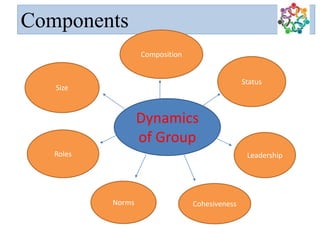
This document discusses group dynamics and provides information on key concepts related to groups and their development. It defines what constitutes a group and lists their key features. It also summarizes several theories of group formation proposed by theorists like Kurt Lewin, Wilfred Bion, and William Schutz. Tuckman's four-stage model of group development is explained. The document then discusses the composition, types and components of group dynamics, as well as characteristics of effective versus ineffective teams. It concludes by outlining the responsibilities of a group leader.