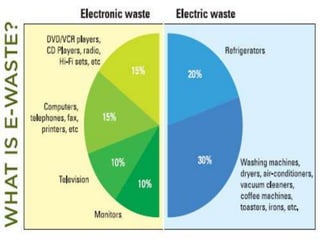
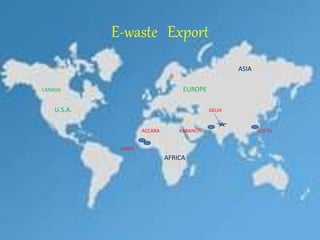
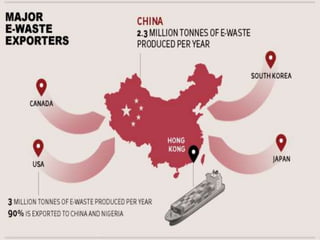
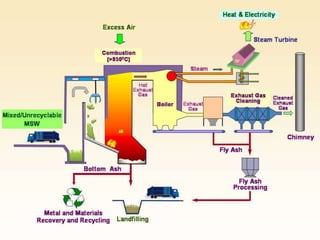
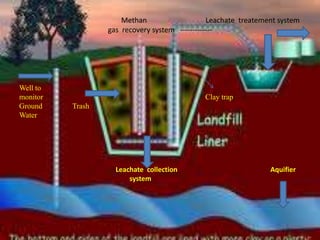
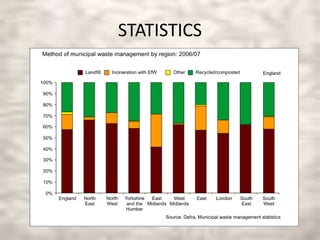
This document discusses green electronics and e-waste management. It begins by defining green electronics as emphasizing the elimination of harmful substances in electronics and proper disposal of electronic waste. It then discusses how e-waste is generated, the hazardous substances it contains, and common methods of e-waste disposal including incineration, landfilling, and recycling. Statistics on e-waste amounts and export locations are also mentioned. The document highlights advantages like a healthier environment from proper e-waste handling and disadvantages like pollution if not disposed of correctly. It stresses the importance of sustainable e-waste practices.