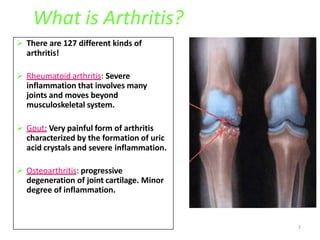
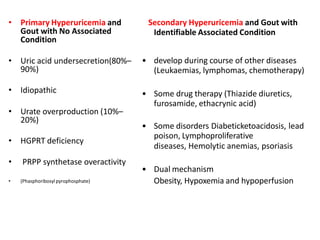
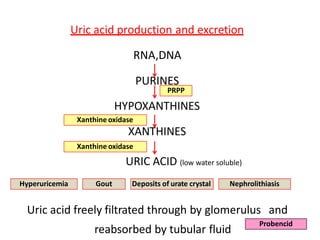
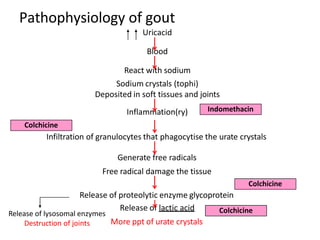
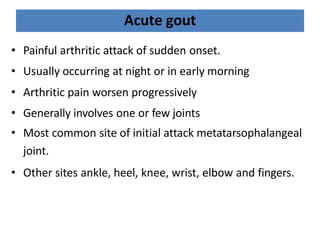
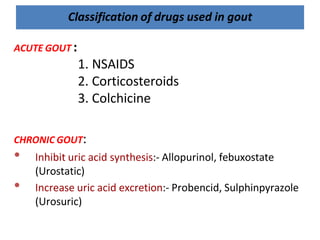
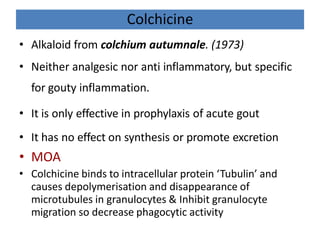
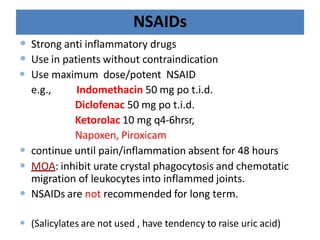
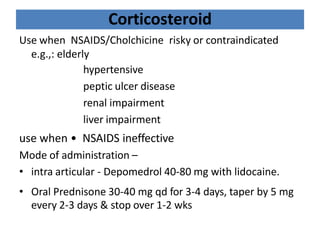
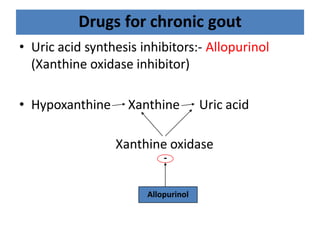
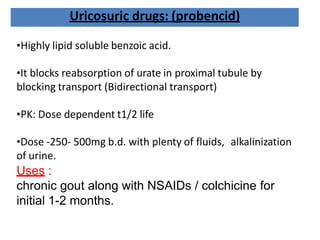
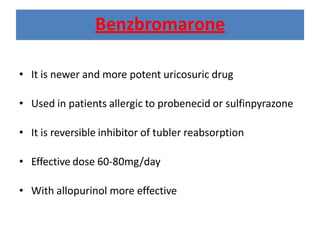
There are over 127 types of arthritis. This document discusses gout, which is caused by uric acid crystals forming in the joints due to abnormally high levels of uric acid in the blood (hyperuricemia). Gout can cause acute attacks of severe pain and inflammation. Treatment involves drugs to terminate attacks, prevent complications, and manage chronic gout through reducing uric acid production or increasing excretion. Key drugs discussed are colchicine, NSAIDs, corticosteroids for acute gout and allopurinol, probenecid, sulfinpyrazone for chronic management and uric acid control.