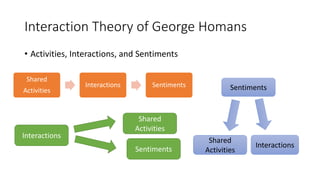
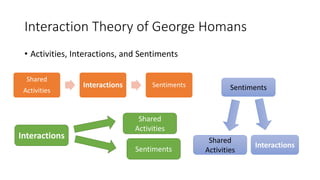
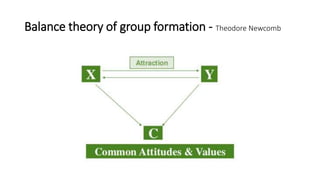
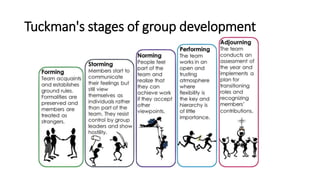
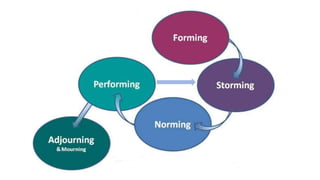
The document discusses group dynamics, highlighting the characteristics and behaviors of group members and the impact of interactions within a group. It provides insights into historical perspectives on group dynamics, key techniques, and the importance of group cohesion for decision-making and conflict resolution. Additionally, it examines reasons individuals form groups and concludes that understanding group behavior is vital for success.