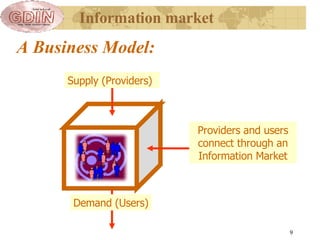
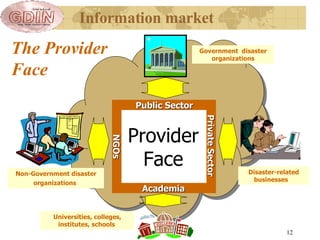
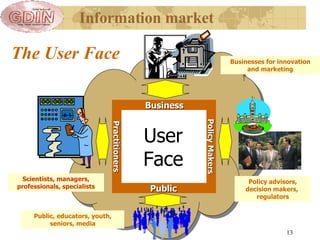
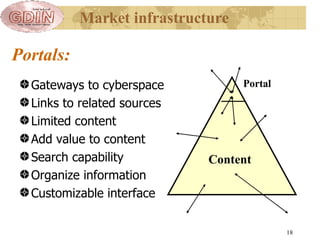
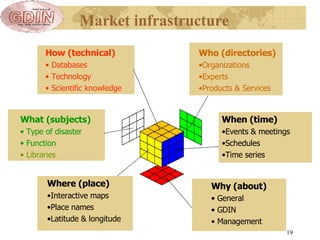
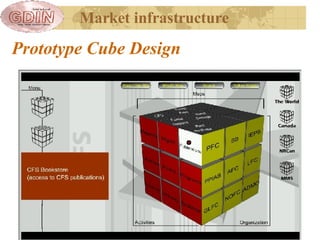
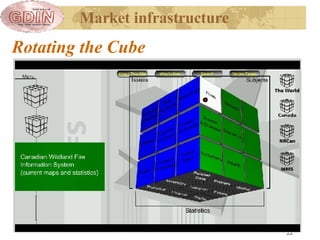
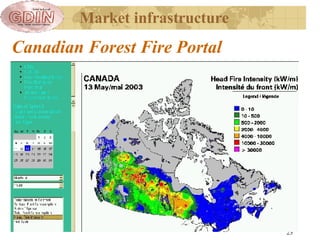
The document proposes the creation of a global disaster information marketplace aimed at improving the accessibility and efficiency of disaster-related information. It outlines the importance of sharing information, addressing barriers such as fragmentation and lack of integration, and suggests an infrastructure that includes various information exchange mechanisms. The proposal emphasizes the need for collaborative efforts among diverse stakeholders, including governments, NGOs, and academic institutions, to enhance disaster response and preparedness.