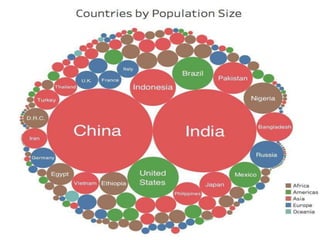
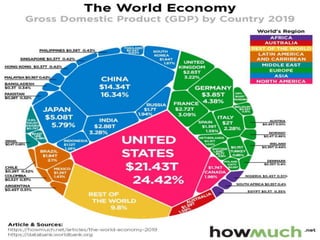
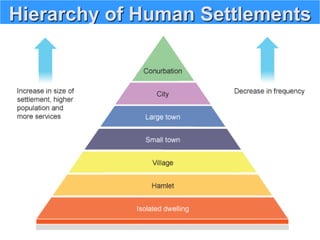
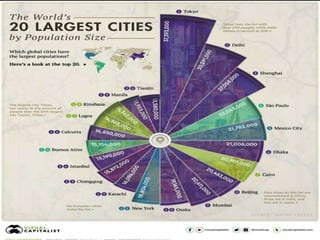
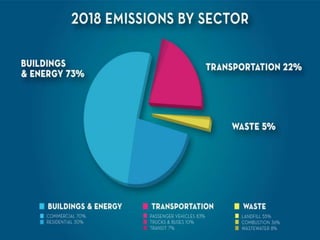
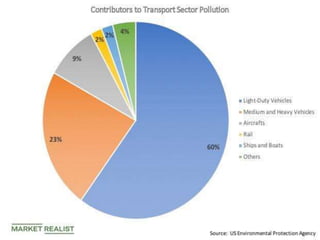
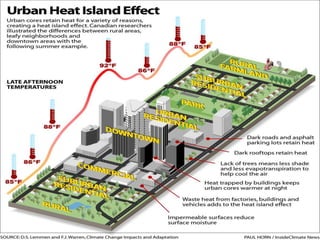
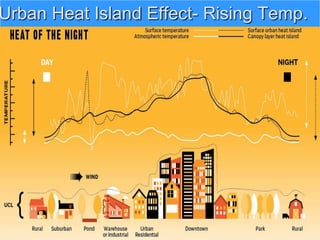
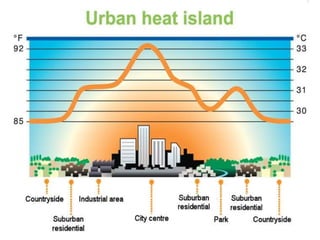
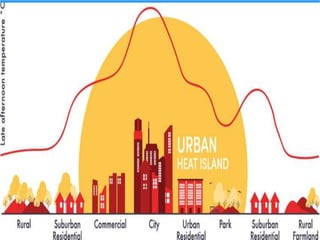
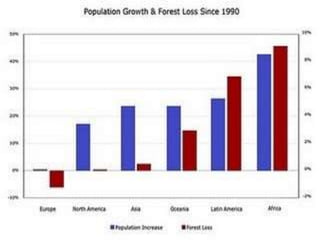
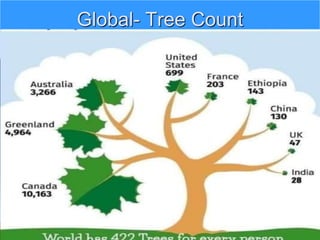
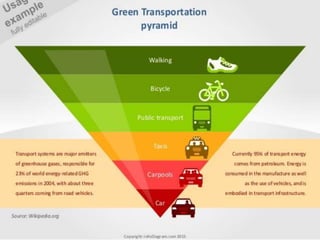
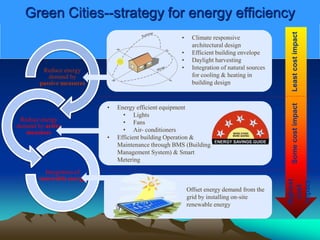
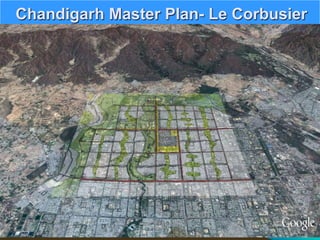
The document discusses the impact of cities on nature, highlighting their role as centers of economic growth, population concentration, and environmental challenges. It emphasizes the need for sustainable urban development to address issues such as pollution, resource consumption, and climate change while proposing strategies for creating greener, more resilient cities. Additionally, it outlines the urgency of implementing sustainable development goals and innovative urban planning practices to combat urbanization's negative effects on the environment.