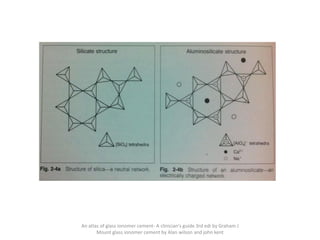
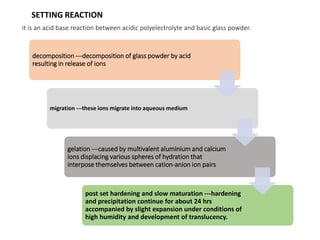
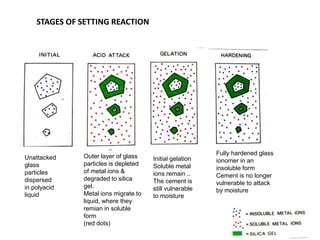
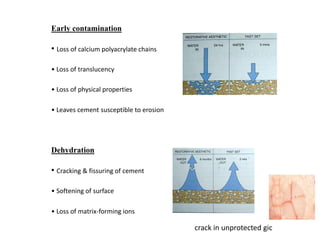
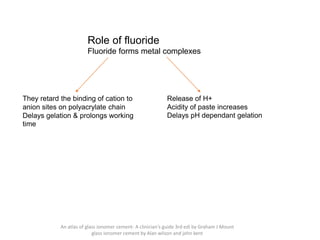
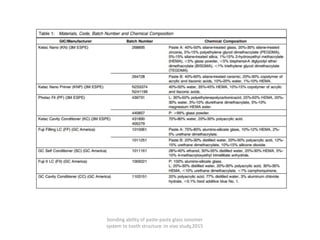
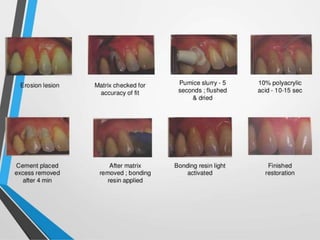
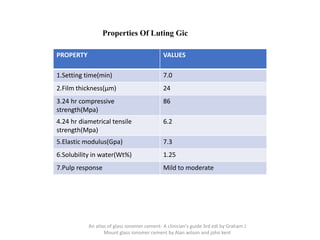
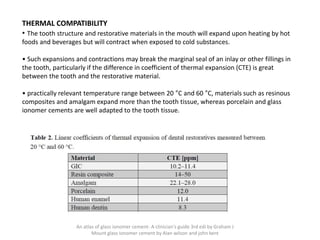
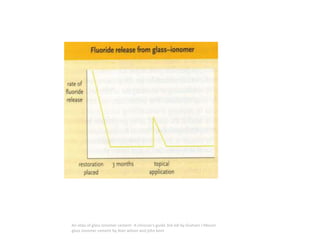
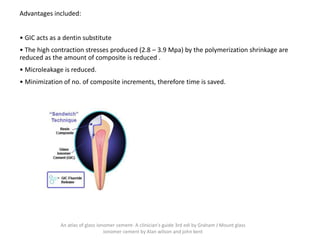
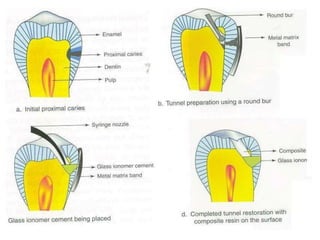
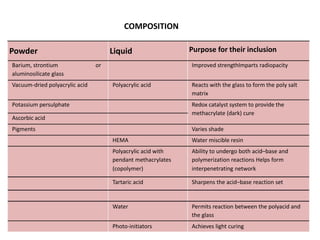
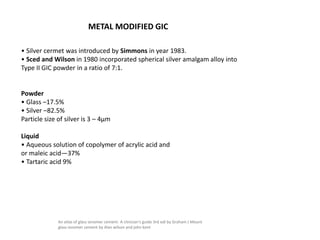
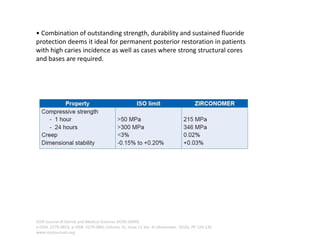
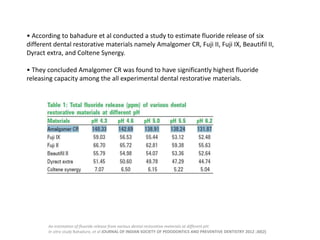
Glass ionomer cement is a dental restorative material that sets via an acid-base reaction between a basic glass powder and an acidic polymer liquid. It was invented in 1969 and first reported in 1971 as a tooth-colored alternative to amalgam. Glass ionomer cement adheres well to tooth structure and releases fluoride to help prevent decay. It is used for applications such as luting, lining, filling cavities, and sealing fissures. The material consists of a calcium aluminofluorosilicate glass powder and an aqueous solution of polyacrylic acid or other polymers. When mixed, an acid-base reaction occurs where ions are extracted from the glass and migrate into the liquid phase to precipitate as polyan