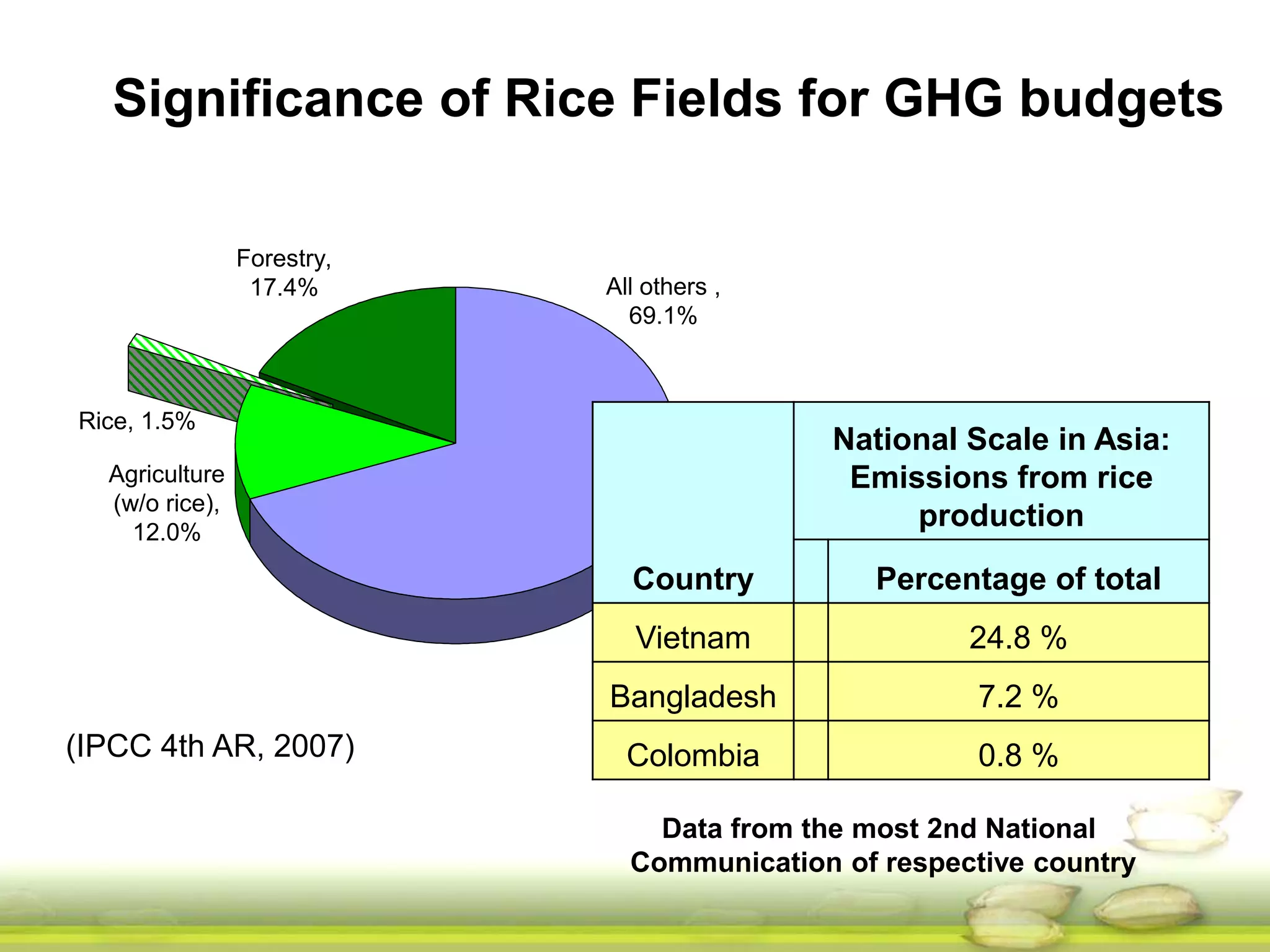
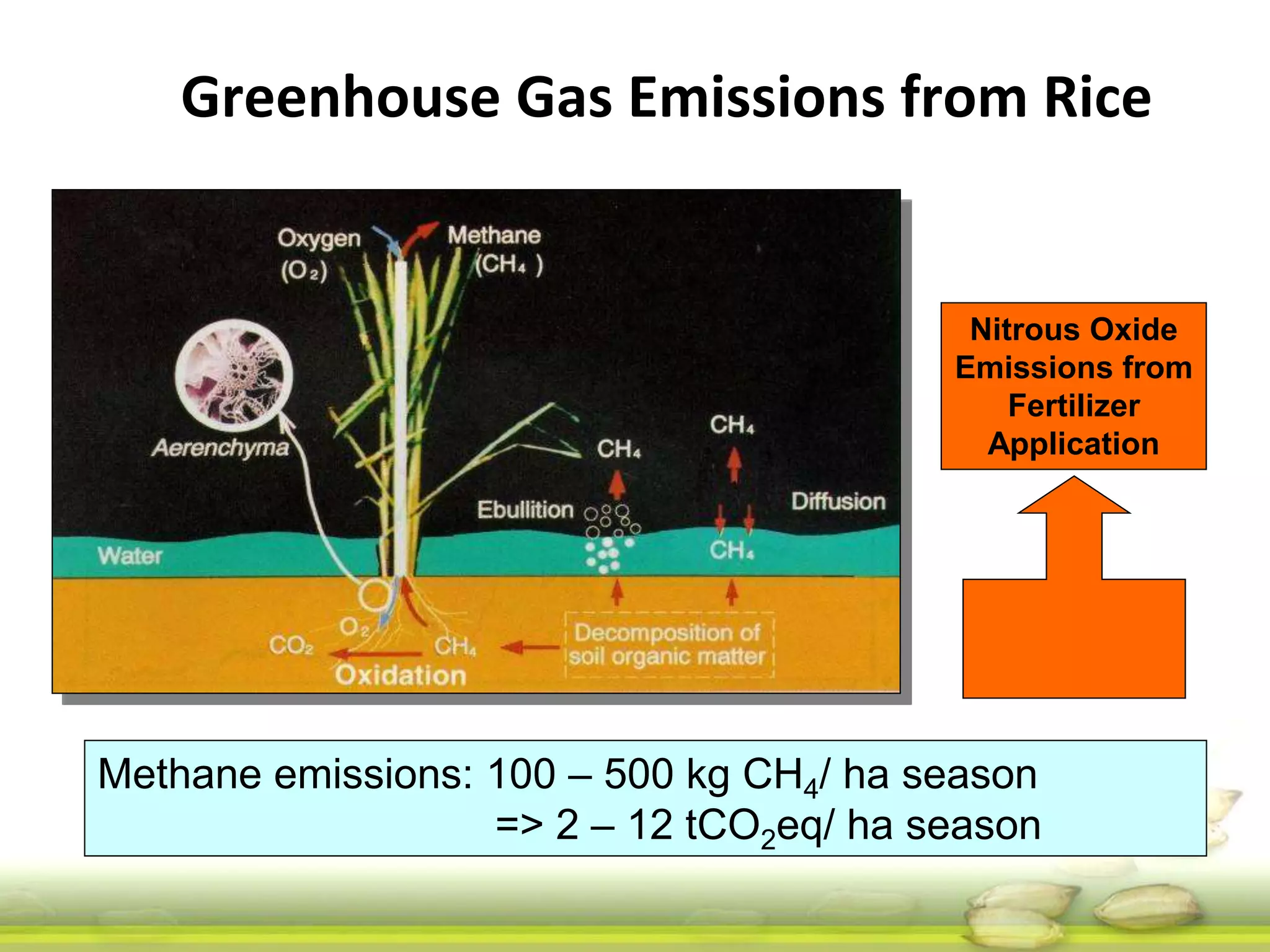
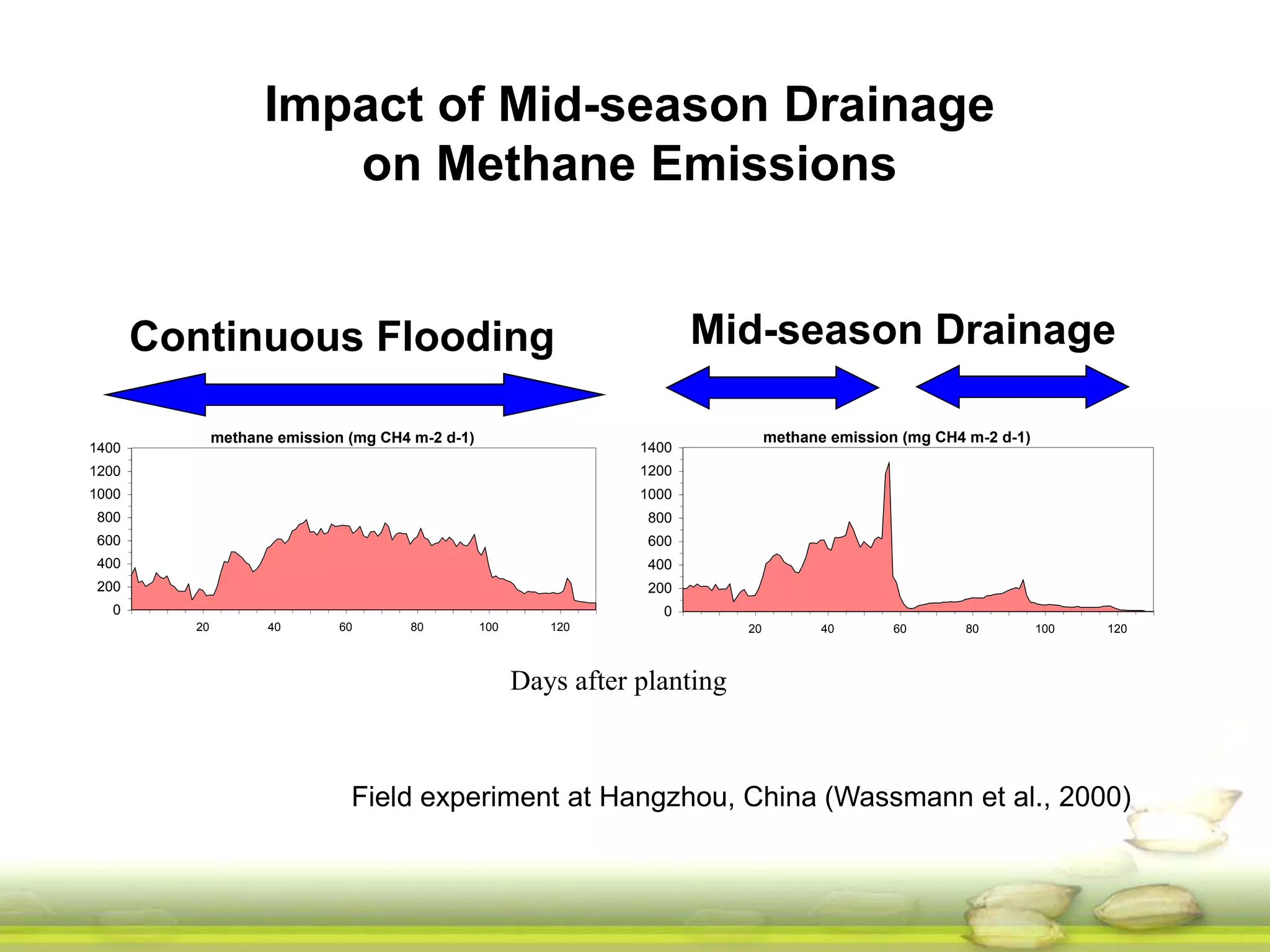
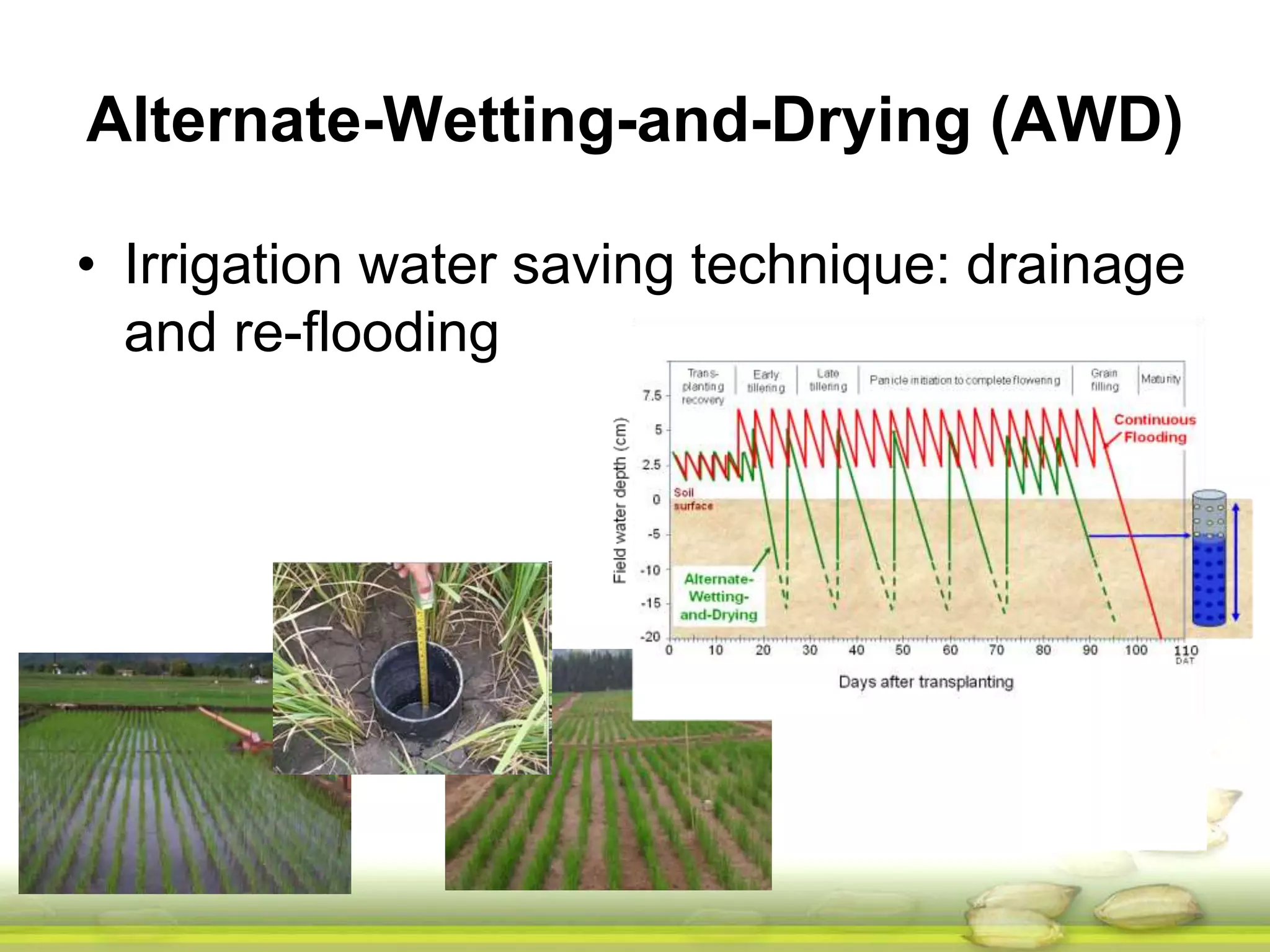
