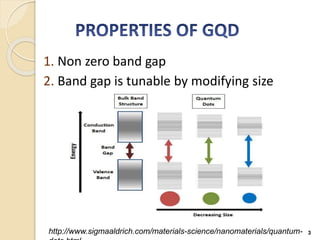
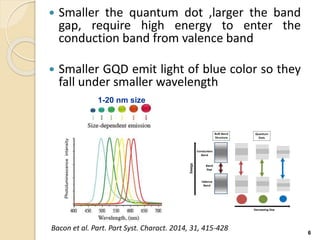
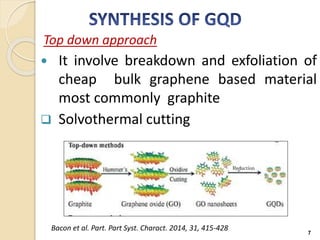
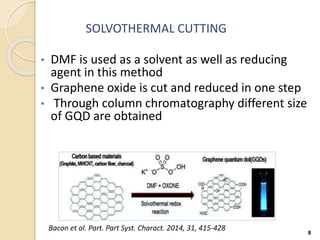
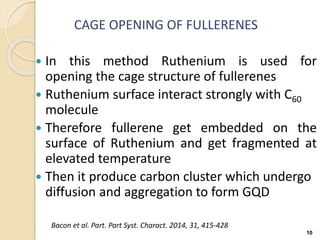
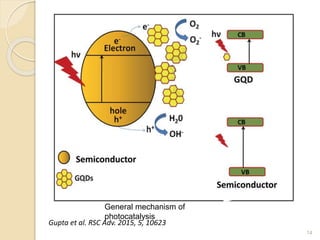
Graphene quantum dots are crystalline semiconductor nanoparticles between 1-20 nm in diameter that exhibit quantum confinement effects. They have a tunable and non-zero bandgap dependent on size, and fluorescence of different colors based on size. Graphene quantum dots are produced through top-down methods that break down bulk materials like graphite, or bottom-up synthesis from aromatic precursors like fullerenes. They have applications in areas like bioimaging, photovoltaics, LEDs, and photocatalysis due to their photoluminescent and catalytic properties. When combined with semiconductors like ZnO to form heterojunctions, graphene quantum dots can act as efficient photocatalysts for degradation of poll