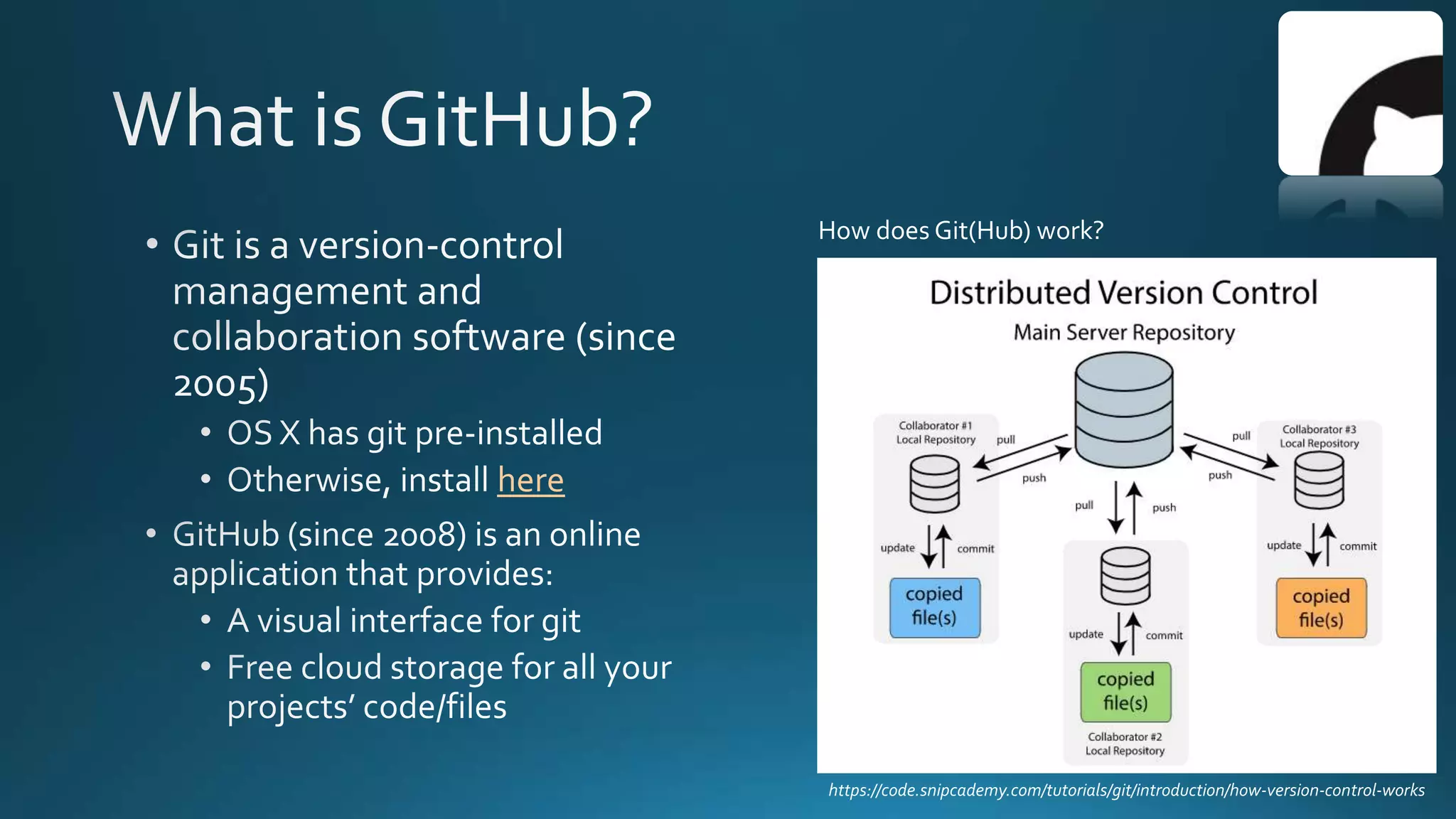
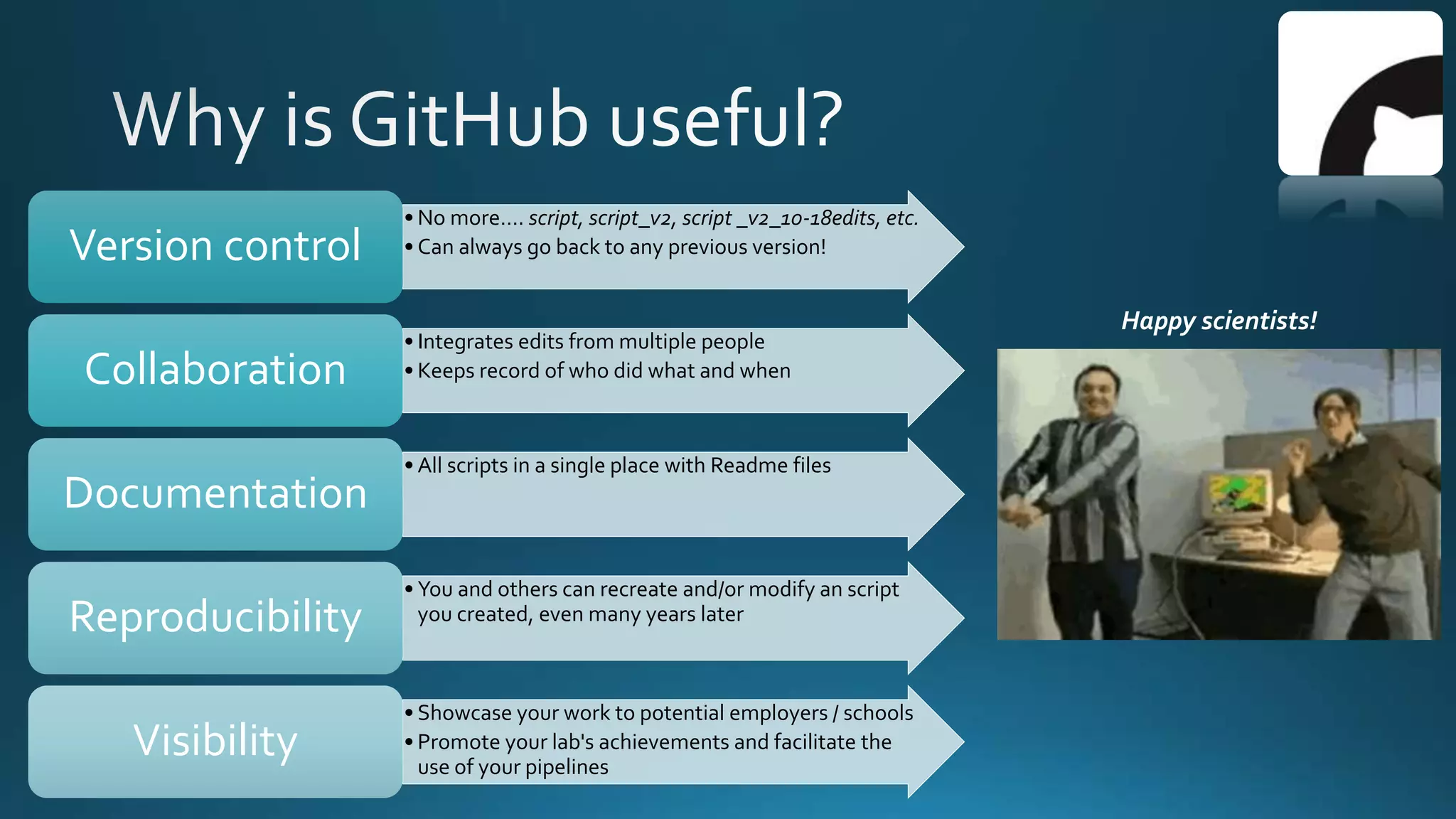