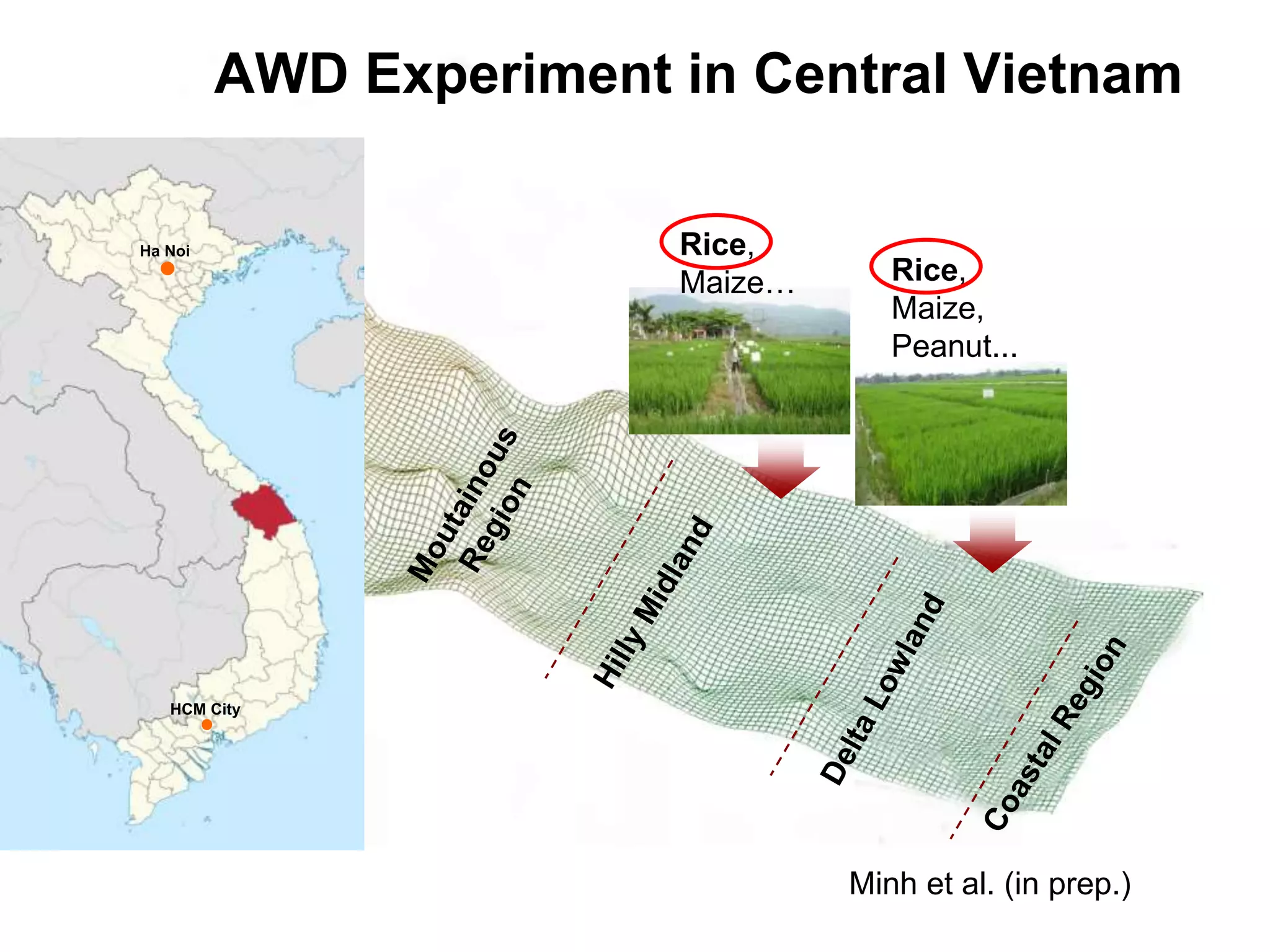
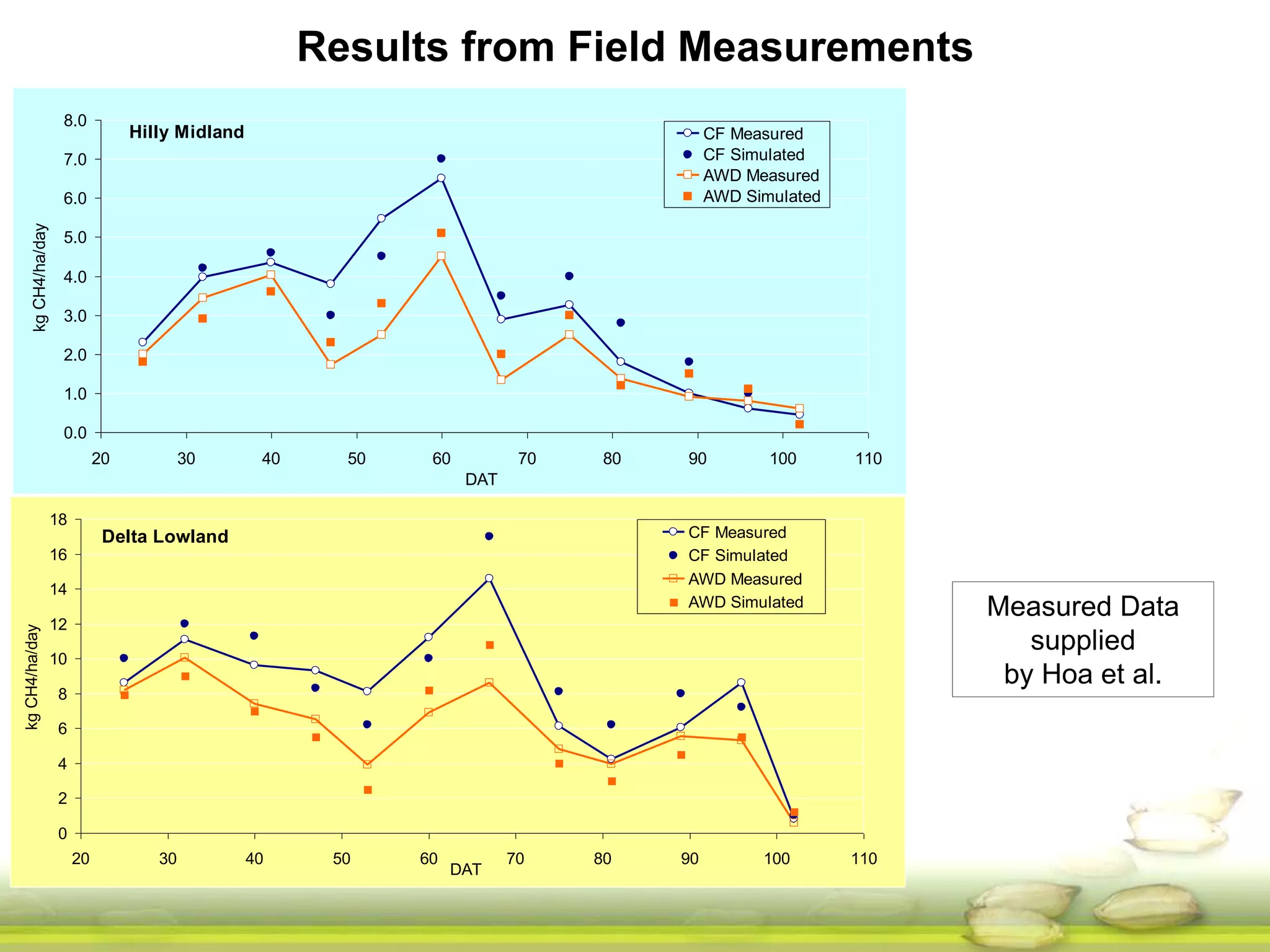
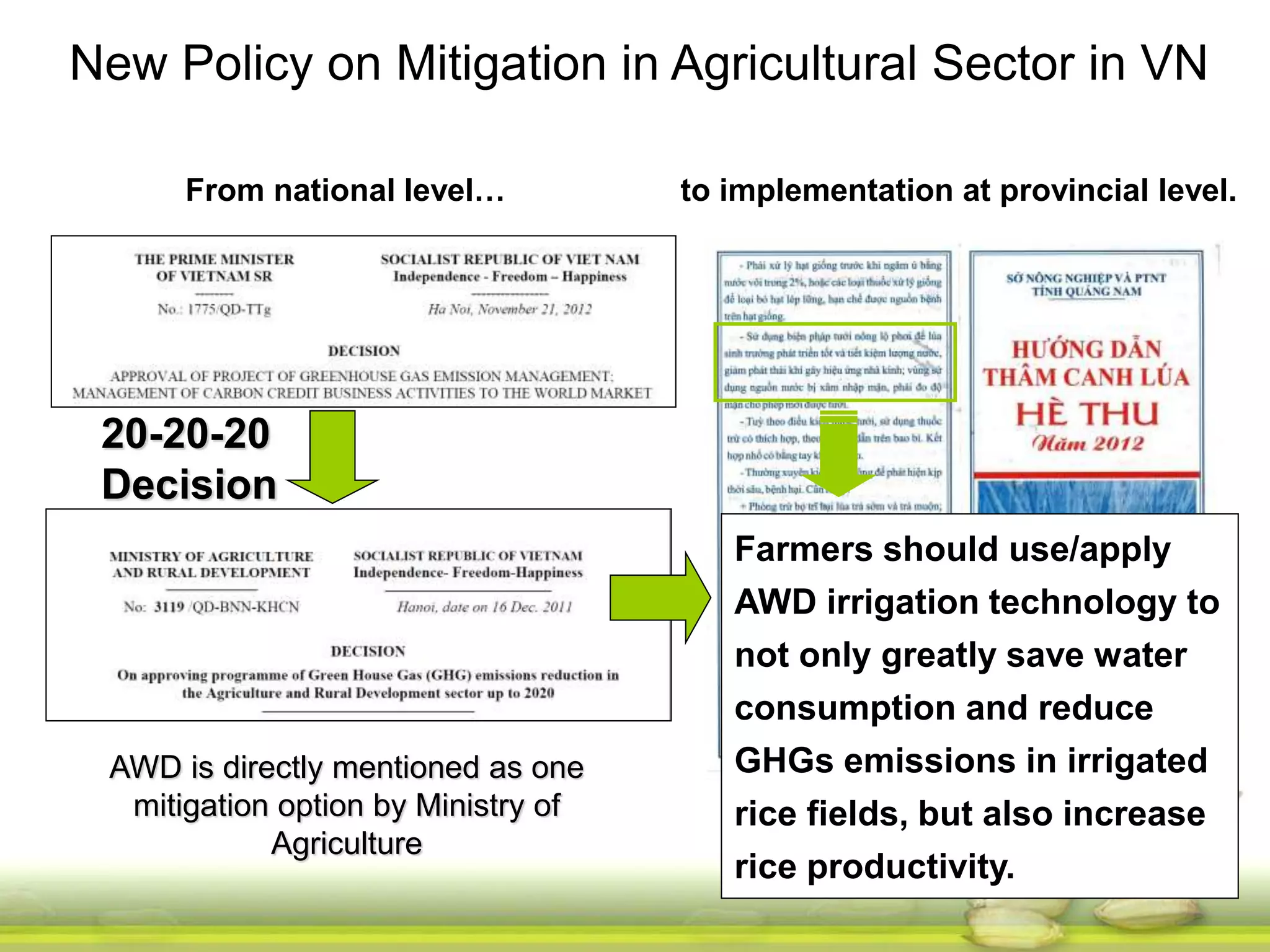
