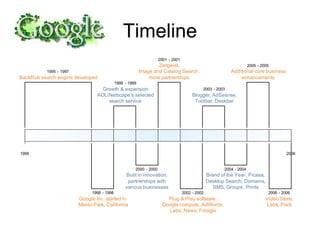
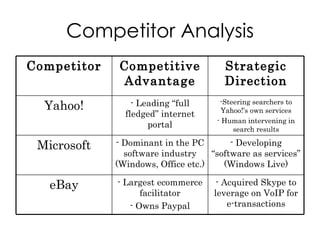
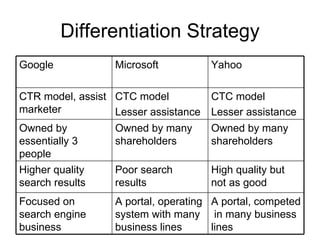
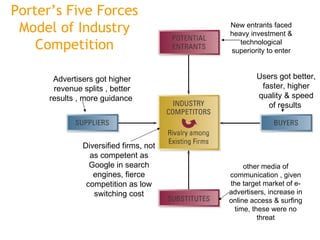
The document discusses Google's business strategy and potential areas for expansion. It summarizes that Google started as a search engine and used innovative paid listing and algorithmic models to grow rapidly. While competitors pursued diversification, Google achieved differentiation through superior search quality and a focus on innovation. The summary recommends that Google continue focusing on its core search competency in line with its 70-20-10 strategy, given its competitive advantages in this area. Direct competition with established players in other domains like portals, ecommerce or operating systems would be challenging.