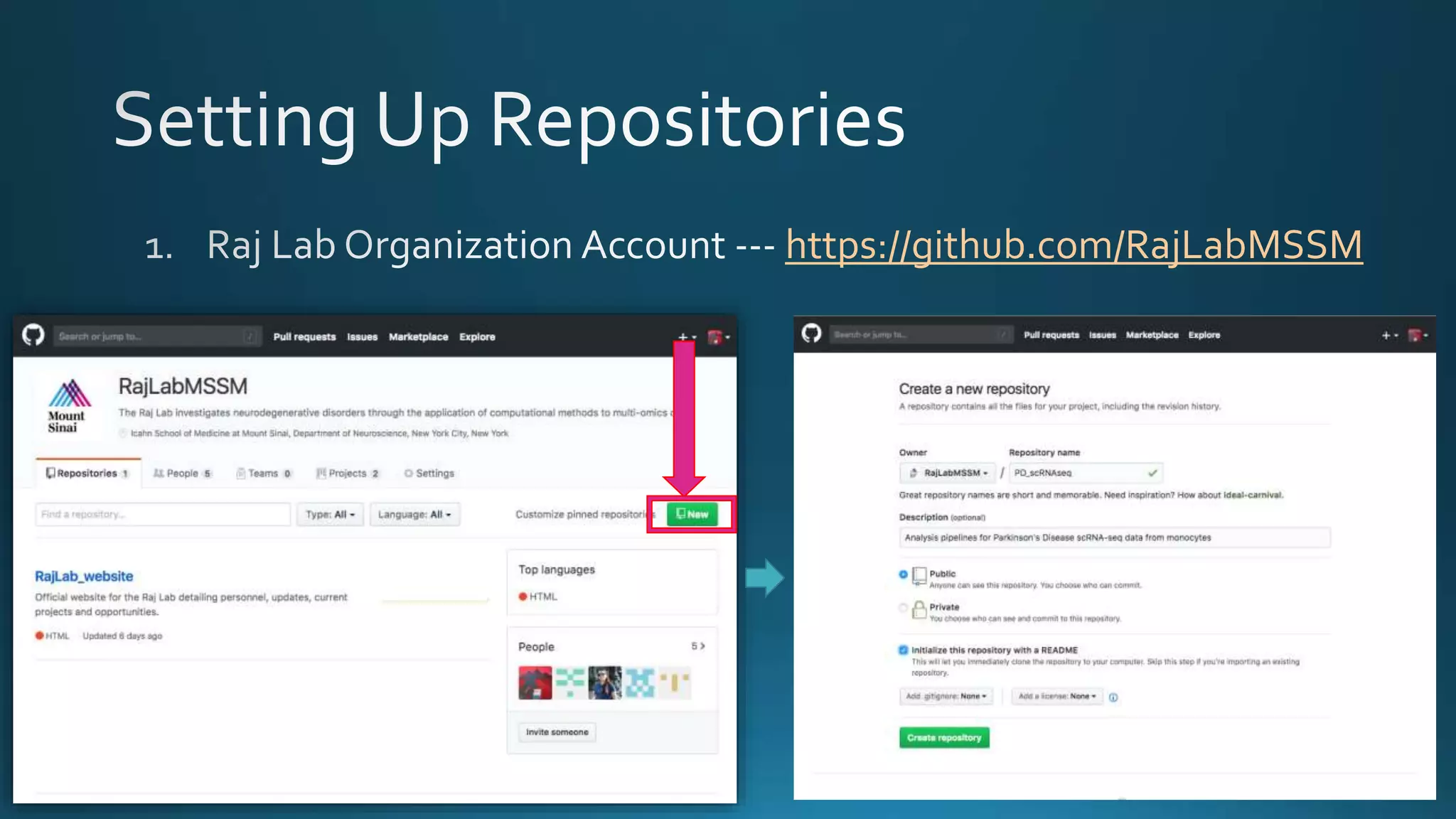
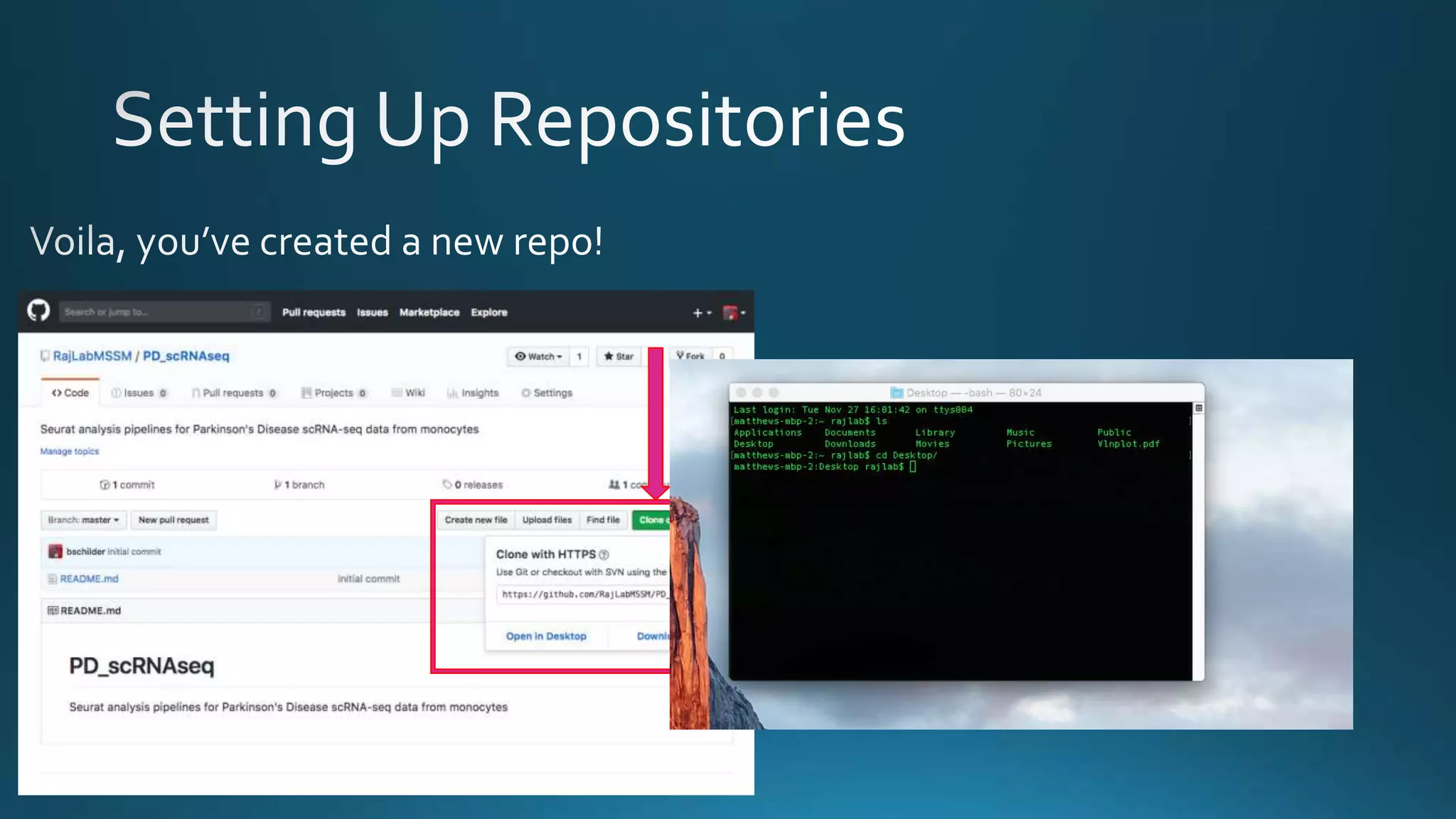
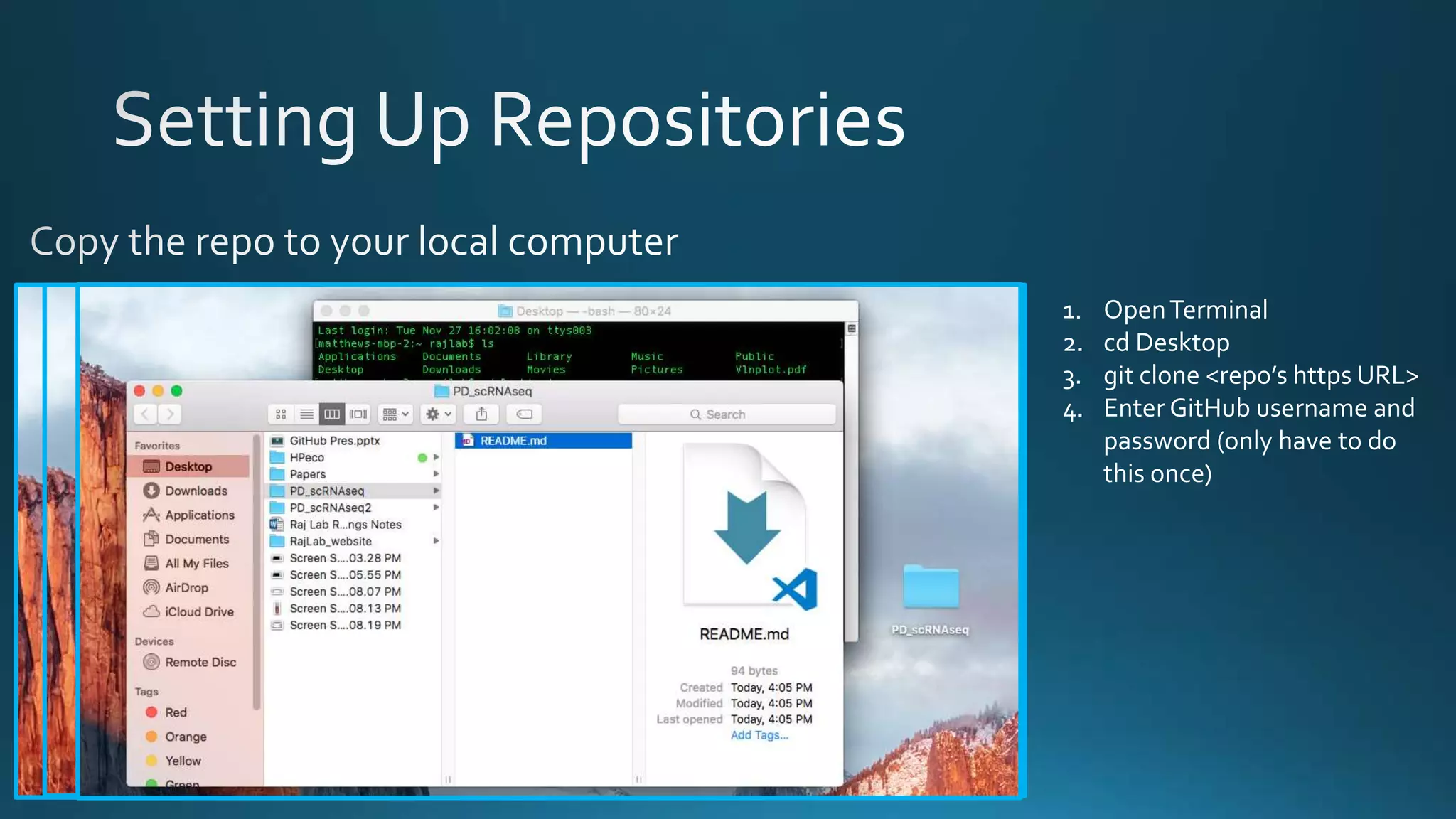