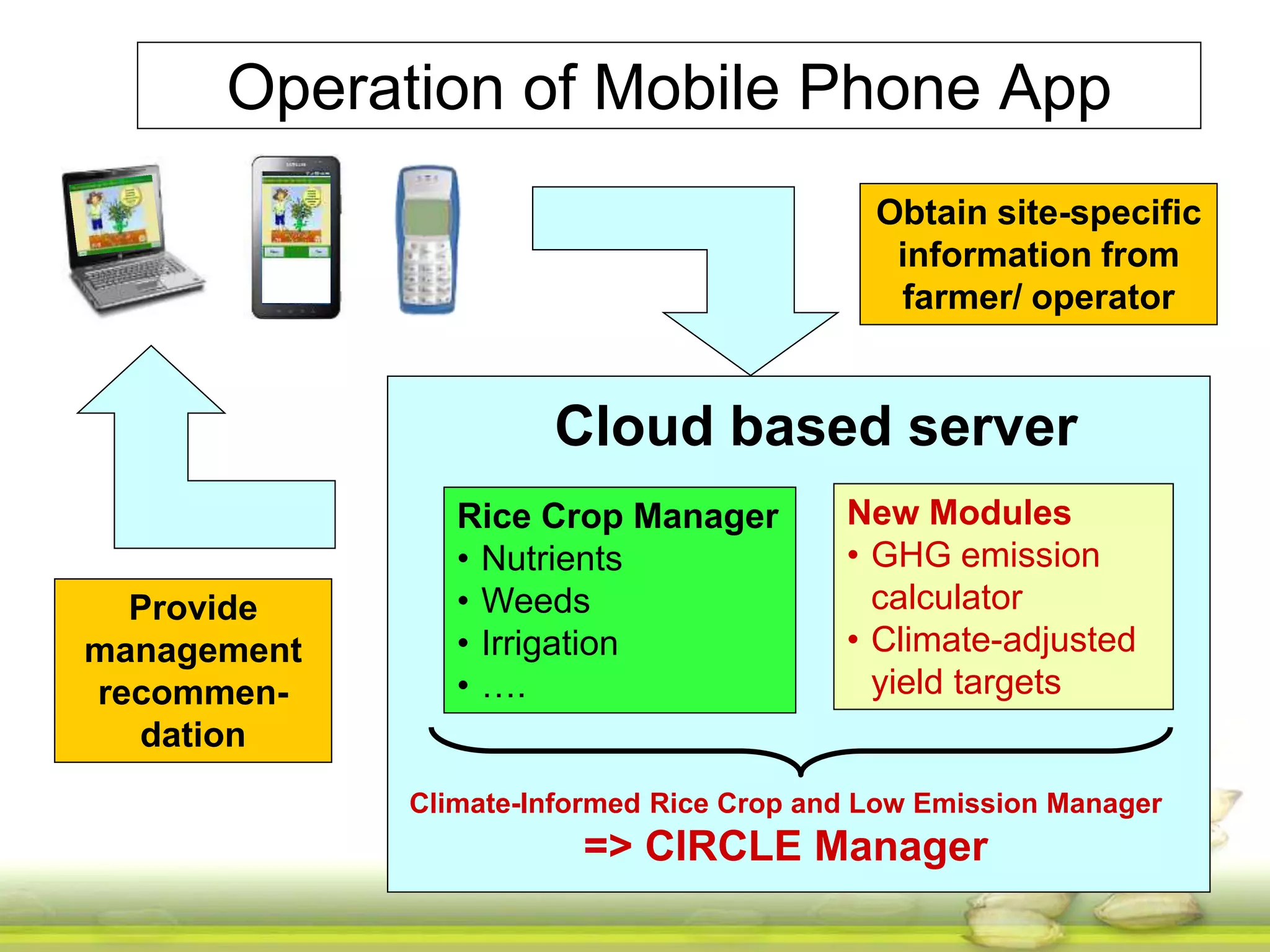
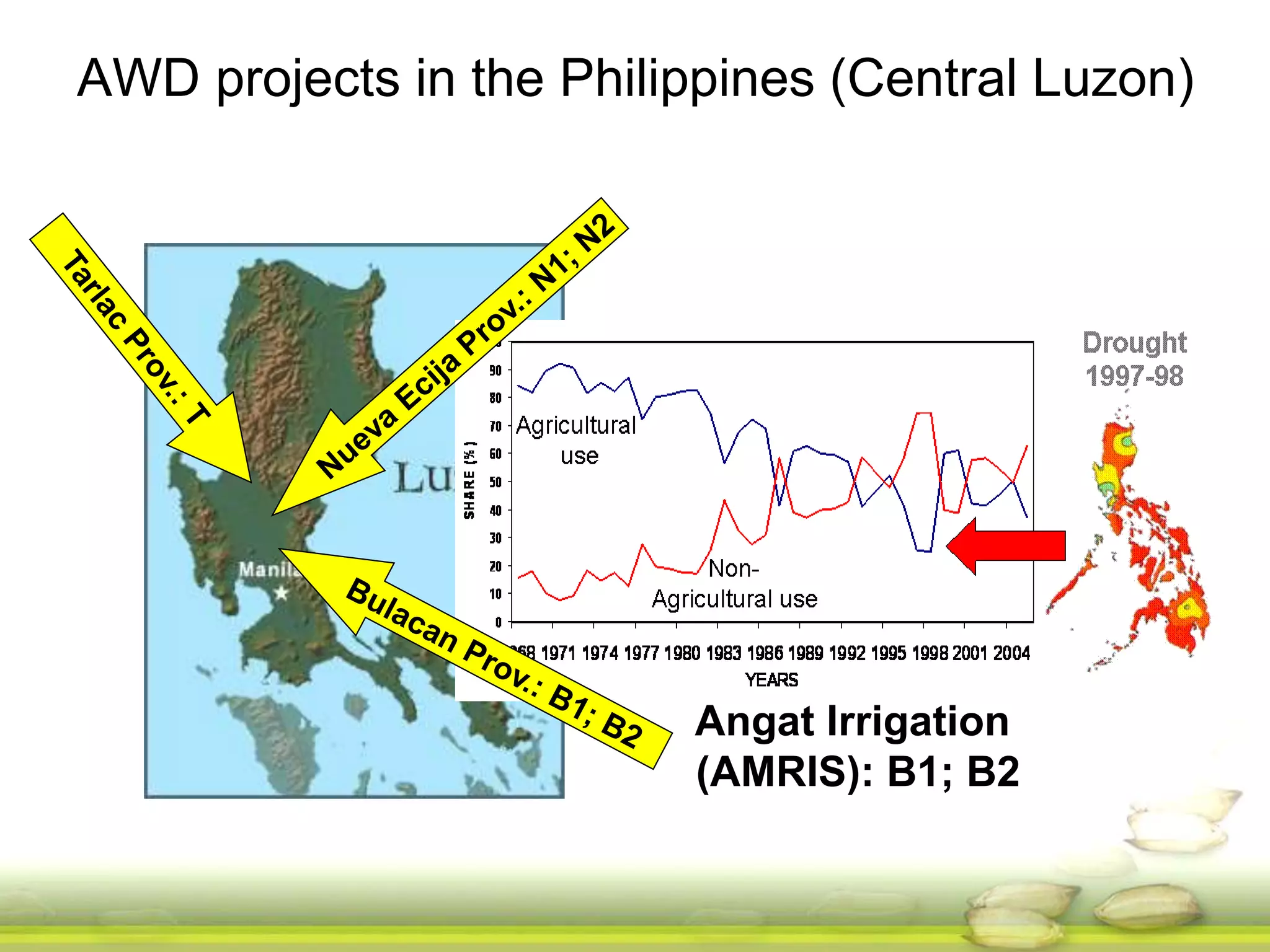
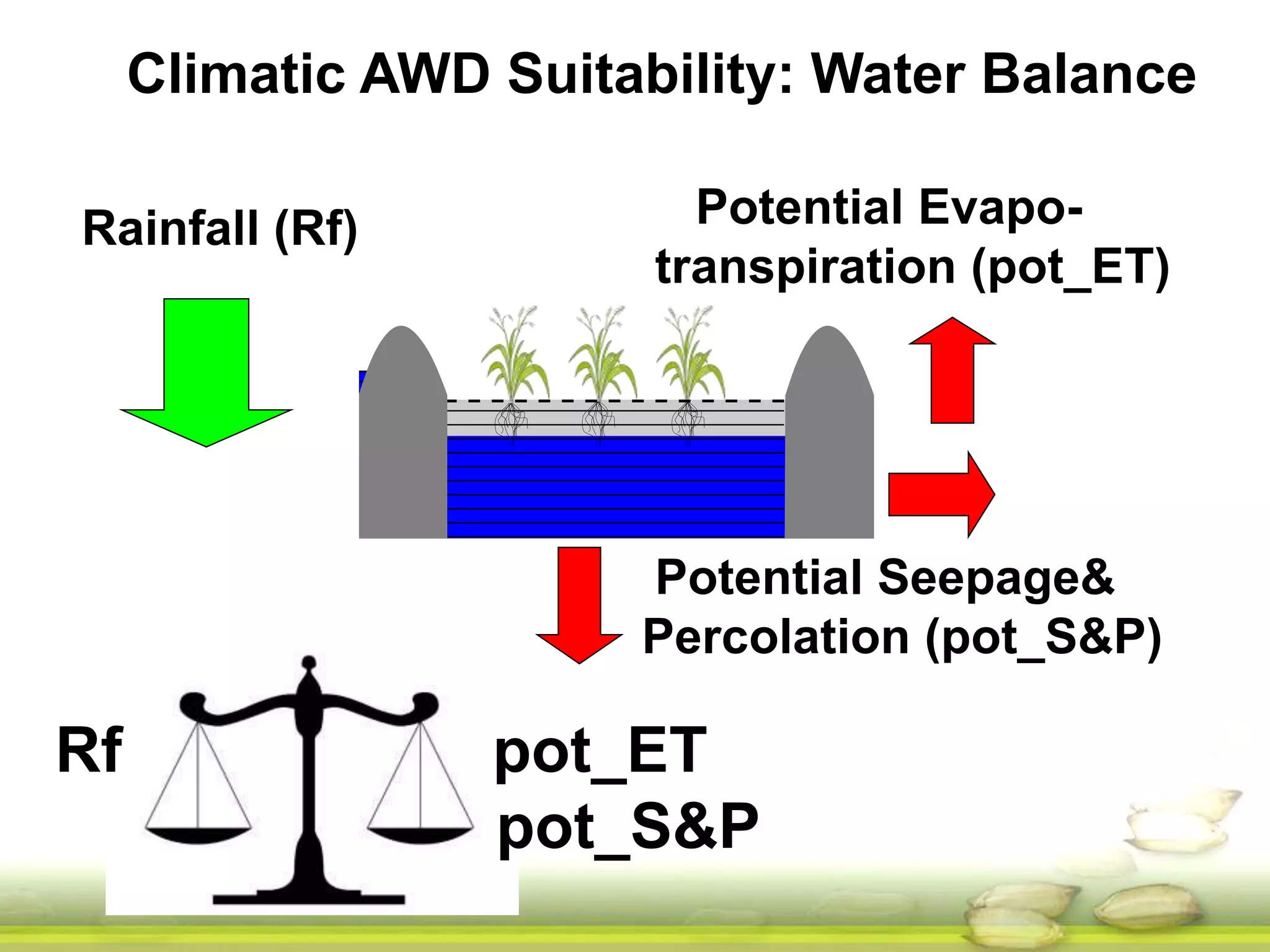
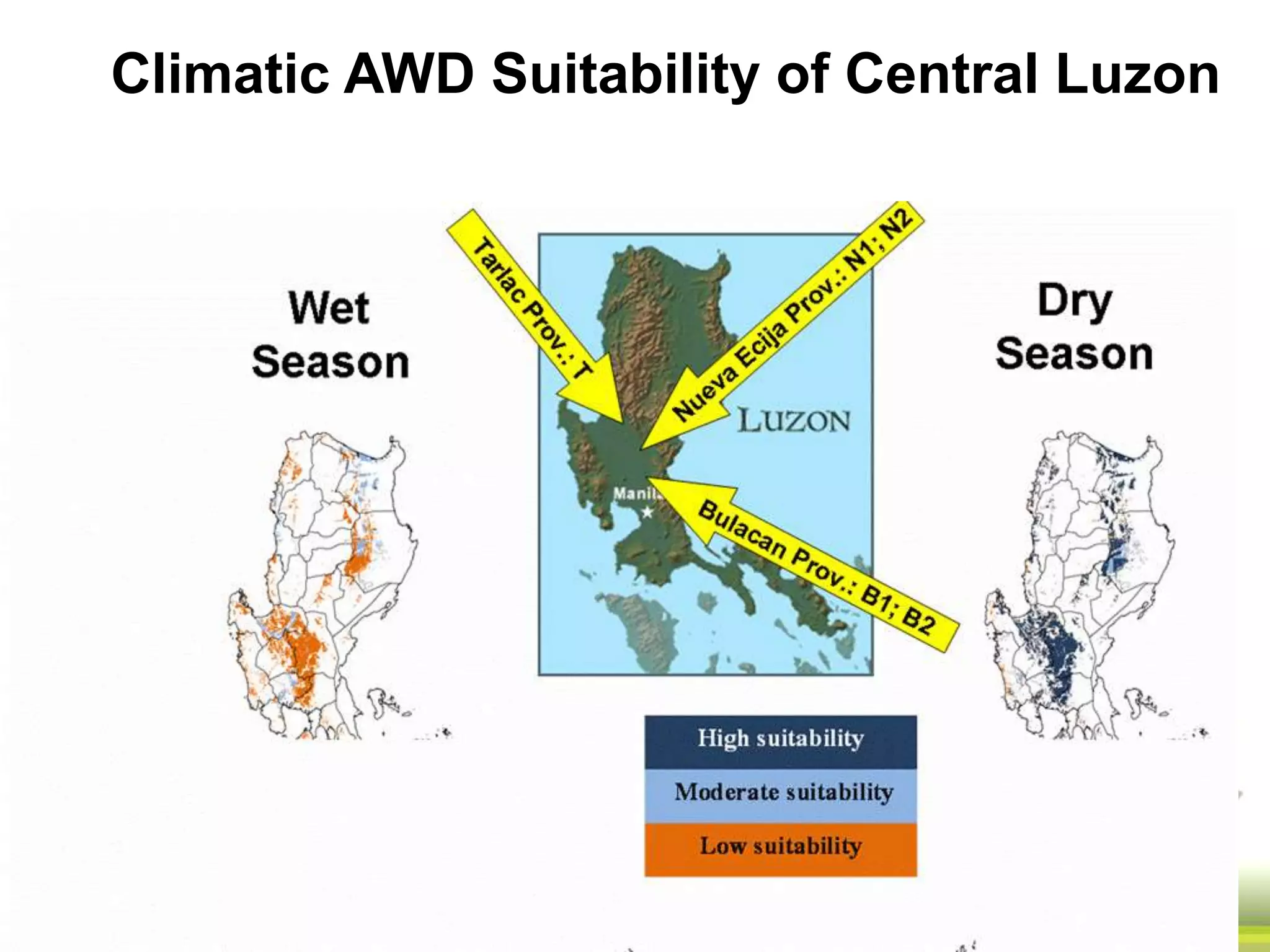
