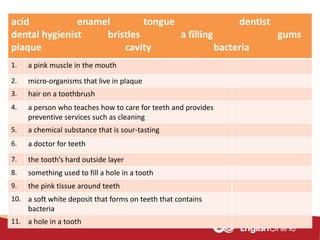
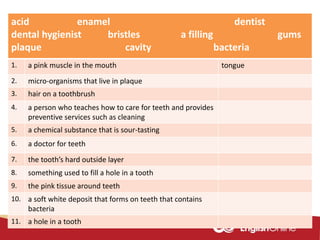
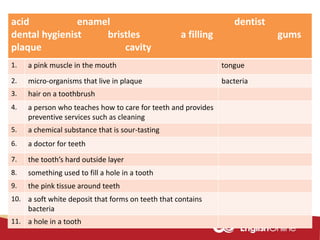
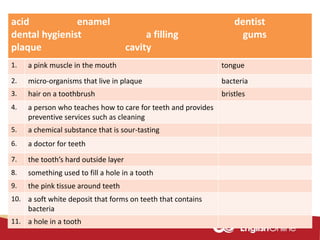
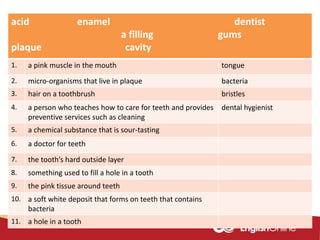
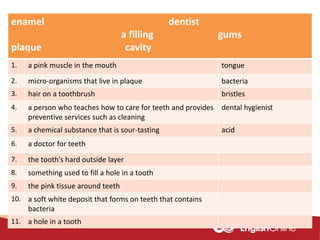
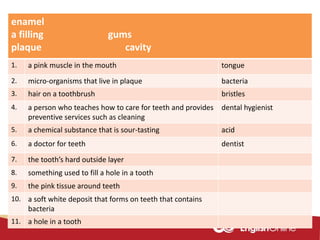
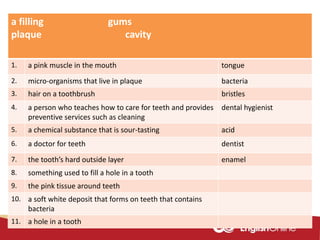
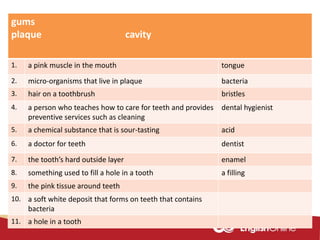
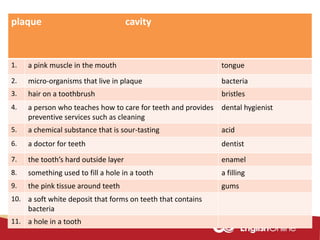
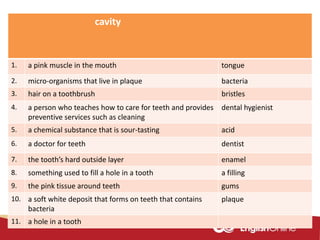
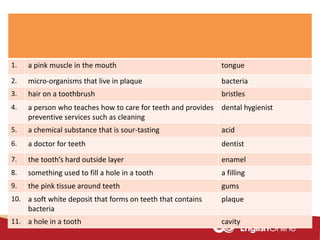
The document provides information about dental health and caring for teeth. It discusses the importance of proper dental hygiene, such as brushing twice a day, flossing once a day, and seeing a dentist regularly. It explains that plaque and sugar can cause tooth decay if not removed. The document also notes that babies' gums should be cleaned and bottles should not contain juice or pop. Parents should help young children brush their teeth until age 8 to ensure all surfaces are cleaned.