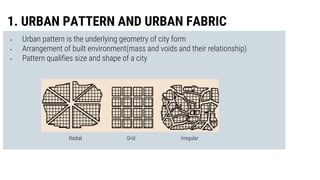
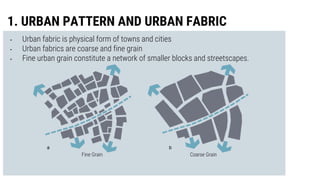
Urban design involves arranging all elements of cities, including buildings, public spaces, transportation, and amenities. It considers urban patterns, building forms, streetscapes, connections within a city, movement systems, public open spaces, and infrastructure. The key elements of urban design are urban fabric, which is the physical form of cities made up of blocks and streets, building forms that define street walls and spaces, and connections within a city through visual lines and physical routes to facilitate movement.