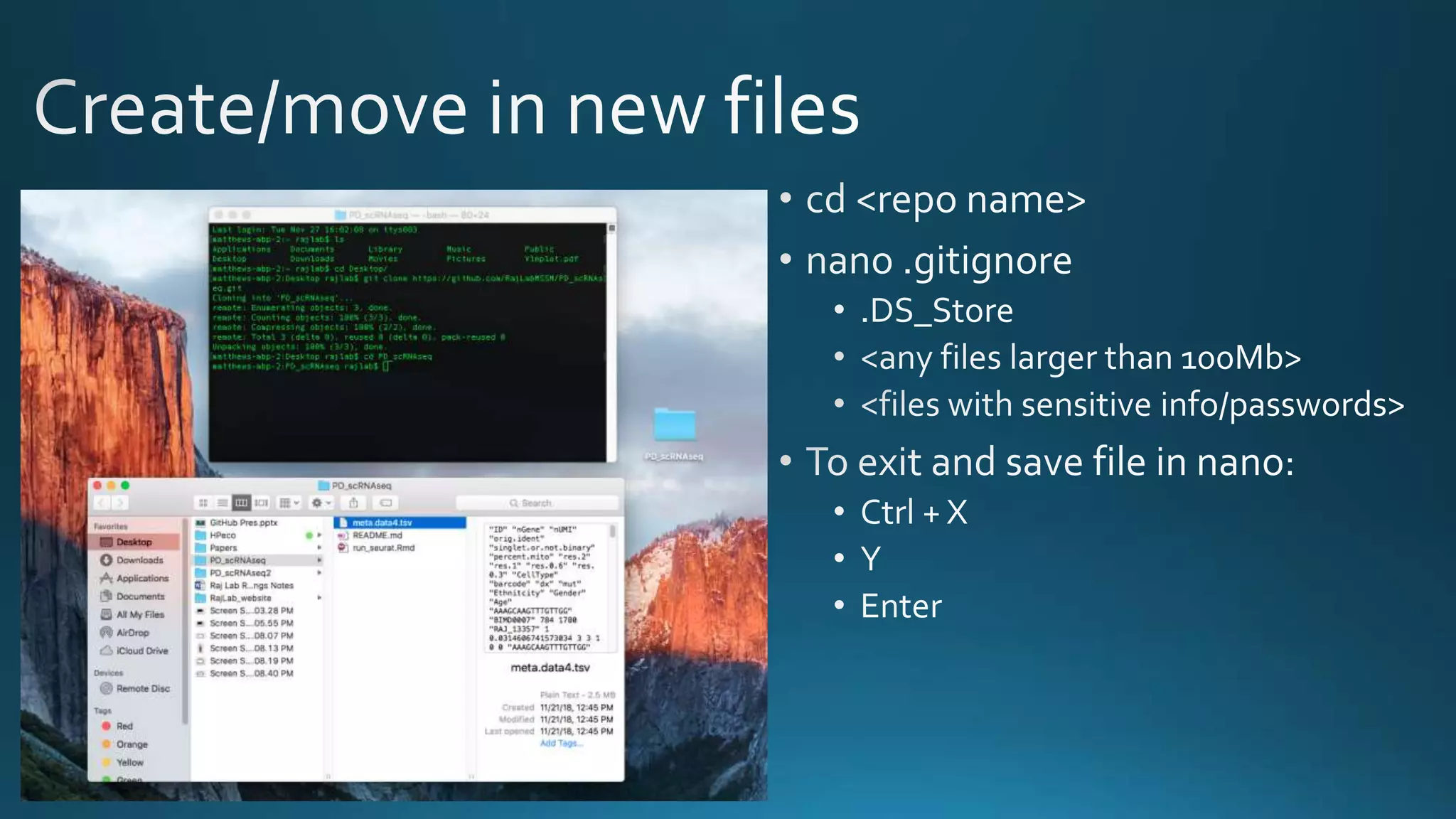
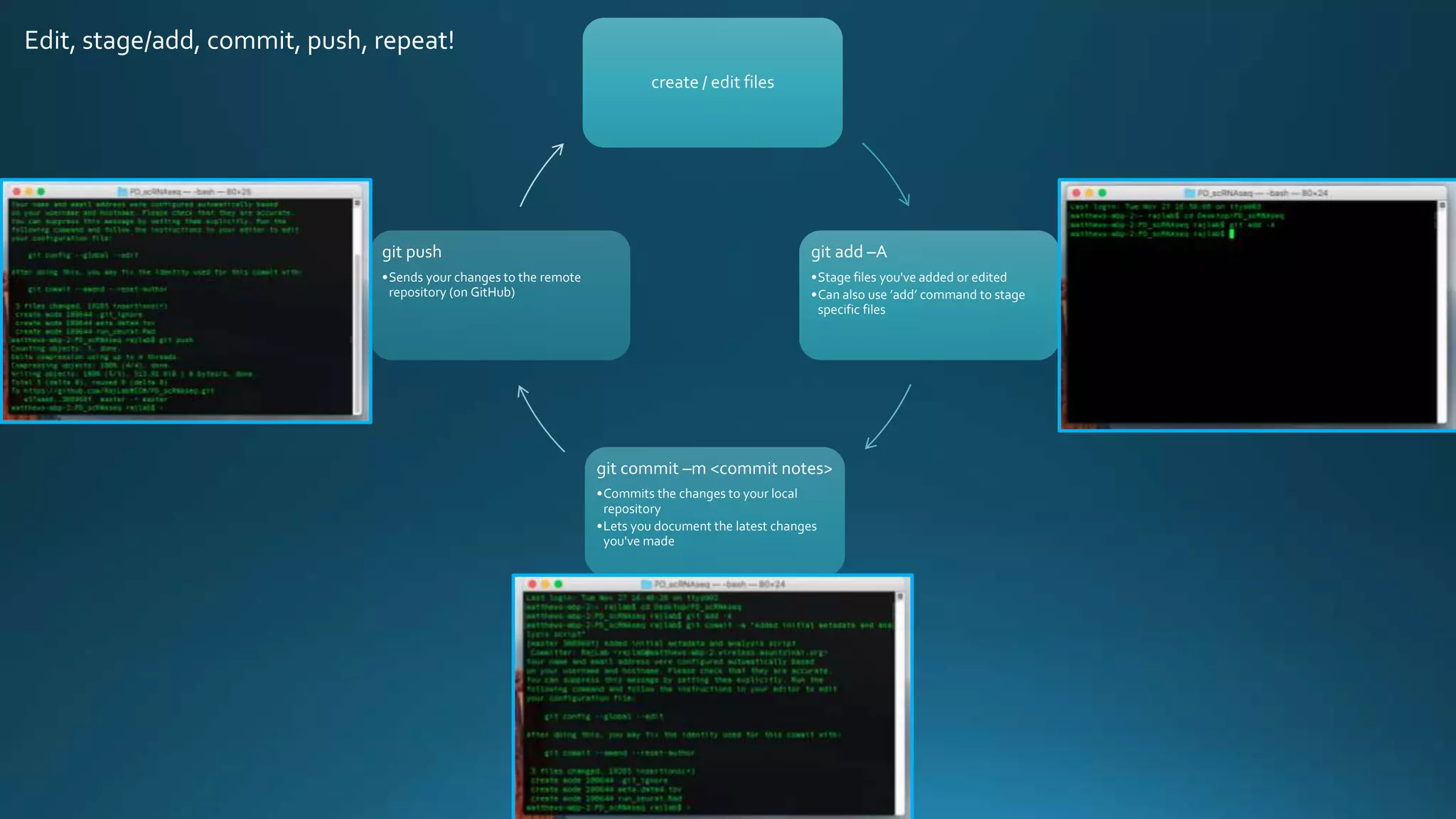
