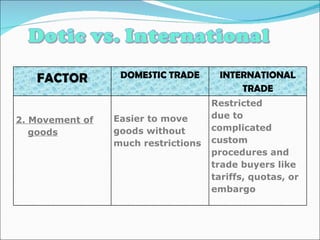
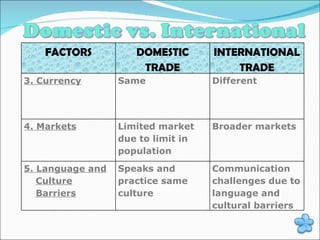
International trade involves the exchange of goods and services between countries. It provides benefits like job creation, increased consumption, and economic growth. However, it also faces problems from trade barriers like tariffs and quotas imposed by governments. International organizations like the World Trade Organization seek to reduce trade barriers and help resolve trade disputes between nations to further global trade.