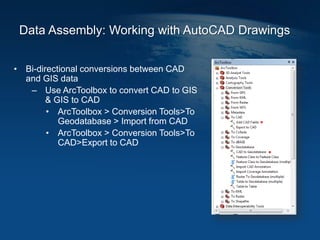
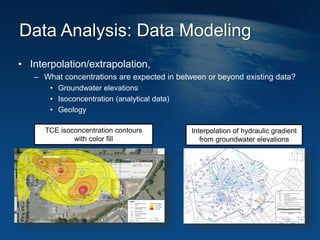
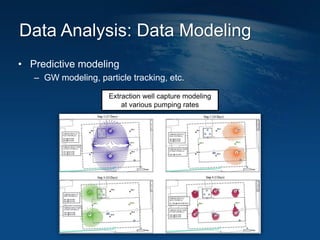
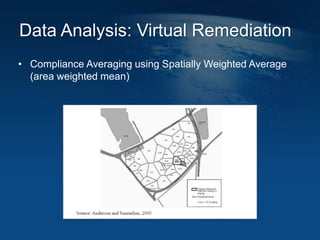
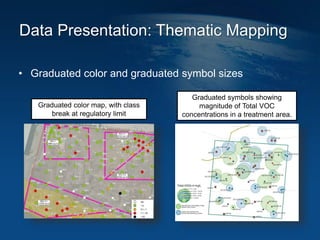
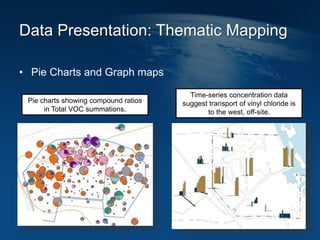
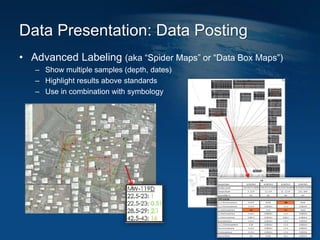
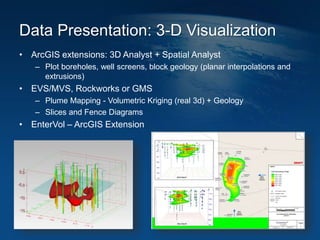
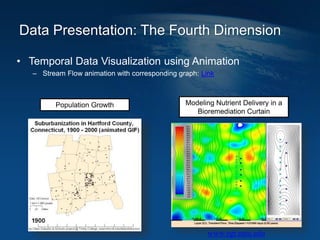
This document discusses how geographic information systems (GIS) can be used to support site remediation projects (SRP). It describes a three step iterative process for GIS analysis: 1) data assembly, 2) data analysis, and 3) data presentation. For data assembly, GIS is used to organize disparate data sources by relating data to geographic coordinates. For data analysis, GIS enables simple observations and modeling to build an understanding of site conditions. For data presentation, GIS creates maps, graphs and other visualizations to communicate spatial relationships and trends in the data. The document provides examples of how GIS can be applied throughout the different phases of an SRP.