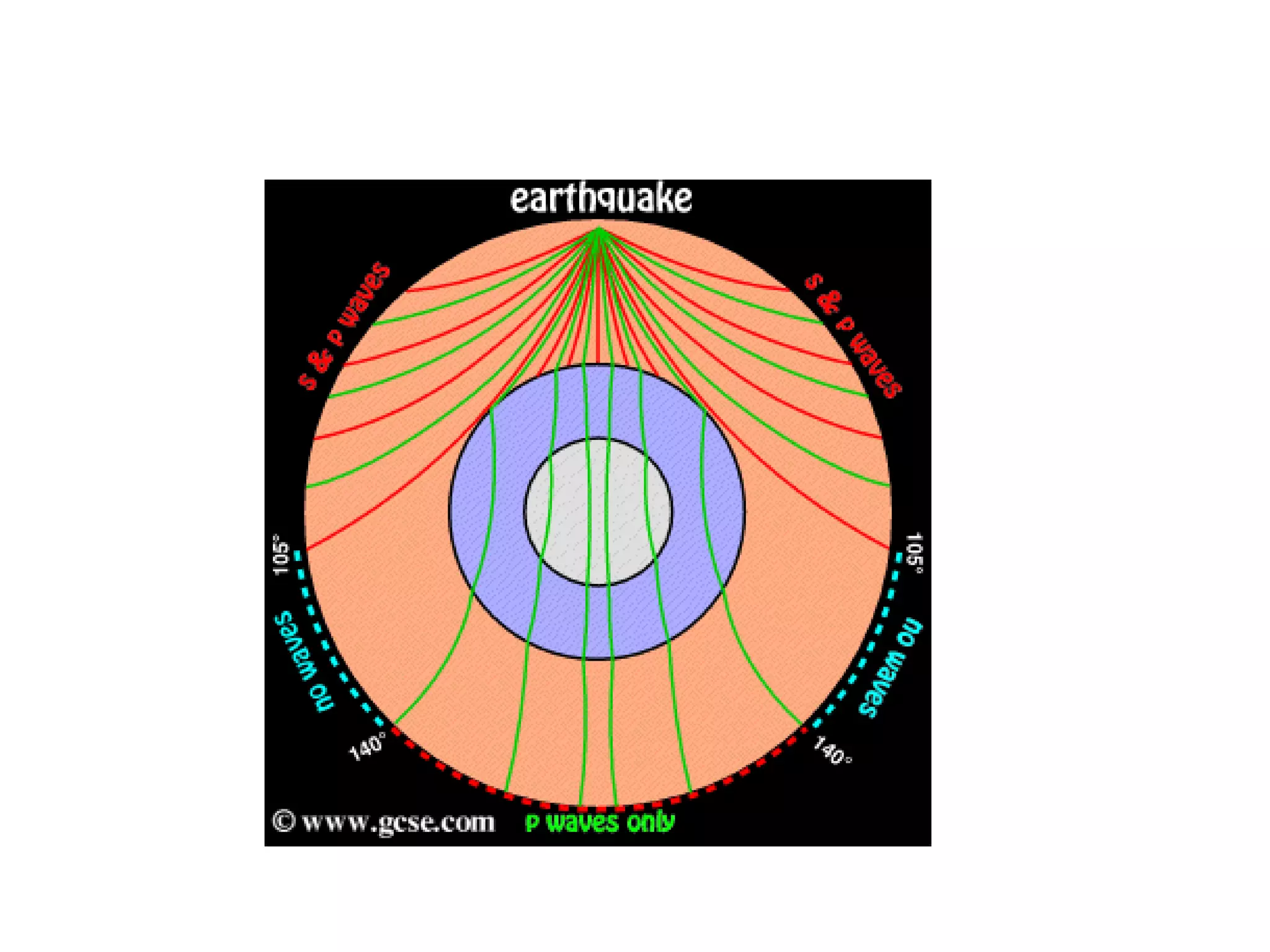
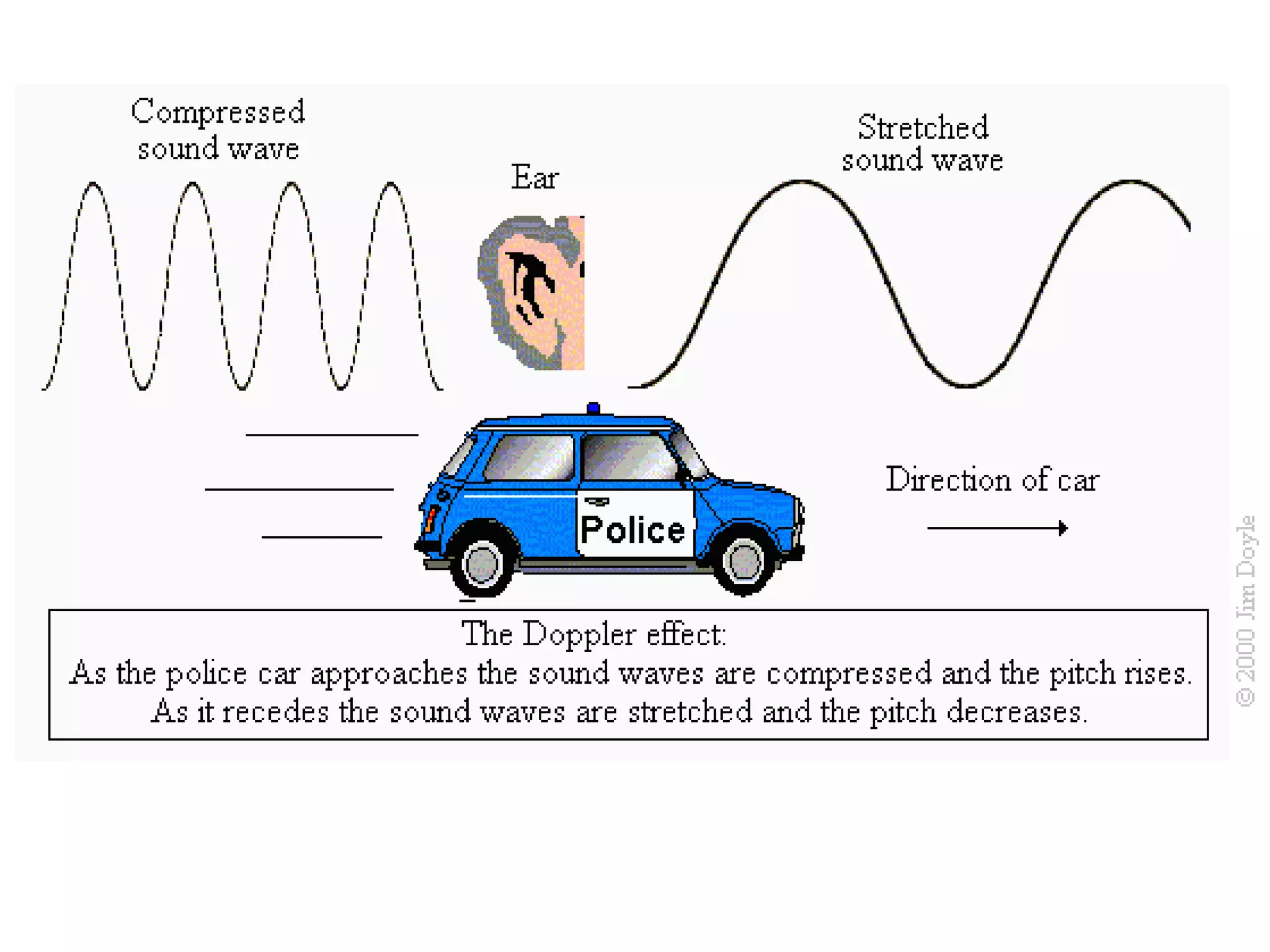
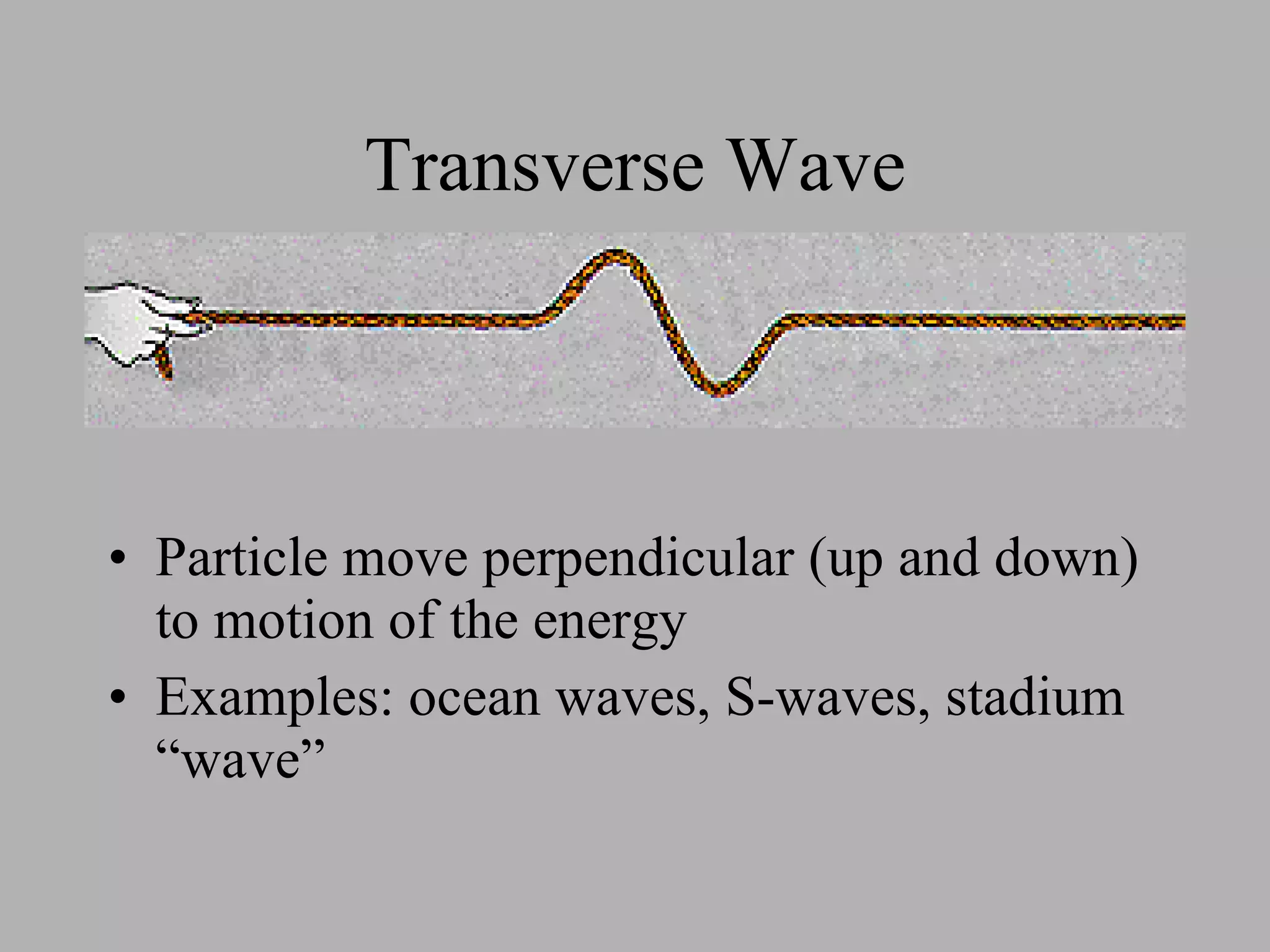
Waves can be mechanical or electromagnetic. Mechanical waves require a medium and include longitudinal and transverse waves, while electromagnetic waves can travel through a vacuum. Key wave properties include amplitude, wavelength, frequency, and speed which depends on the medium. Earthquakes generate both P and S body waves - P waves are longitudinal while S waves are transverse and travel slower. Seismographs are used to measure and record earthquake magnitude on the Richter scale.











![Seismograph –instrument which records the magnitude of an earthquake Seismogram - – data or graph collected by the seismograph [seismograph (graph) and seismometer (instrument) are also used and becomng the norm]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/waves-1226065006467389-8/75/Waves-13-2048.jpg)