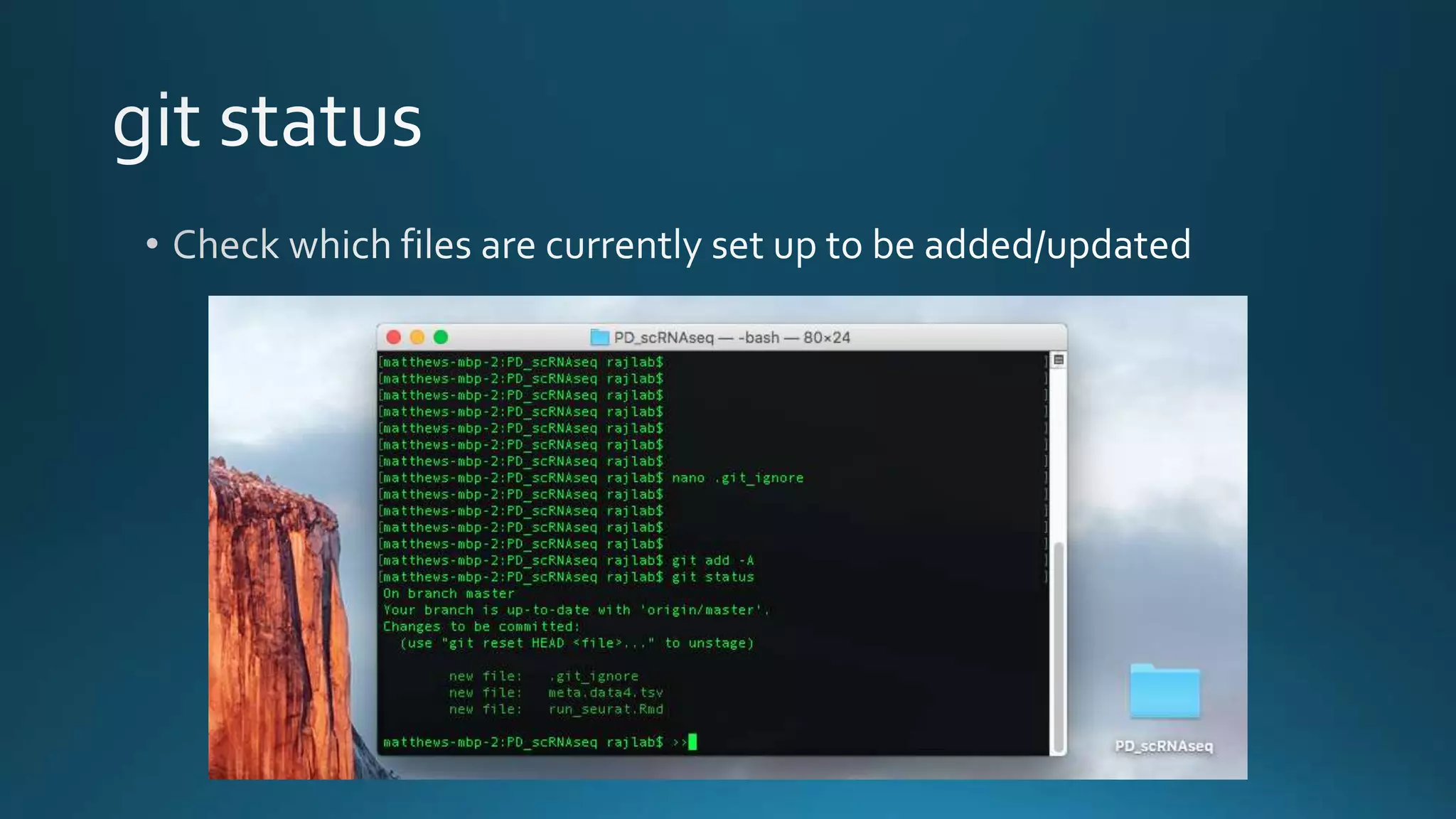
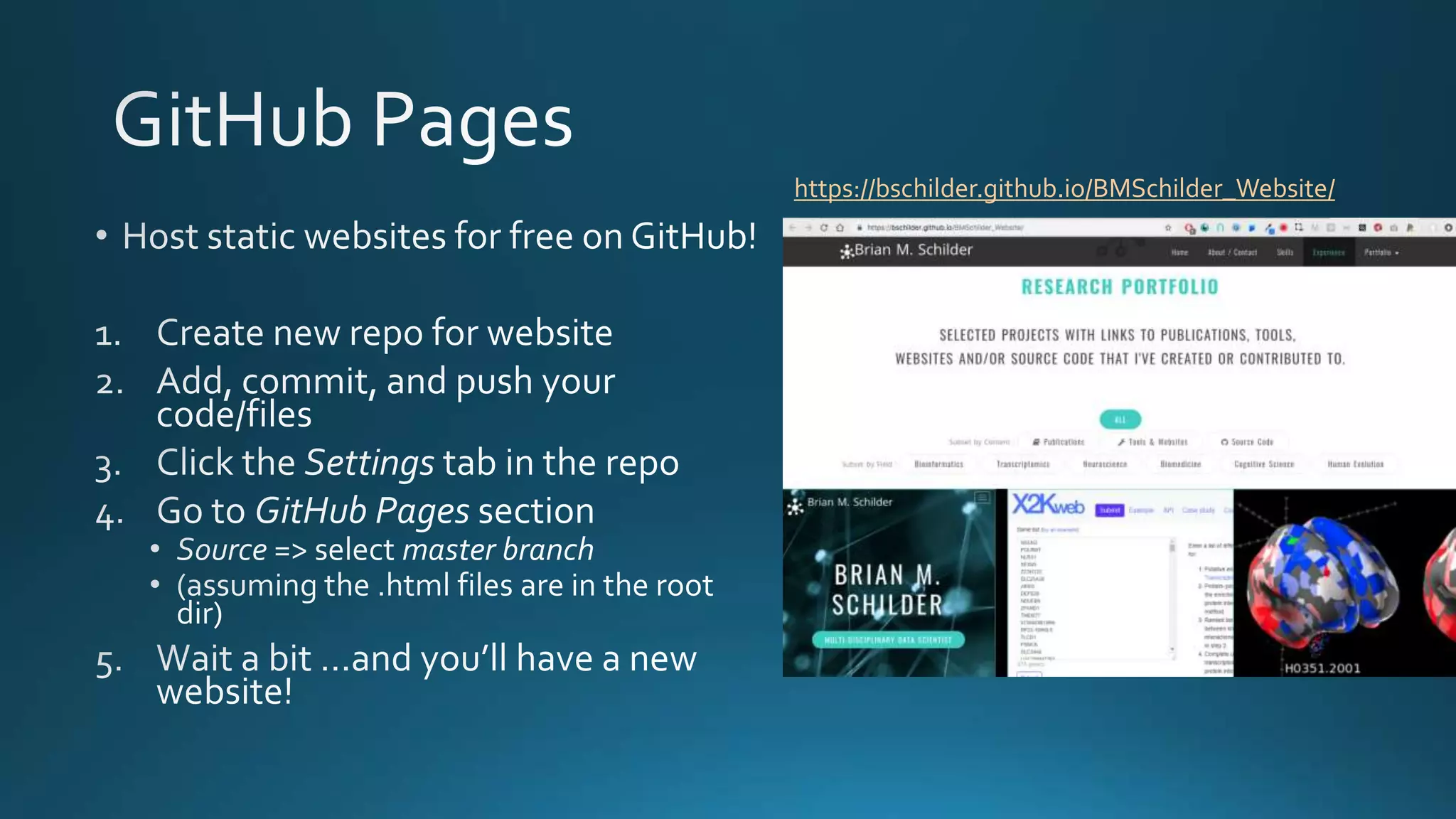
The document explains how Git and GitHub facilitate version control, allowing users to track changes, collaborate on projects, and maintain a history of edits. It highlights key operations such as cloning repositories, staging changes, committing, and pushing updates, along with managing branches for testing new code. The benefits of using GitHub include reproducibility of work, visibility of projects, and improved documentation.