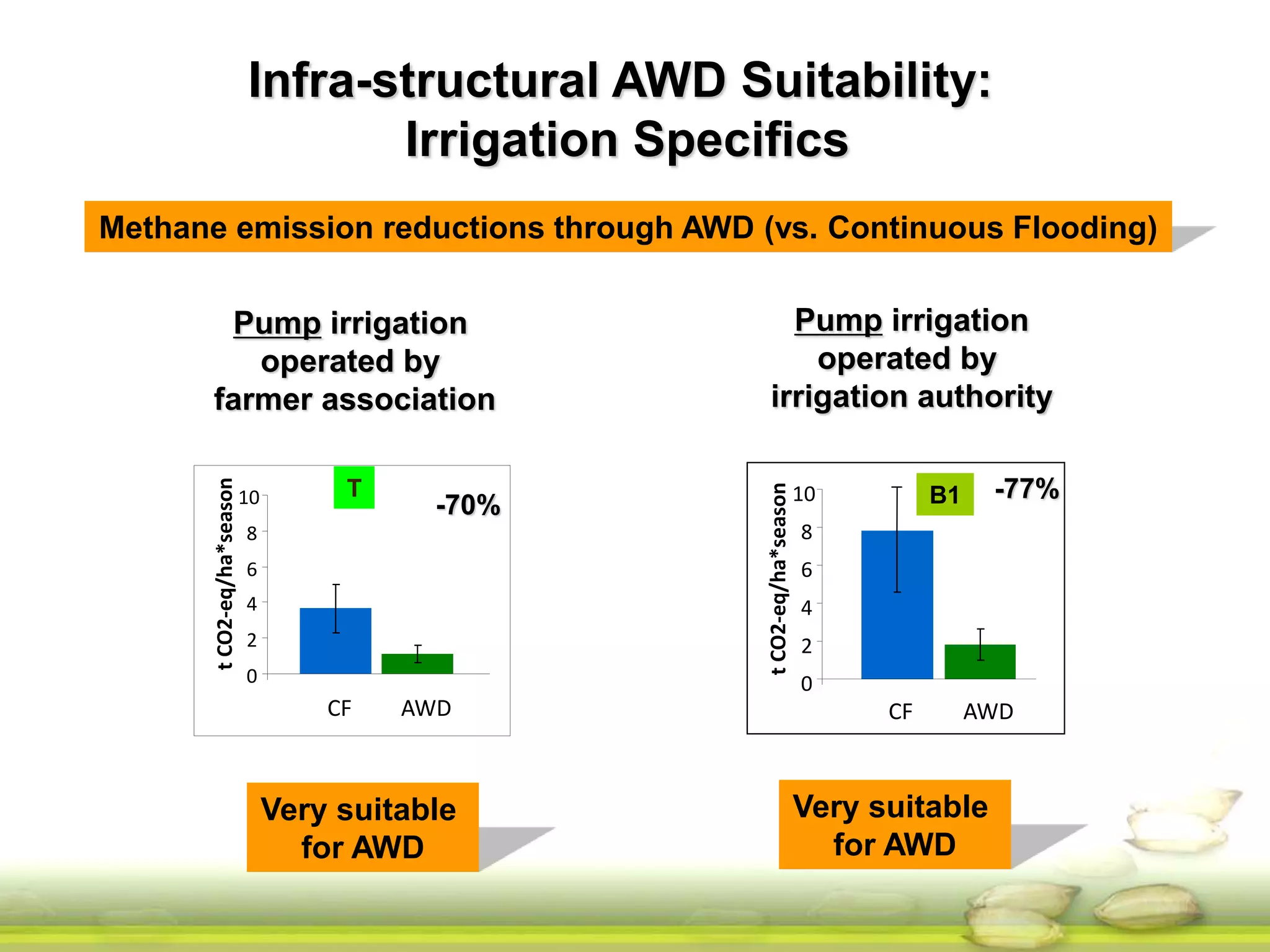
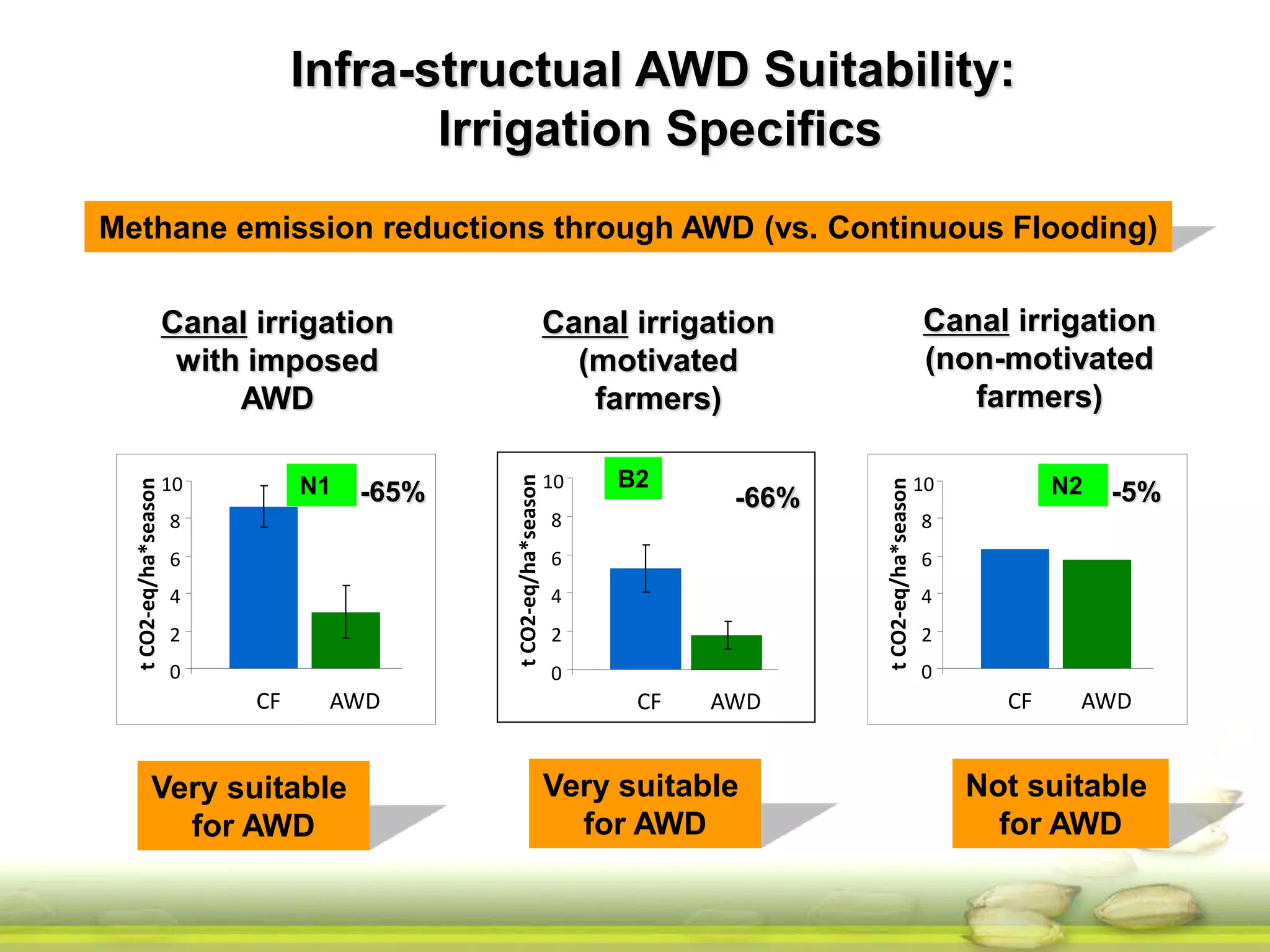
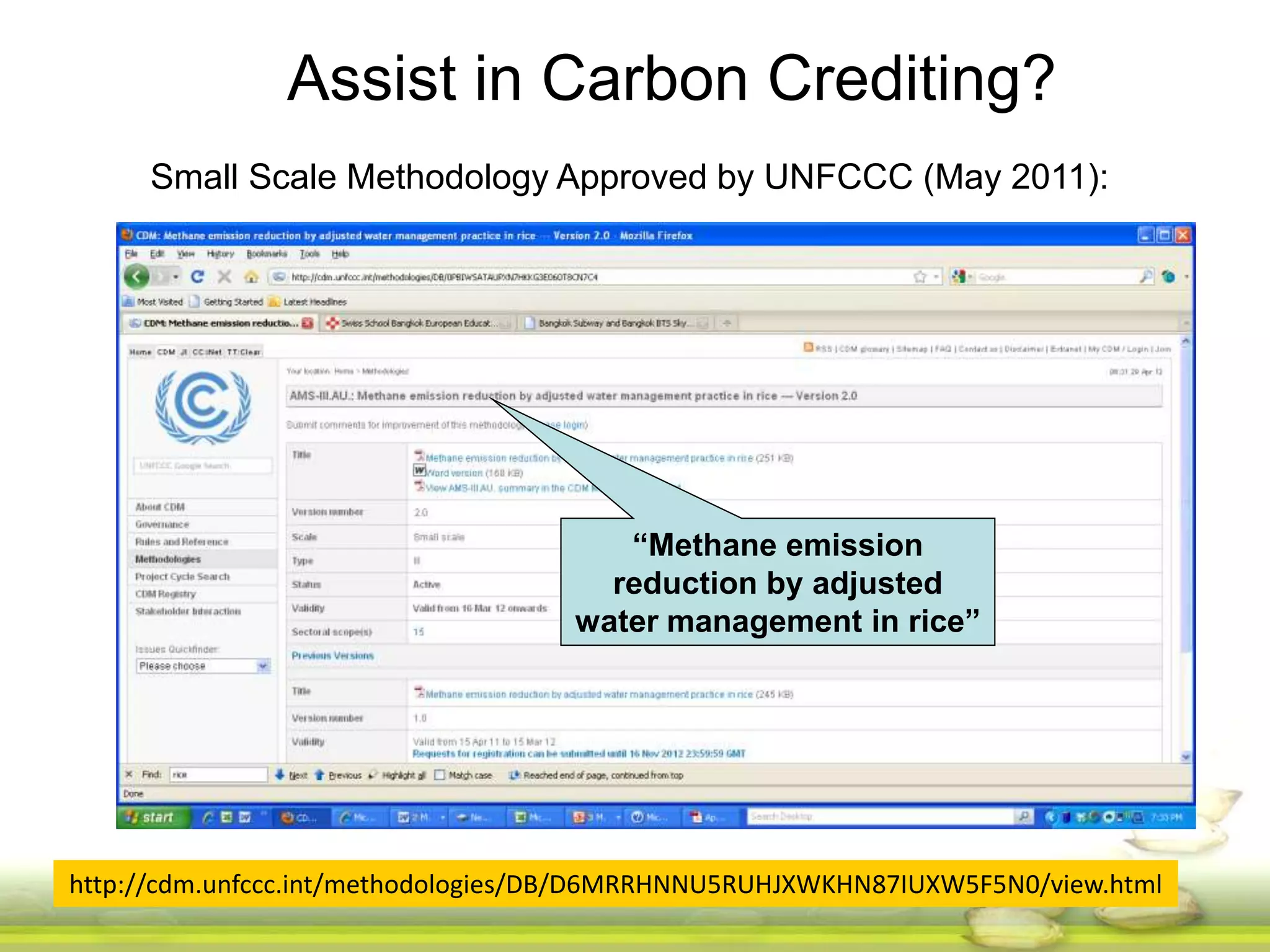
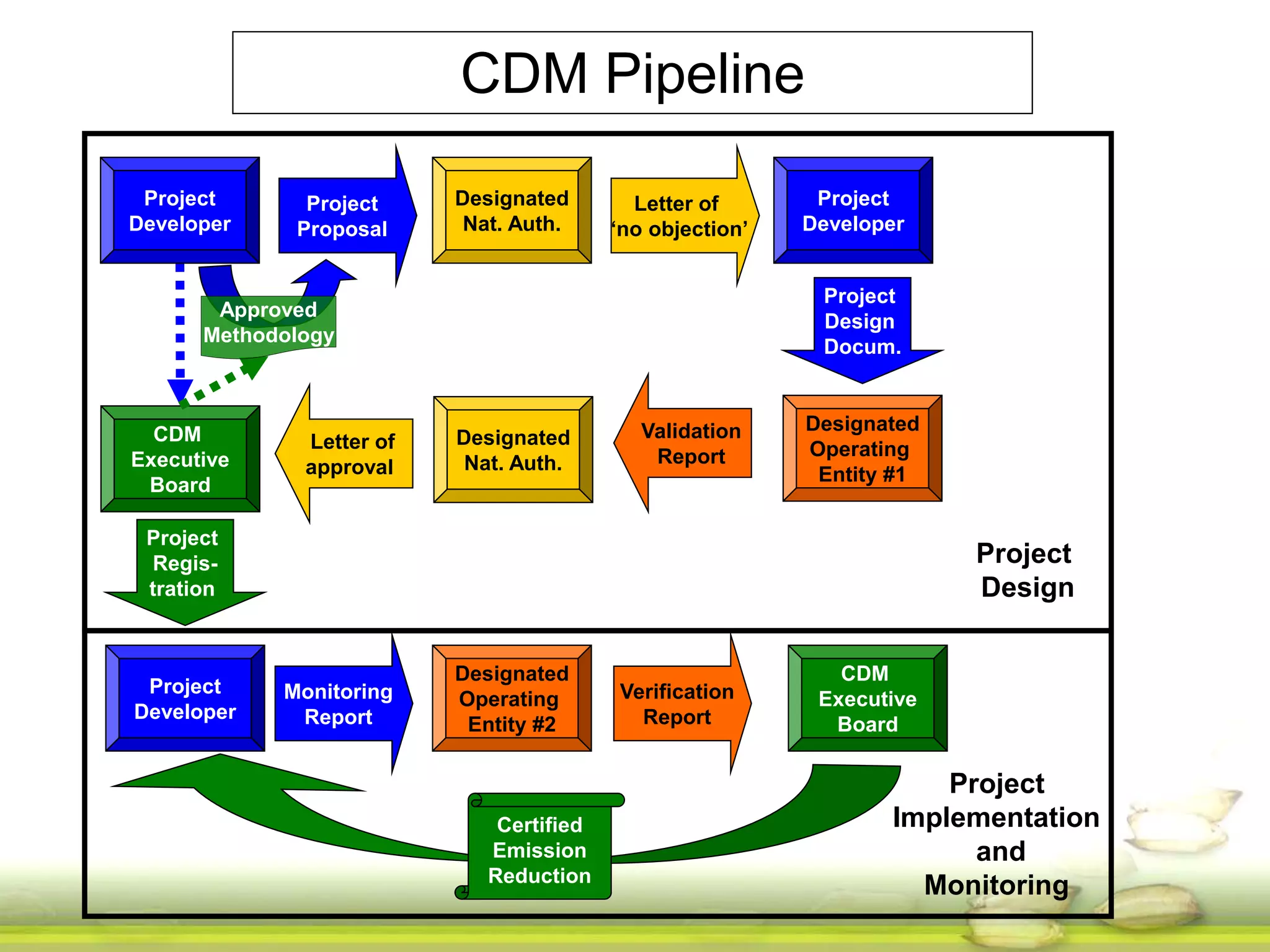
