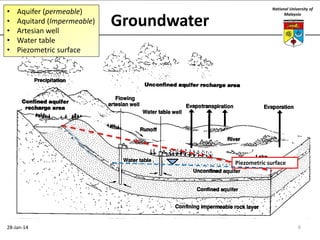
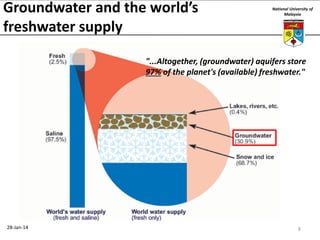
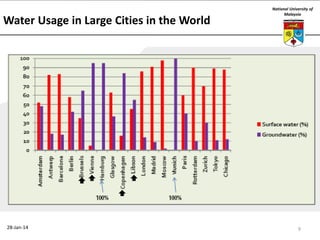
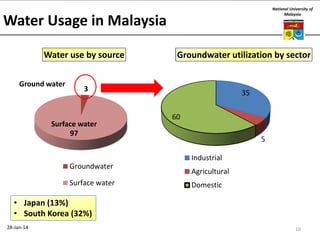
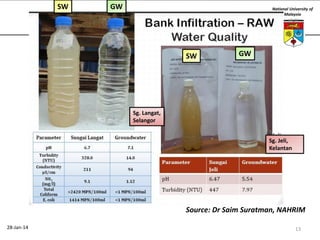
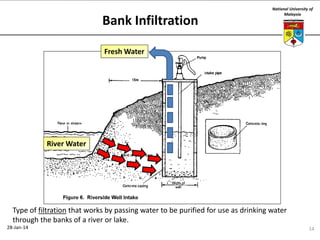
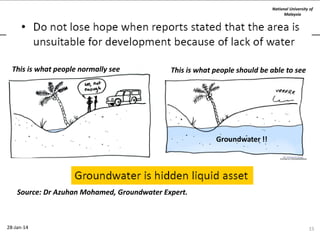
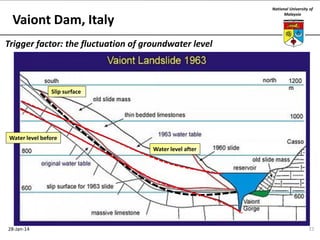
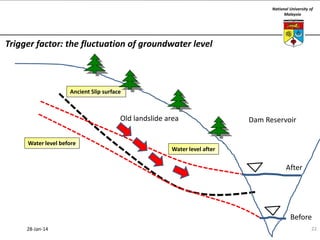
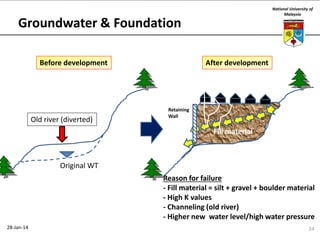
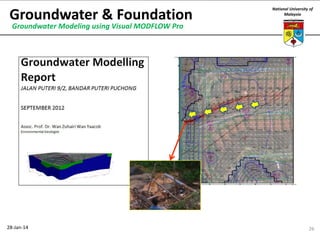
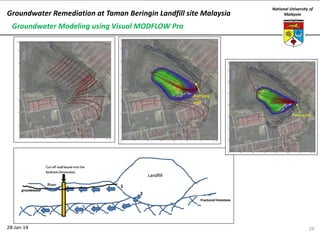
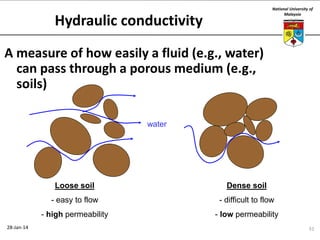
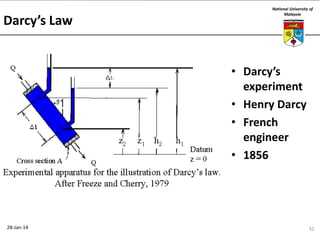
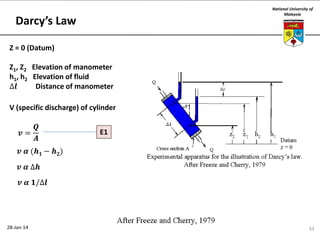
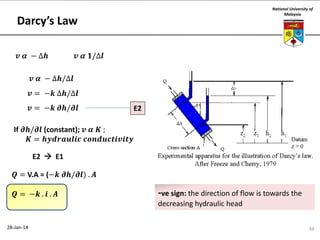
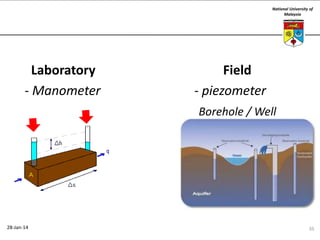
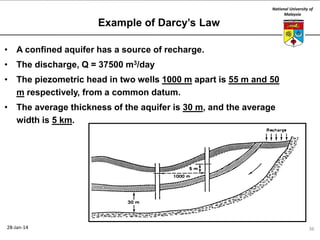
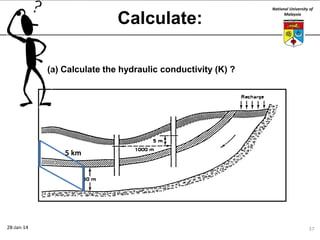
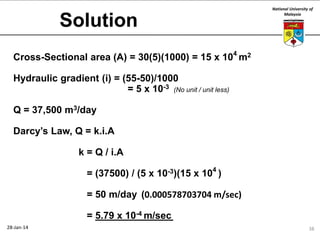
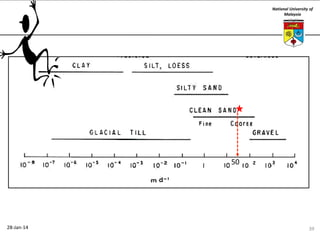
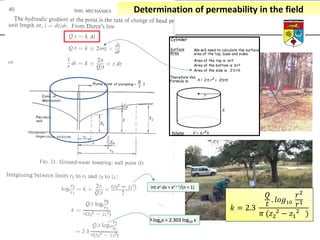
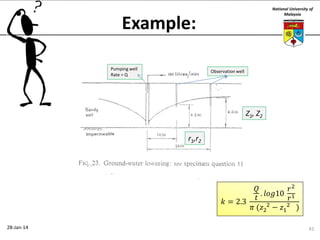
This document summarizes a lecture on groundwater given at the National University of Malaysia. The lecture covered the definition of groundwater, its importance as a resource, and how it relates to geotechnical problems and water movement through soil. It also provided examples of groundwater usage, contamination issues, and modeling techniques. The key points were that groundwater stores most of the world's freshwater, is critical for large cities and industries, and its movement is governed by Darcy's Law.