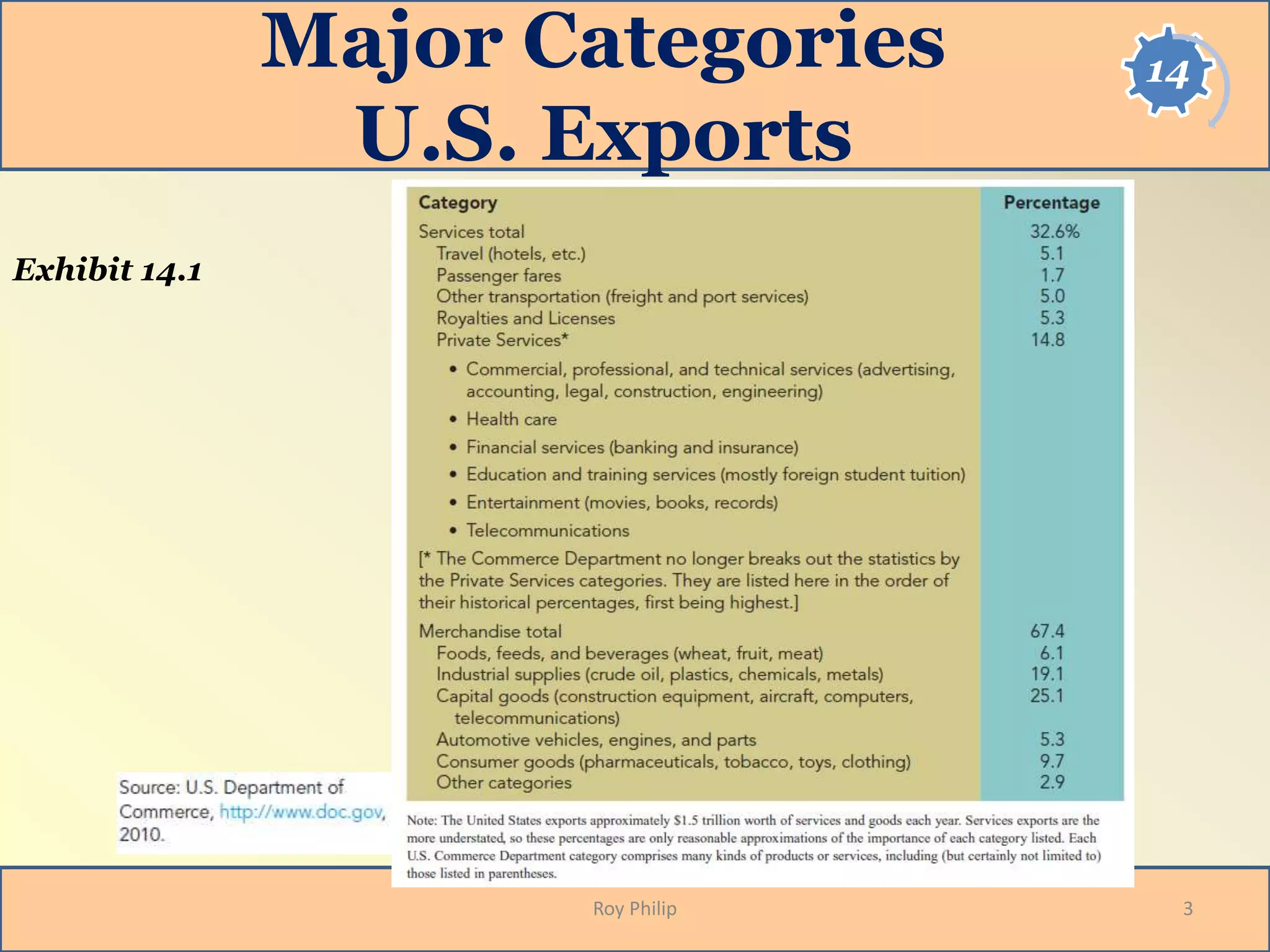
The document explores the complexities of international marketing, emphasizing the differences between industrial and consumer goods, particularly regarding demand volatility and quality standards. ISO 9000 certification is highlighted as a significant quality benchmark that enhances corporate performance and serves as a competitive marketing tool. Additionally, the role of trade shows is stressed as a crucial aspect of business-to-business marketing, facilitating relationships and product demonstrations.