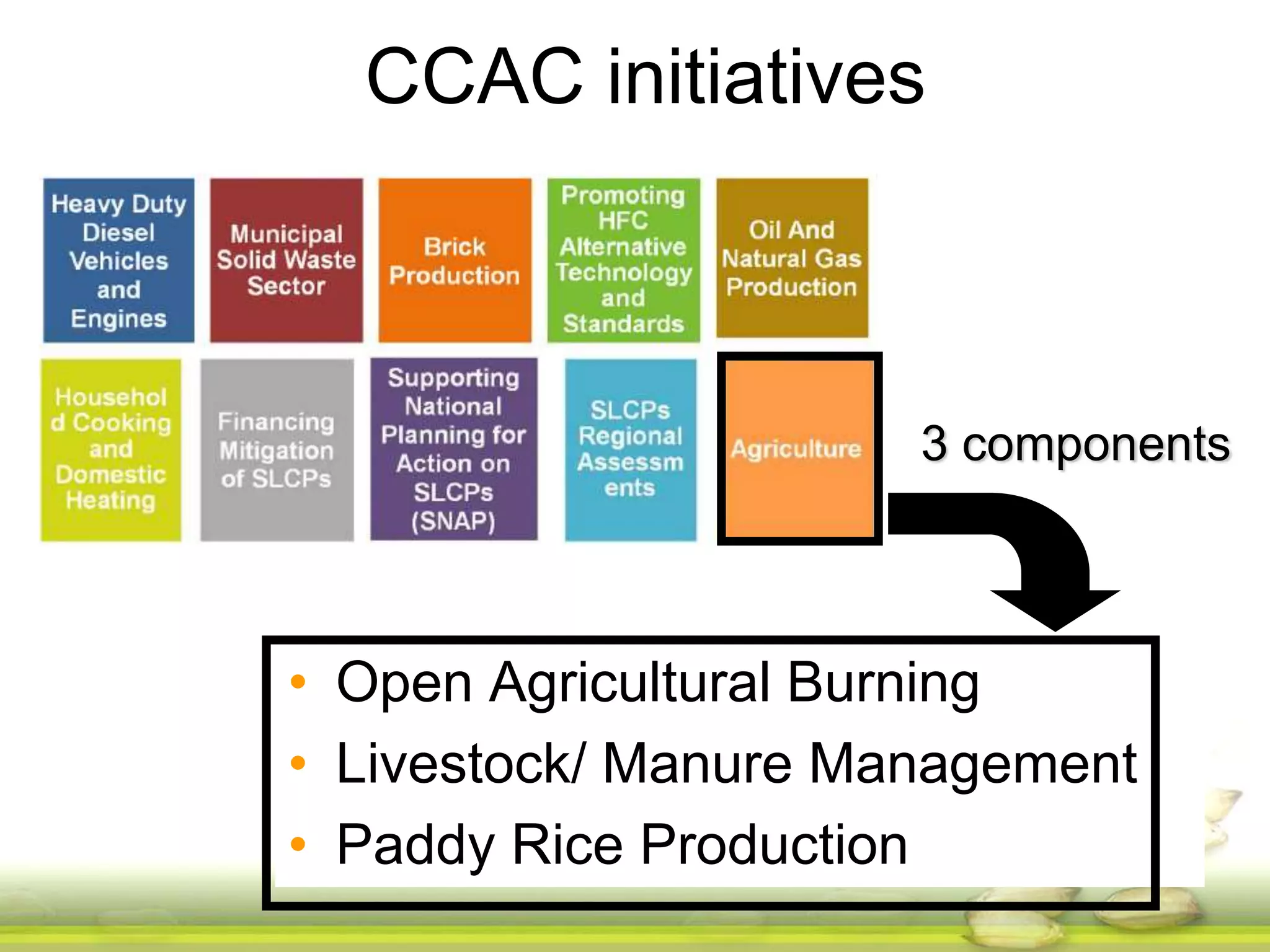
The document discusses the greenhouse gas emissions from rice production and explores mitigation strategies like alternate-wetting-and-drying (AWD) irrigation to reduce methane emissions and conserve water. It highlights the significance of rice cultivation in greenhouse gas budgets and promotes the adoption of AWD as a feasible water-saving technique that can also enhance rice productivity. The report concludes with an emphasis on the need for tailored information and support for stakeholders in implementing these mitigation options.