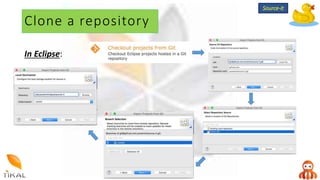
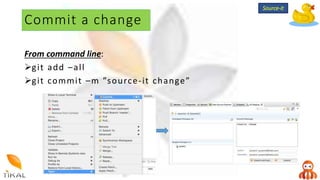
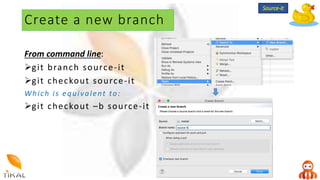
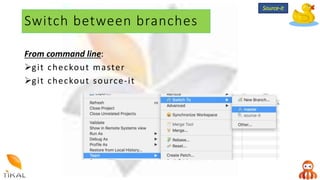
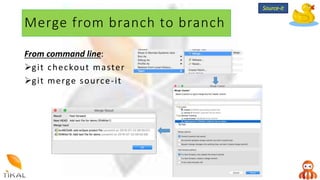
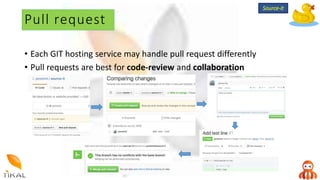
Version control allows collaboration by tracking changes to documents and files. GIT is a free distributed version control system that stores a complete history of changes to files. Basic GIT workflows include cloning a repository, committing local changes, creating and switching between branches, merging changes between branches, and creating pull requests for code review.