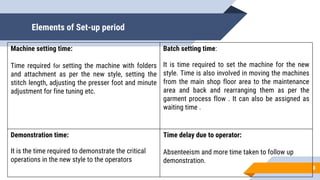
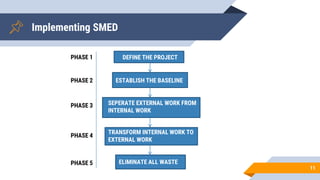
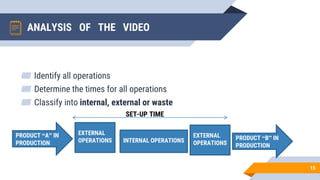
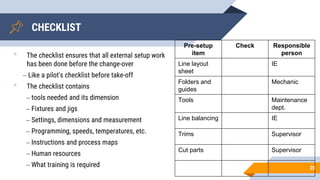
SMED (Single Minute Exchange of Die) is a lean manufacturing technique aimed at reducing changeover times between the production of different products or product variants on a machine. The basic principles of SMED involve identifying internal and external changeover tasks, analyzing each task's purpose, and focusing on low-cost solutions to eliminate changeover time. The history of SMED began in Japan at Toyota in the 1950s when consultant Shigeo Shingo helped reduce changeover times for body molding from 2-8 hours to under 10 minutes. Implementing SMED involves 5 phases - defining the project, establishing a baseline, separating external and internal work, transforming internal work externally, and eliminating all waste from the changeover process.