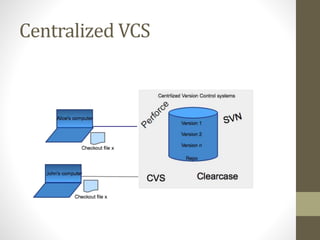
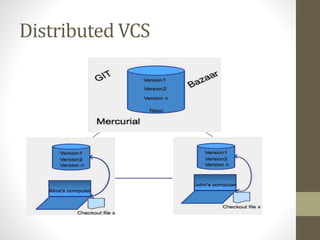
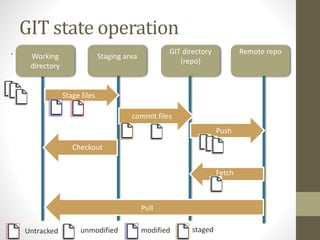
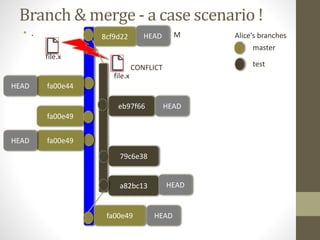
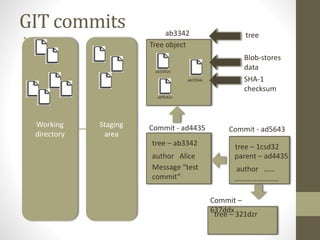
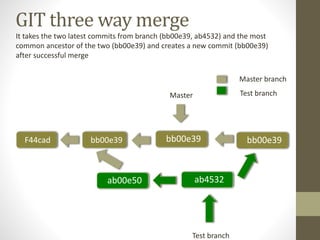
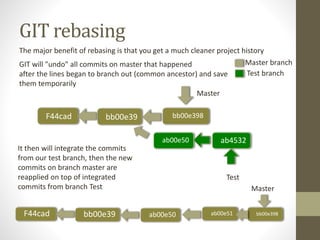
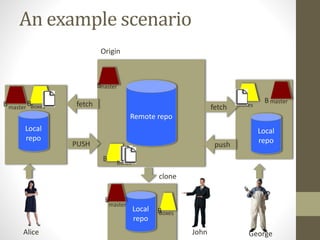
GIT is a free and open source distributed version control system that allows developers to work collaboratively without needing centralized connectivity. It provides powerful branching capabilities that allow creating branches cheaply and merging them easily. Common GIT commands include init, clone, status, add, commit, log, remote, fetch, push, and pull. An example scenario demonstrates how multiple developers can clone a remote repository, make changes on their local repos, fetch and push changes between local and remote repos, and merge branches.