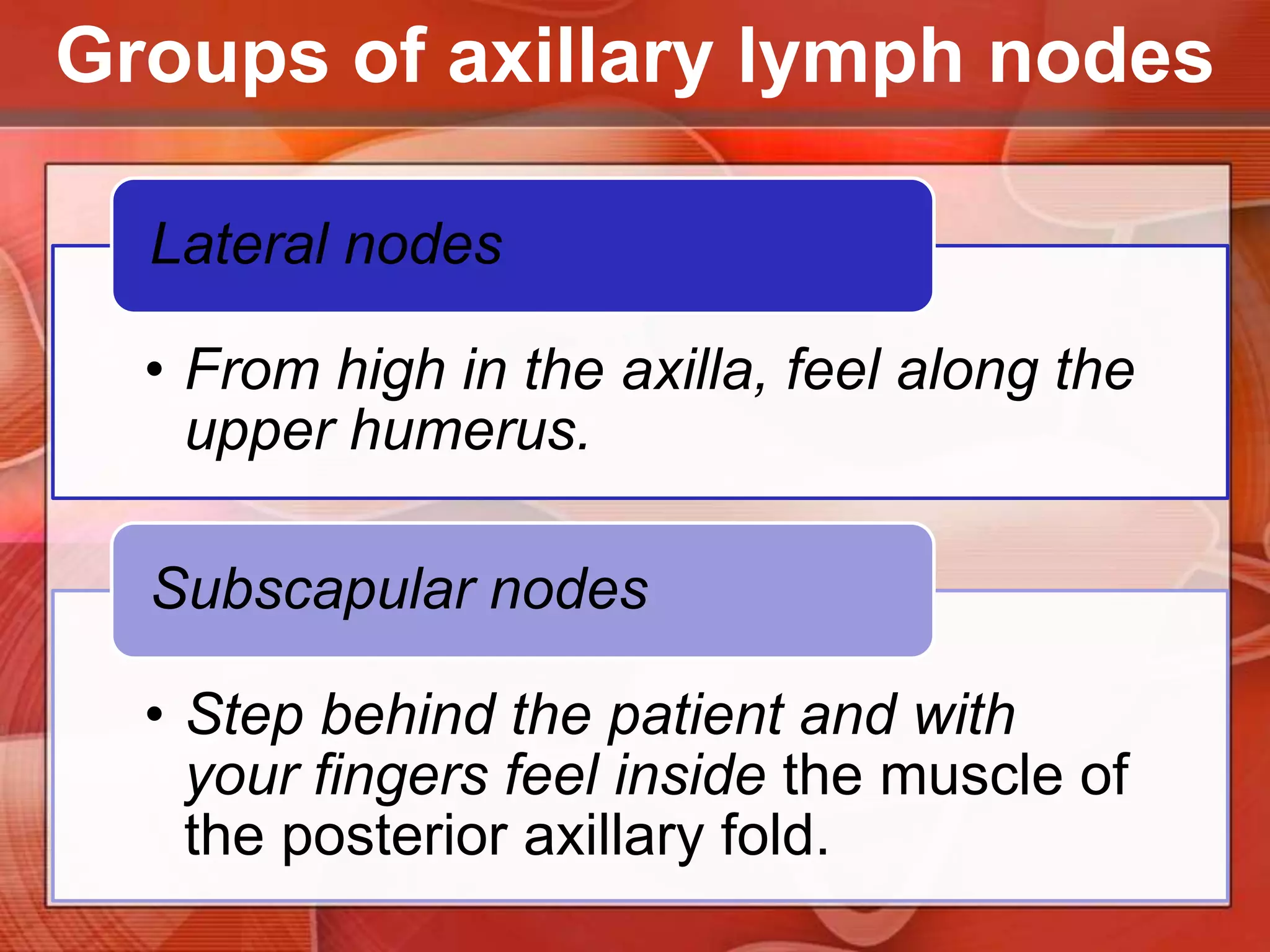
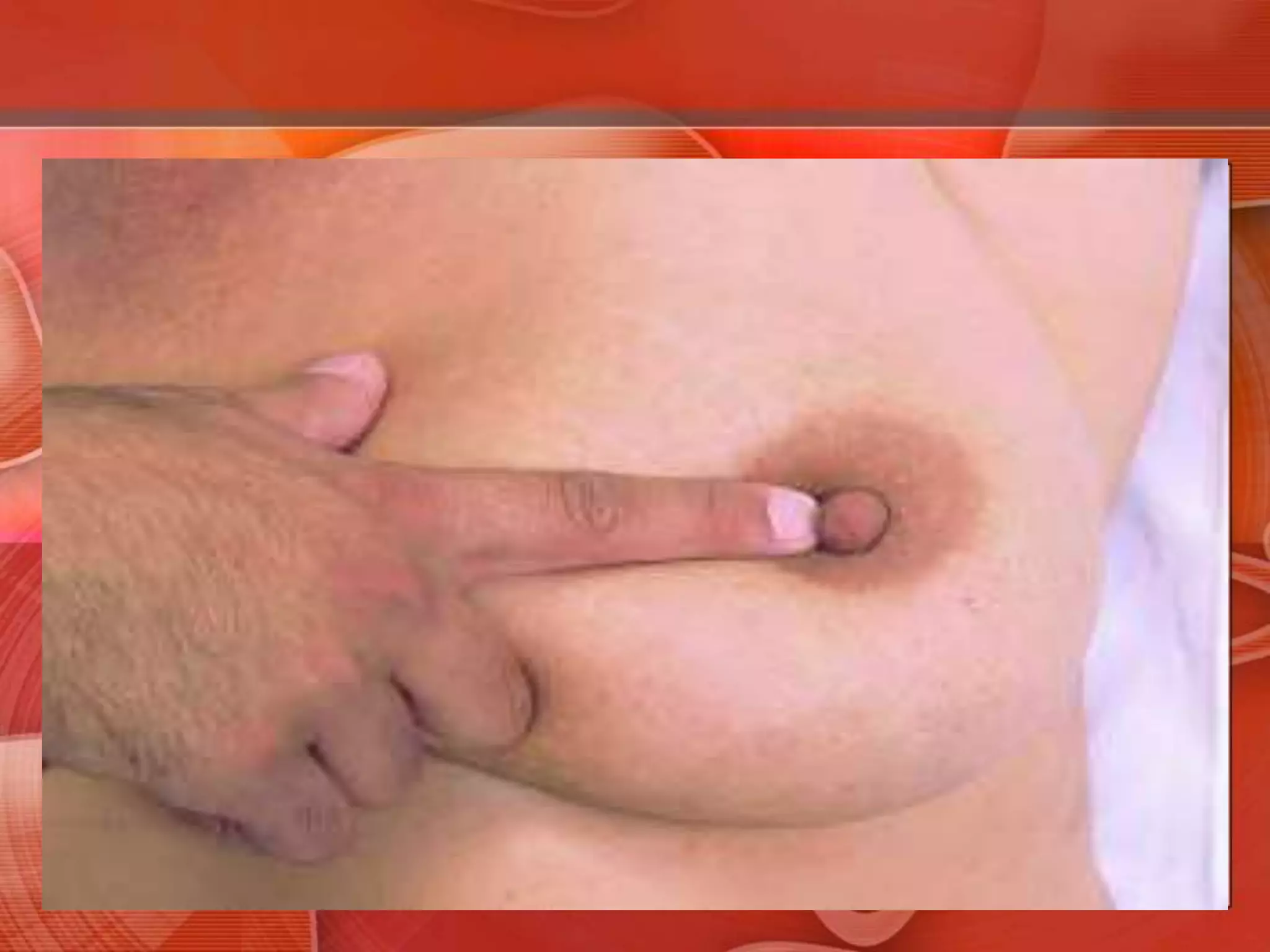
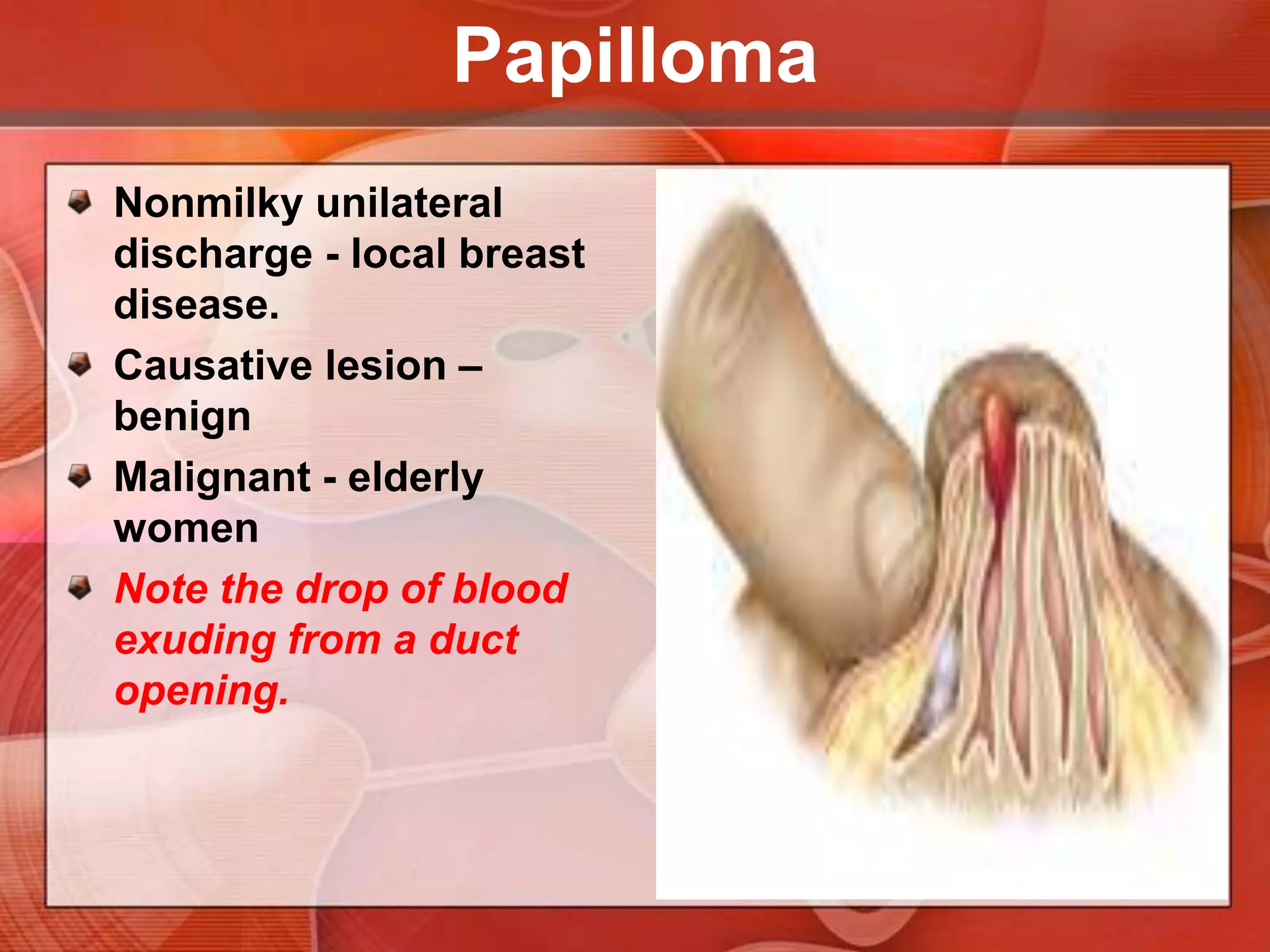
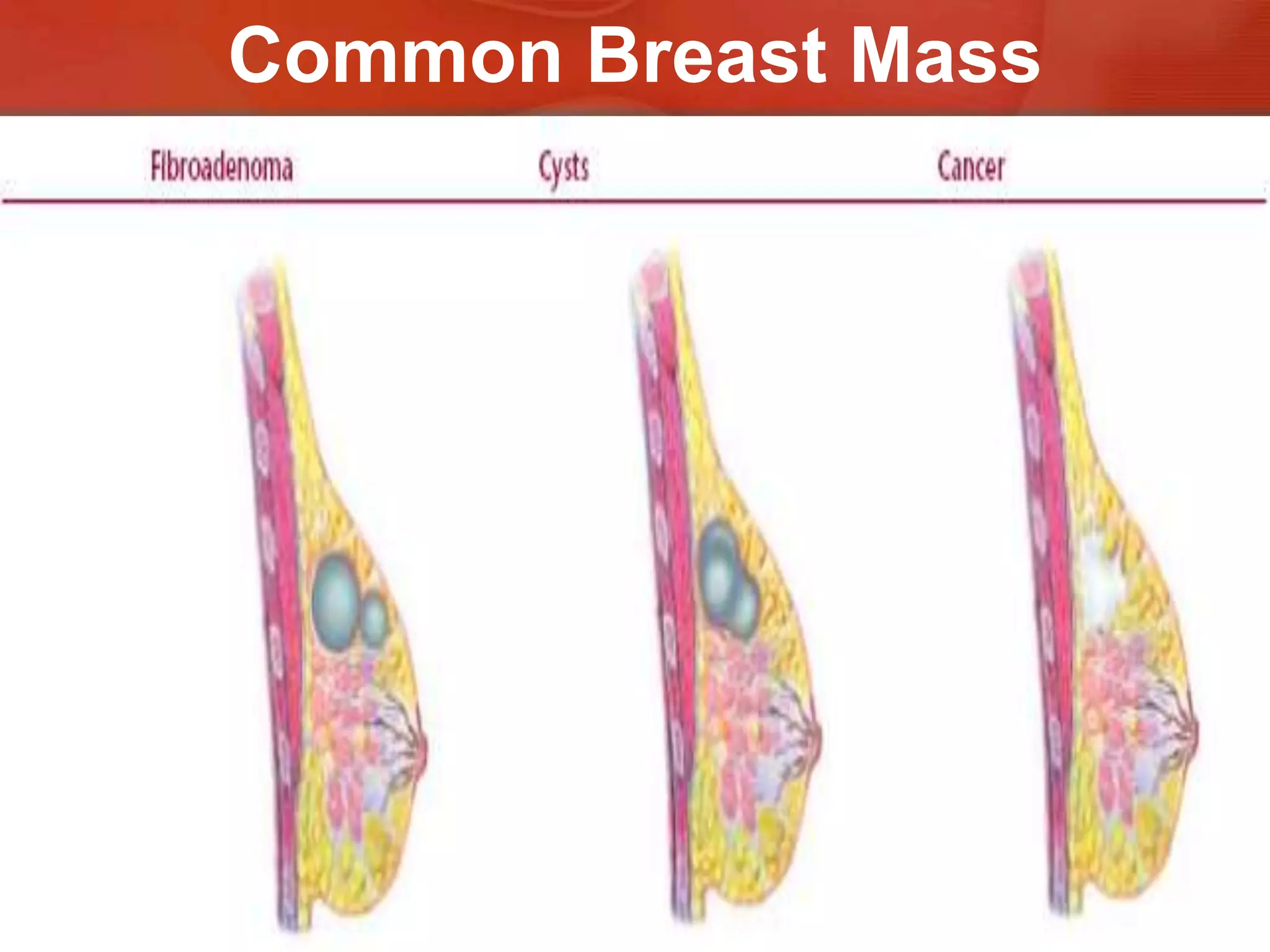
