This document provides an overview of gonioscopy, including:
1. It describes the history and development of gonioscopy, from early pioneers like Trantas who coined the term, to modern innovations like the Goldmann lens.
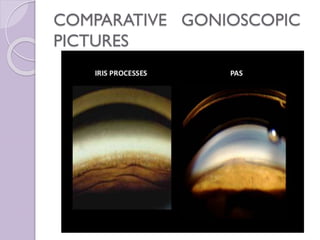
2. The purpose and principles of gonioscopy are explained, such as allowing visualization of the anterior chamber angle to assess for angle closure risk factors.
3. Different techniques for gonioscopy are covered, including direct methods using a Koeppe lens and indirect methods using multi-mirror lenses like the Goldmann lens viewed through a slit lamp.
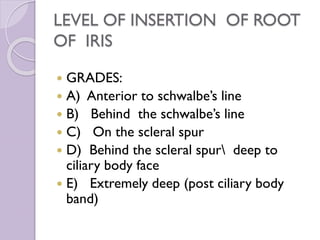
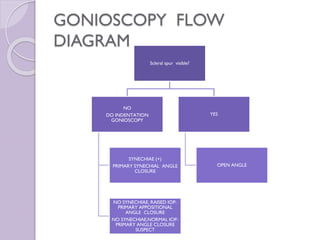
4. Common angle structures are defined, and grading systems for assessing angle width and other characteristics are outlined.