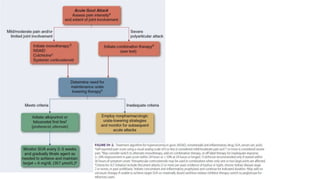
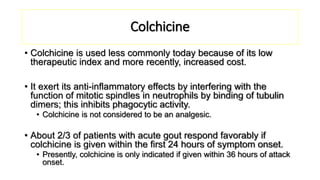
This document provides information on gout and hyperuricemia. It discusses the pathophysiology of gout, including how uric acid crystals form in the joints and cause inflammation. It also covers risk factors, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and treatment approaches. Treatment involves acute relief of gout attacks with medications like NSAIDs or colchicine, as well as long-term urate-lowering therapy with drugs like allopurinol or febuxostat to prevent future attacks by lowering uric acid levels.






































![Febuxostat
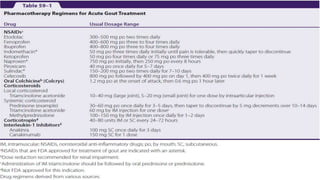
• Febuxostat is a nonpurine XOI structurally distinct from
allopurinol that is FDA approved for chronic hyperuricemia
associated with gout.
• The initial dose is 40 mg orally once daily. The dose may be
increased to 80 mg orally once daily if the SUA does not
decrease to 6 mg/dL (357 μmol/L) or less after 2 weeks of
treatment.
• No dosage adjustment is necessary in patients with mild or
moderate renal impairment; however, febuxostat is not
recommended in patient with severe renal insufficiency (CrCl <
30 mL/min [0.5 mL/s]).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/goutandhyperuricemia-230220154556-cdd040d3/85/Gout-and-Hyperuricemia-pptx-44-320.jpg)