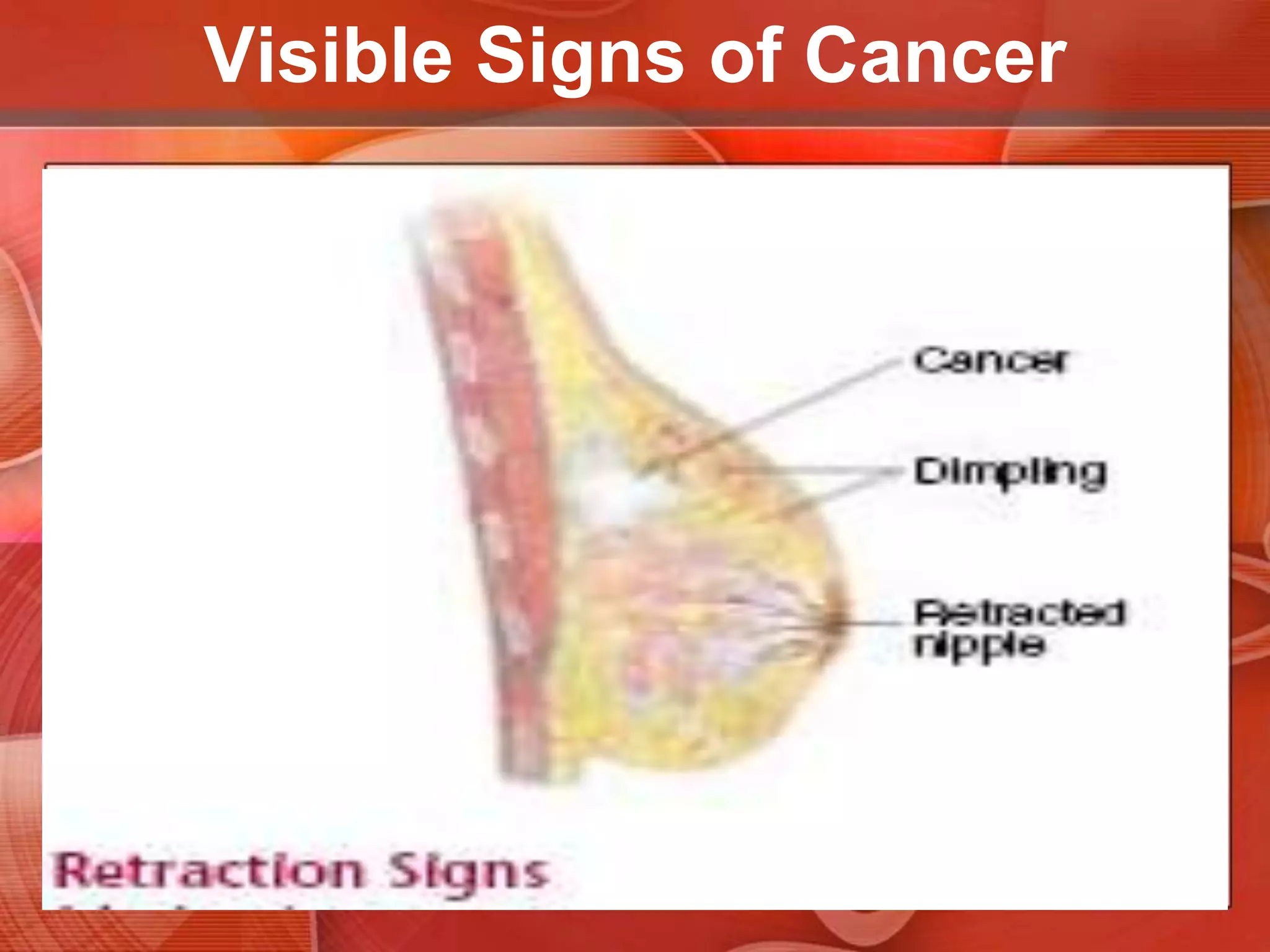
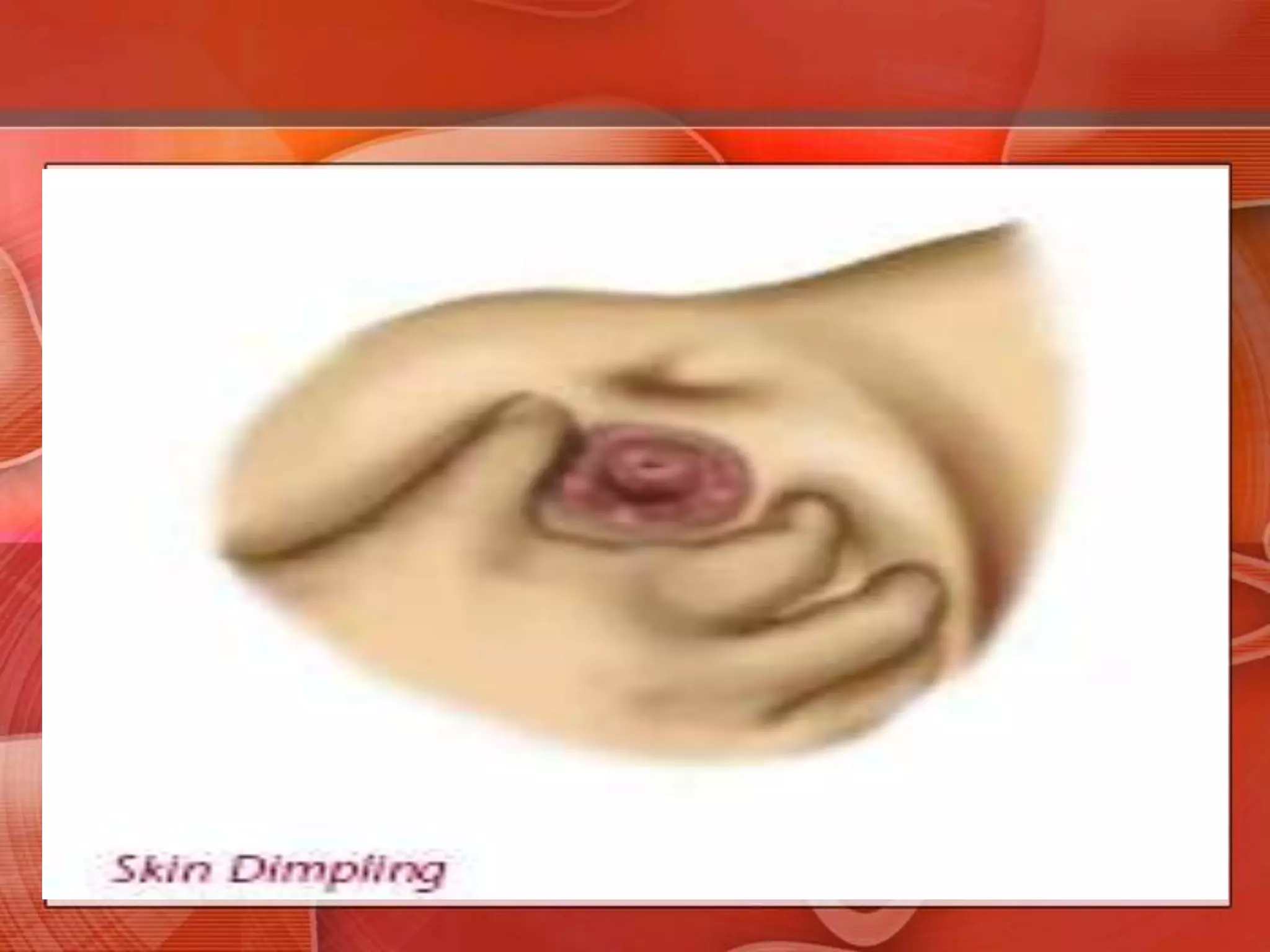
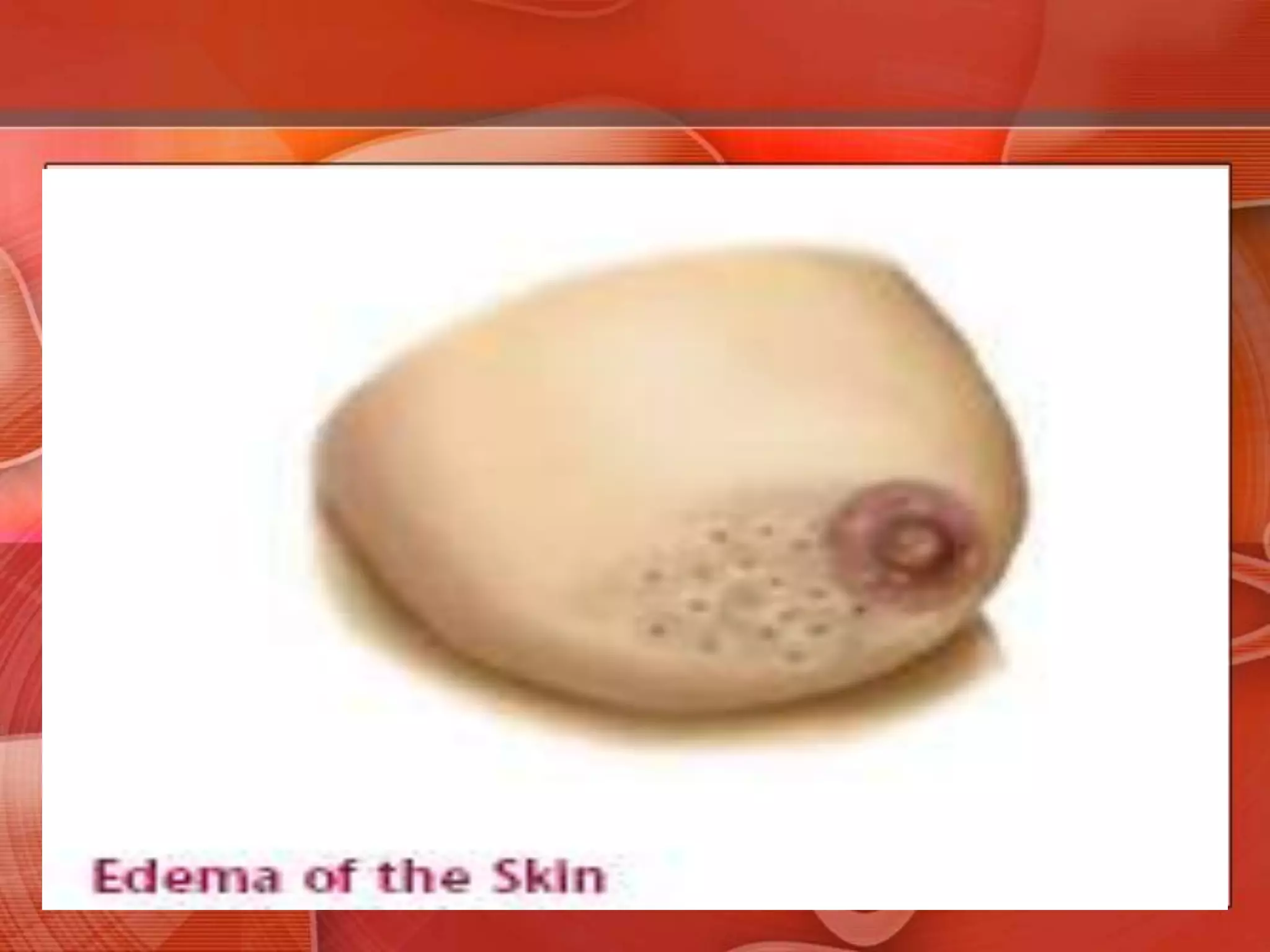
