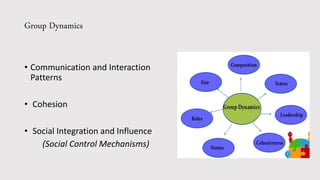
The document outlines the concepts of group dynamics and team building, emphasizing the importance of communication patterns, cohesion, social integration, and social control mechanisms within groups. It discusses how effective team building leads to higher performance by leveraging individual talents and fostering collaboration. Additionally, it identifies helpful and harmful behaviors in group settings, providing guidance to enhance team effectiveness.