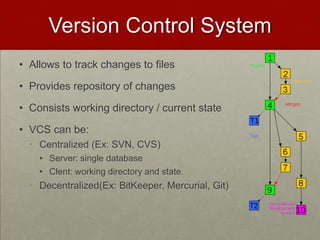
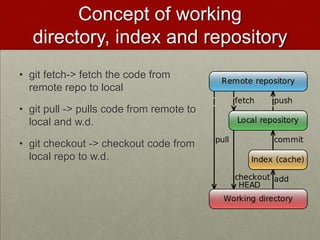
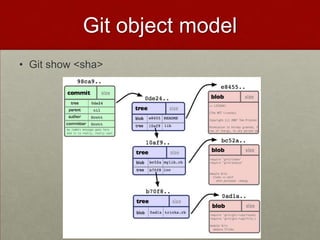
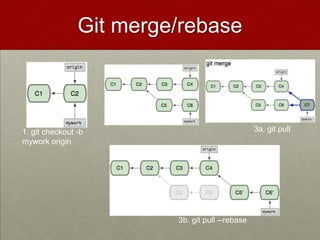
Git is a free and open-source distributed version control system that allows users to track changes in files and facilitates collaboration across projects of all sizes. Key features include a complete history, disconnected operation, and efficiency in handling small to large projects. The document also covers basic commands, the git object model, and comparisons with other version control systems like SVN.