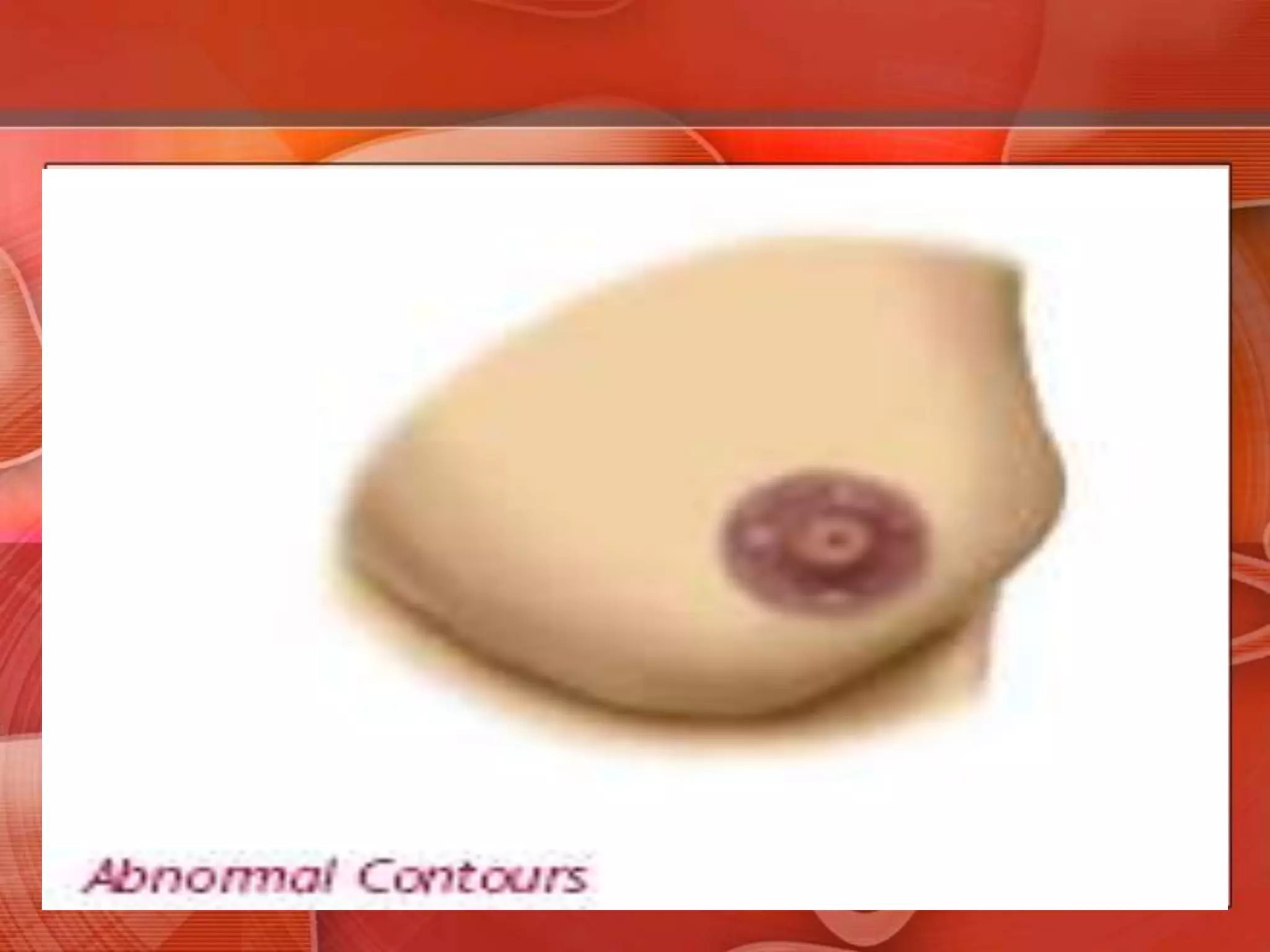
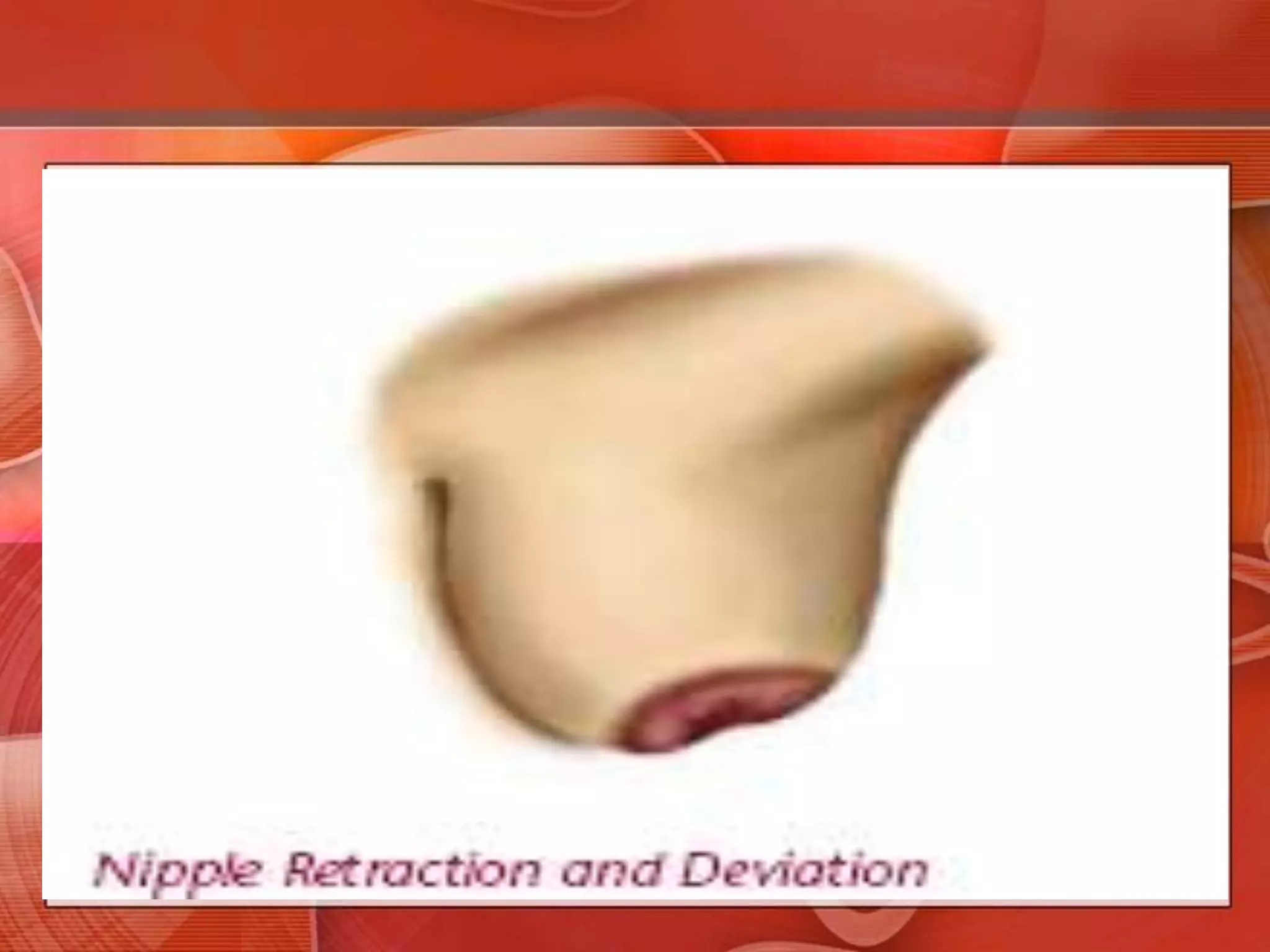
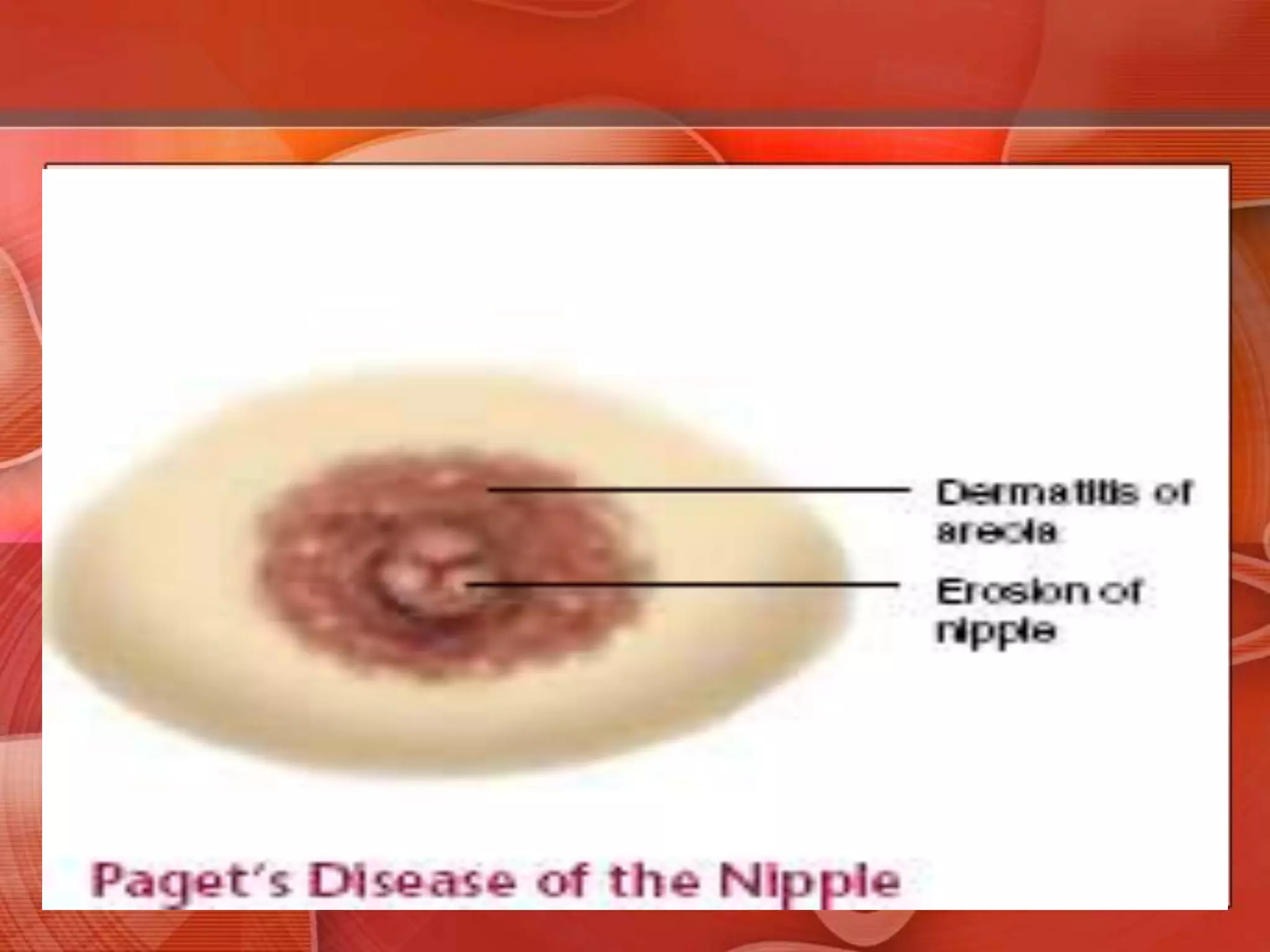
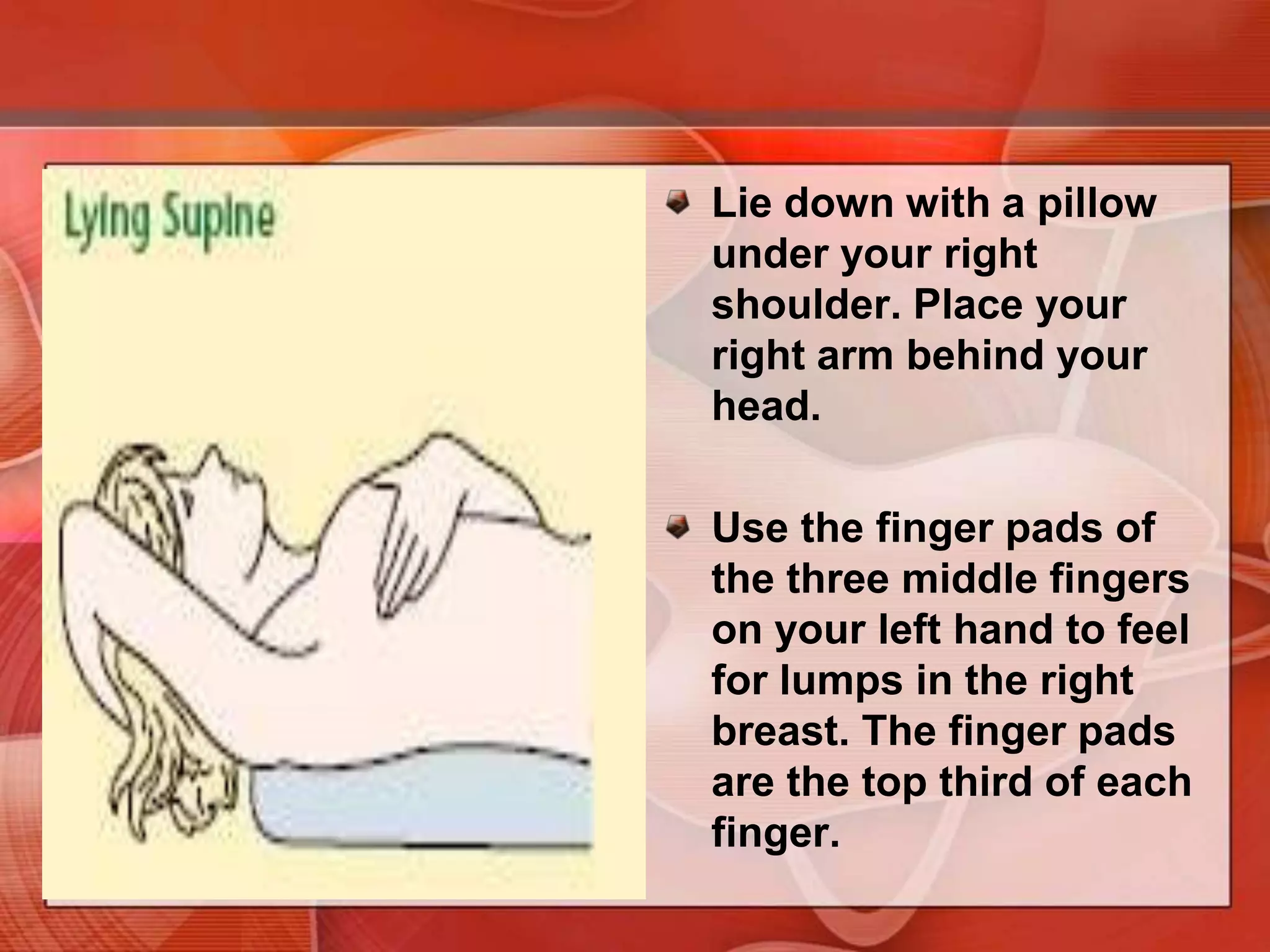
