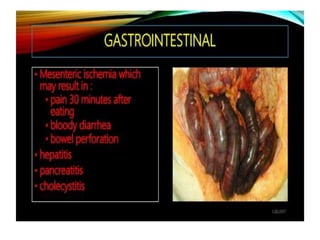
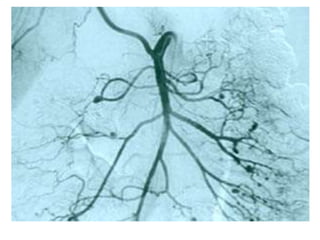
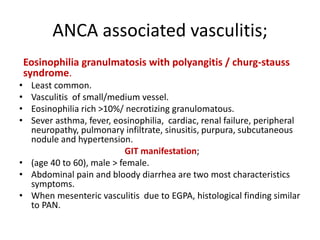
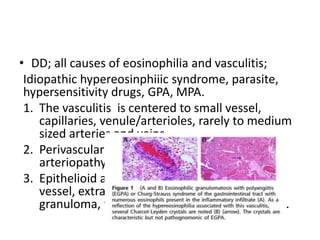
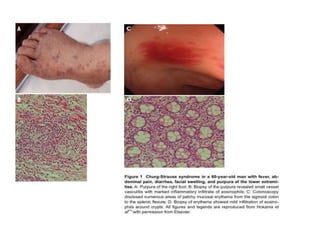
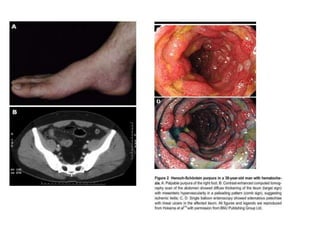
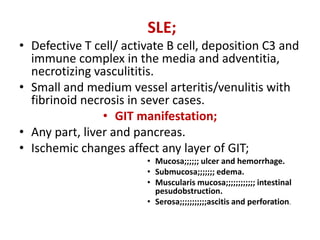
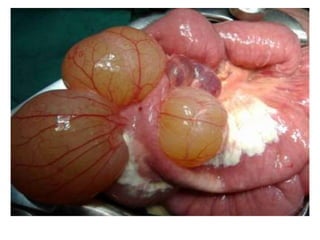
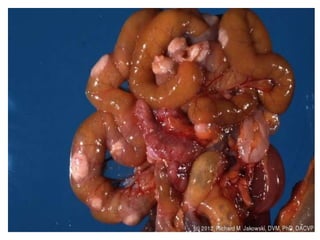
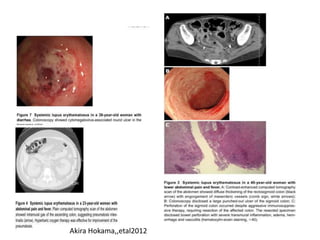
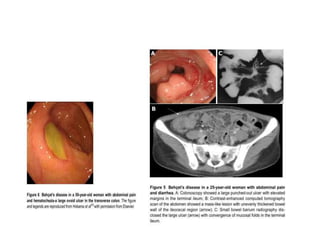
This document discusses gastrointestinal (GIT) vasculitis. It begins by noting that GIT vasculitis can affect blood vessels of all sizes and cause local or diffuse pathological changes in the GIT. Clinical features include ulcers, edema, hemorrhage, bowel ischemia, and perforation. The document then discusses various types of vasculitis that can involve the GIT, including large vessel vasculitis like Takayasu arteritis, medium vessel vasculitis like polyarteritis nodosa, and small vessel vasculitis like ANCA-associated vasculitis. Specific GIT manifestations of different types of vasculitis are described. The document emphasizes that diagnosis requires clinical suspicion along with radiological and histological confirmation via endoscopy