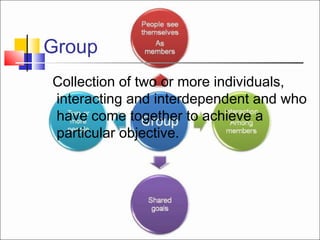
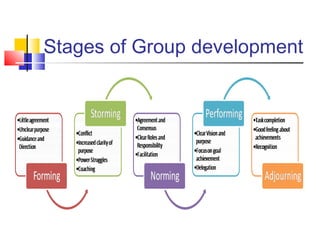
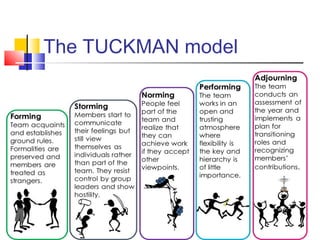
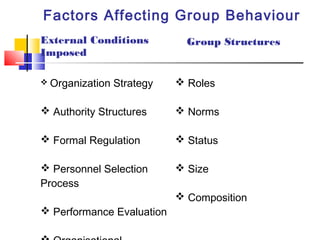
The document discusses group dynamics and defines it as the social process by which people interact and behave in a group environment. It provides characteristics of groups such as having two or more persons who directly interact and have a collective identity and common purpose. The document also discusses types of groups like formal, informal, task, and interest groups, as well as stages of group development and factors that affect group behavior.