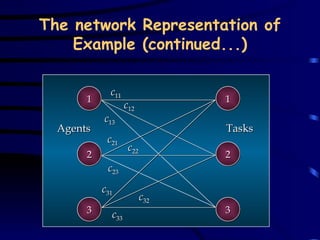
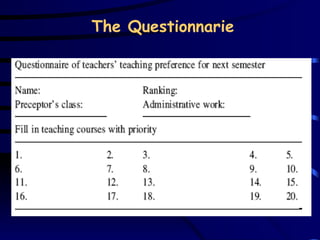
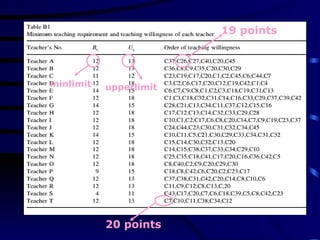
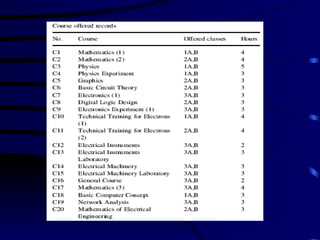
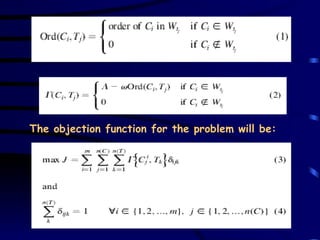
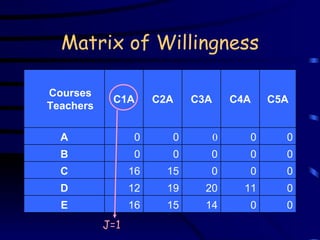
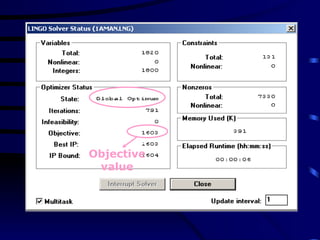
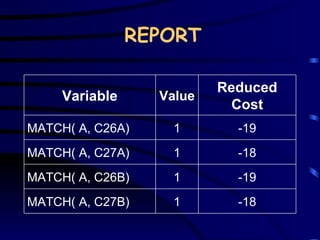
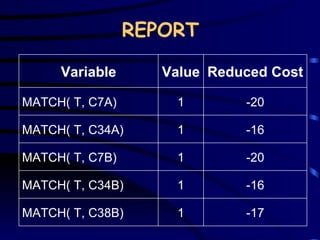
The document discusses assignment problems and their applications. It provides examples of assignment problems involving assigning workers to jobs or tasks. The goal is typically to minimize costs or maximize satisfaction. The document then summarizes a research article that uses a genetic algorithm to solve the specific problem of optimally assigning teachers to courses while considering various constraints.