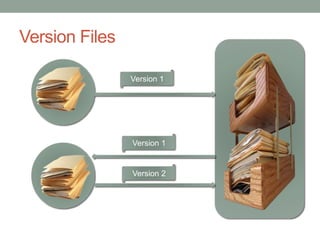
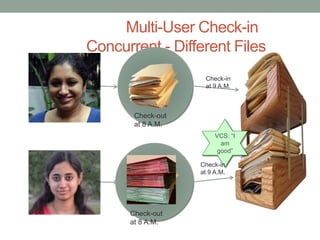
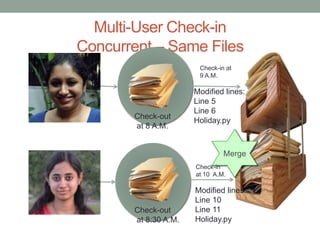
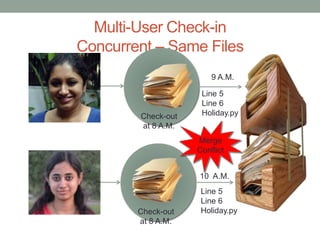
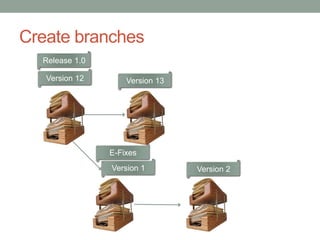
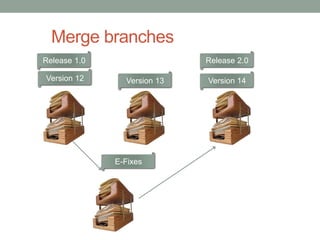
This document discusses version control and Git. It defines key terms like VCS, check-in, check-out and commit. It explains how version control allows versioning of files, manages changes from multiple users by storing files in a central repository. It describes how Git is different from other VCSs in that the repository is seen as a whole rather than individual files, branches are versions of the repository rather than copies, and the entire repository can be accessed locally. It also covers the basic Git commands and workflows for working with files, branches and remote repositories.