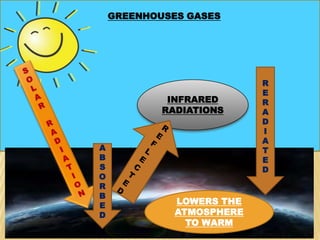
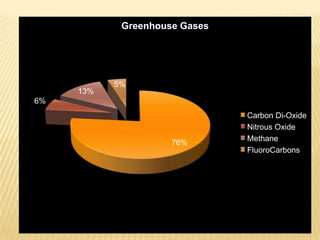
The document defines the greenhouse effect as a process where greenhouse gases in the atmosphere absorb and re-radiate thermal radiation from the surface, trapping heat. It then explains that greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide absorb infrared radiation emitted from the Earth's surface and radiate it in all directions, warming the lower atmosphere and surface. The main sources of greenhouse gases are the burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, livestock, CFC refrigerants, and agriculture such as fertilizer use.