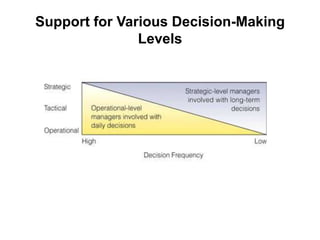
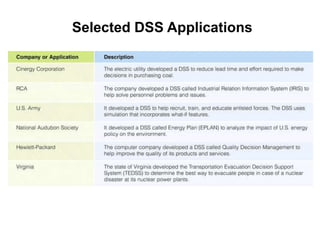
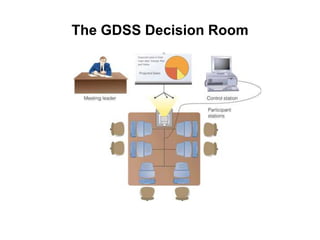
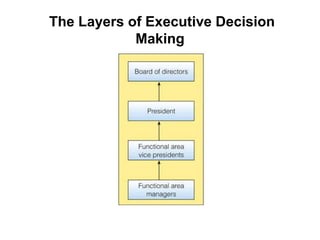
This document provides an overview of decision support systems (DSS), including their capabilities and components. A DSS supports various phases of problem-solving and decision-making at different frequencies and for different types of problems. It also supports decision-making at operational, tactical, and strategic levels. Key components of a DSS include databases, model bases, and model management systems to facilitate quantitative analysis. Group DSS and executive support systems are also discussed as specialized types of DSS tailored for group or executive decision-making.