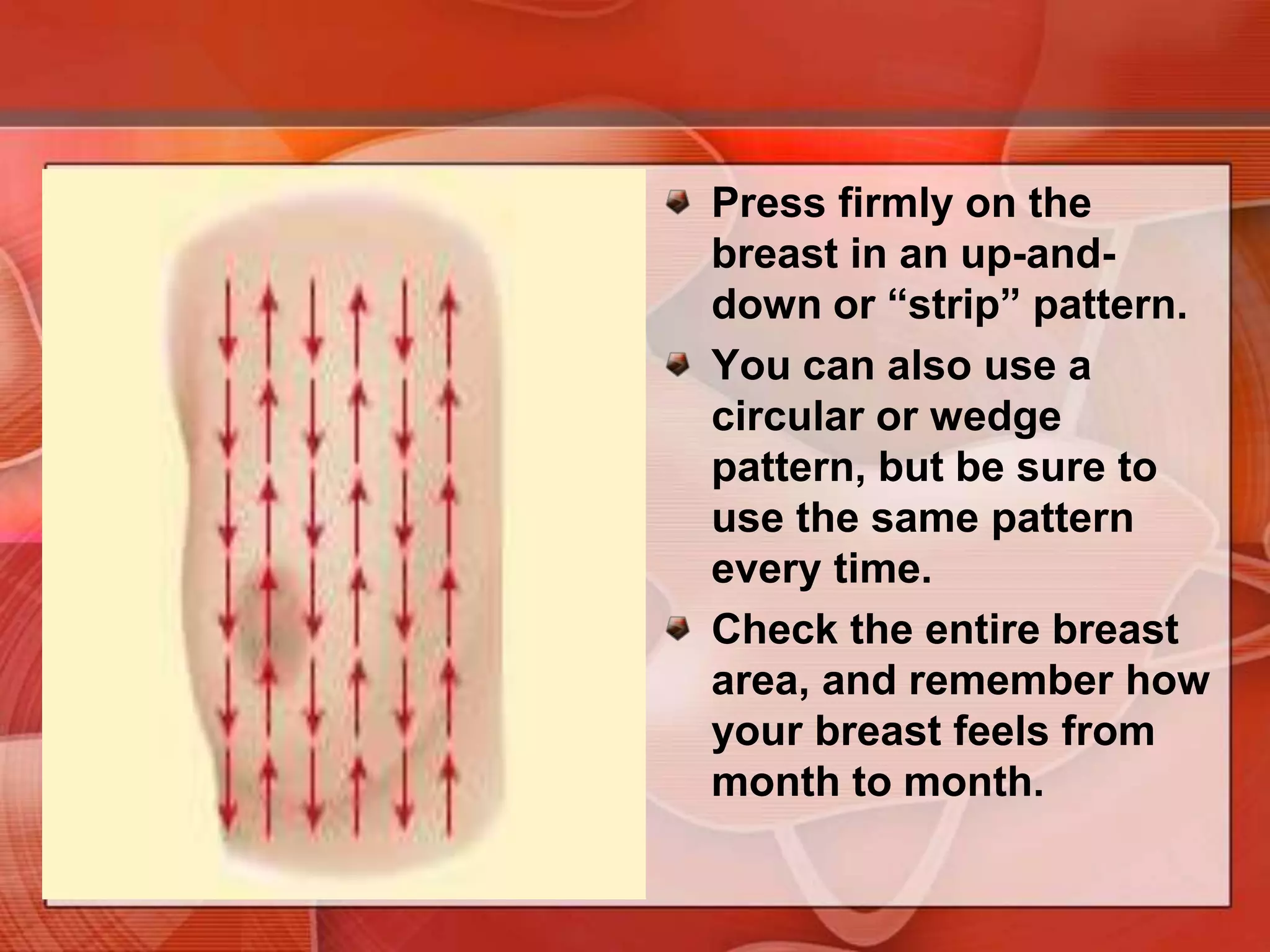
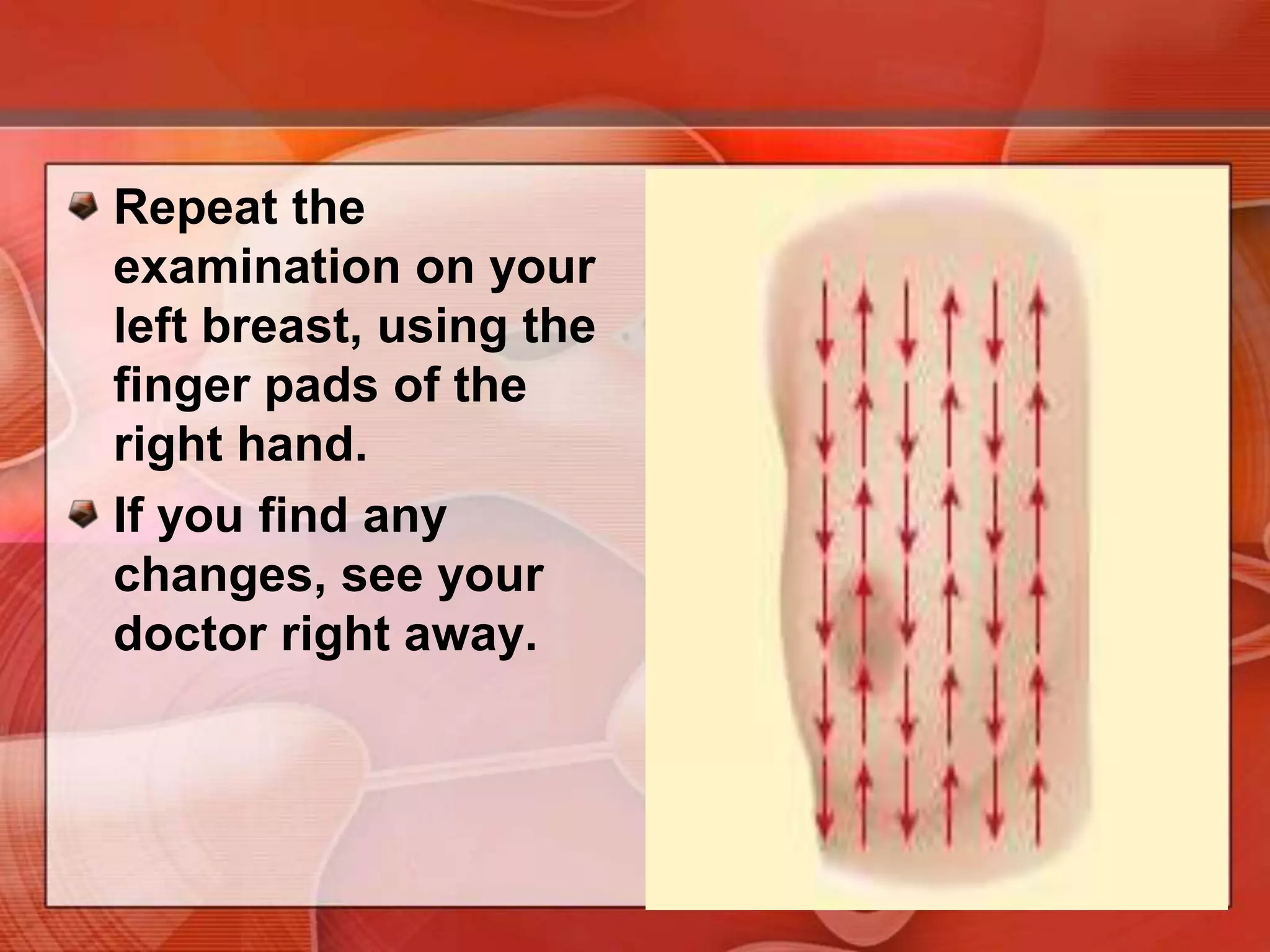
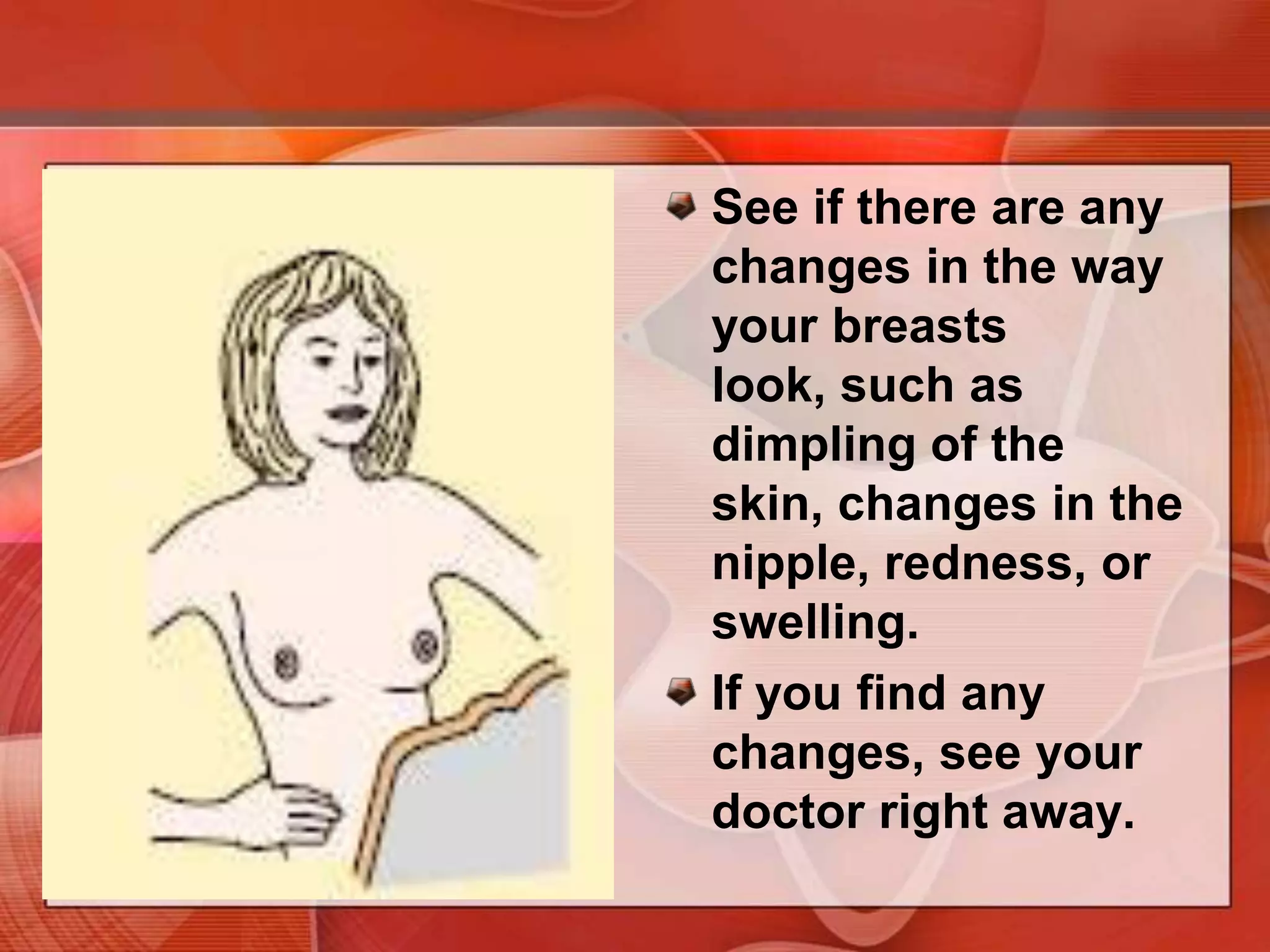
