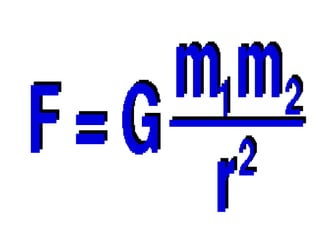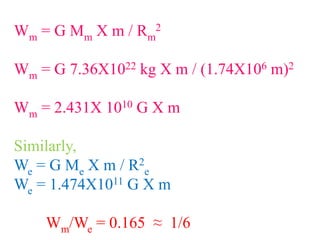This document discusses the universal law of gravitation and its implications. It can be summarized as follows:
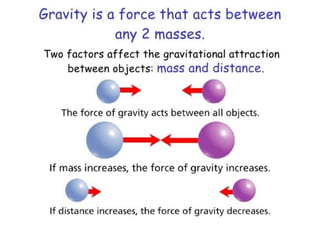
1) The universal law of gravitation states that the gravitational force between two objects is directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
2) This law explains phenomena like the orbit of planets around the sun and the moon around Earth. It also explains why objects fall with an acceleration of 9.8 m/s^2 on Earth.
3) The weight of an object, which is the gravitational force exerted by Earth, differs on other celestial bodies due to differences in their masses and radii. Calculations show an object's weight on