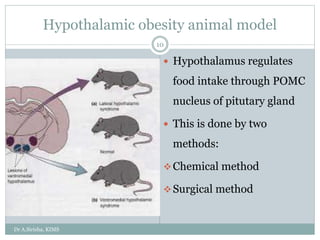
This document discusses animal models used to study obesity. It begins by defining overweight and obesity according to BMI thresholds set by WHO. It then describes the pathophysiology of obesity and various animal models used to study it, including diet-induced, hypothalamic, virus-induced, genetic, transgenic, and in vitro models. Specific details are provided about procedures and parameters examined for several models, such as how diet-induced and hypothalamic models work. Genetic models discussed include yellow mouse, Zucker rat, and transgenic knockout models. In vitro models described aim to study metabolic activity in brown adipose tissue, beta-3 agonism, neuropeptide Y, and the role of leptin.