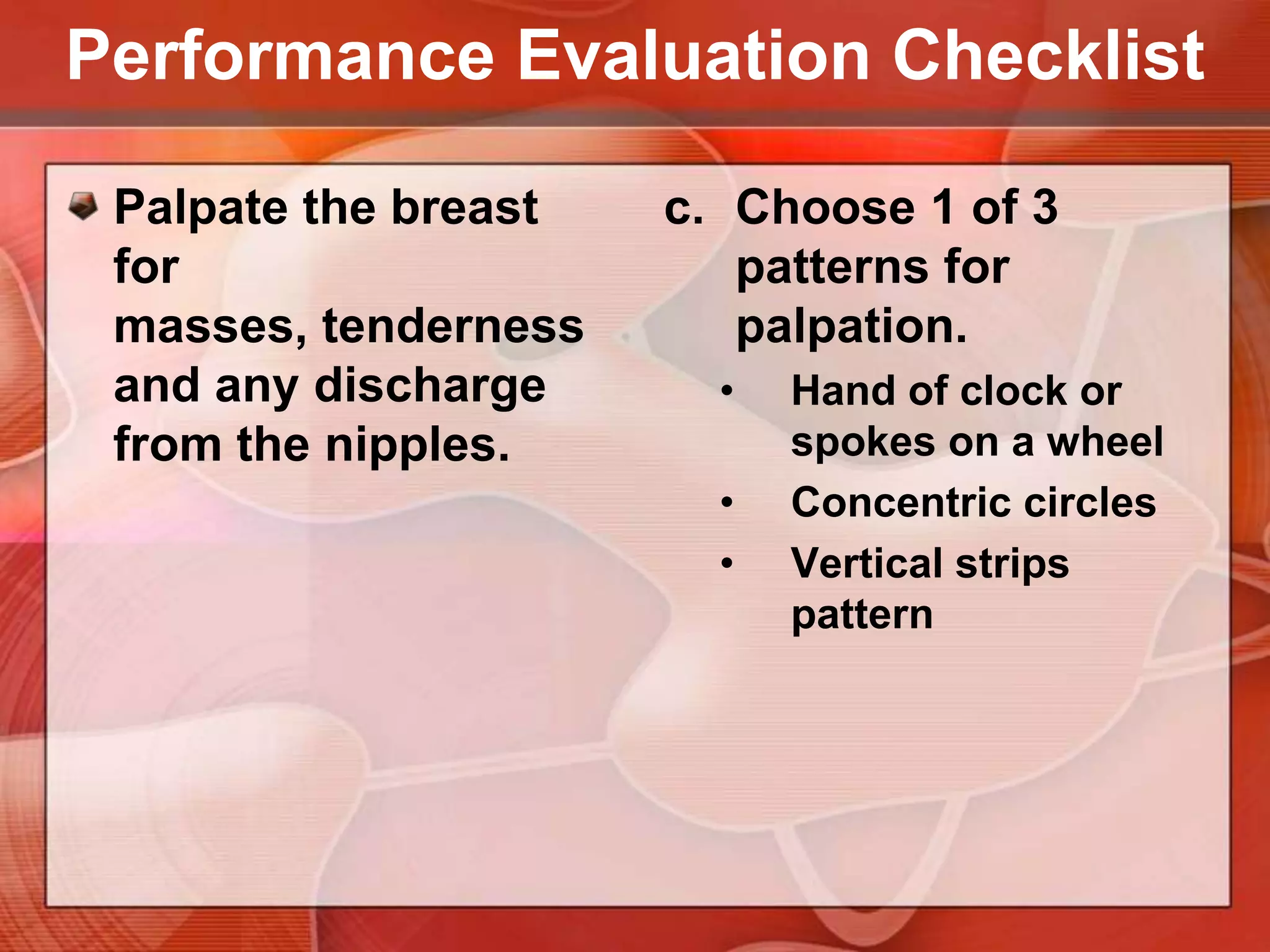
The document provides guidance on examining a patient's breasts and axillae. It describes the anatomy and outlines the procedure which involves inspection and palpation. Inspection involves examining the breasts visually for signs of abnormalities while palpation involves thoroughly feeling the breasts using a systematic approach to identify any masses or irregularities. Any findings should be carefully documented including location, size, shape, consistency and characteristics. The exam also includes inspecting and palpating the axillae and nipple areas.